- Question 1: Financial Risk Analysis for Ippo Ltd.
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Hedging Alternatives and Calculations
- a. Do Nothing
- b. Forward Rate Agreement
- c. Money Market Hedge
- d. Futures Contract
- e. Options Contract
- 3. Recommendation and Conclusion
- Question 2: Monetary Policy and Asset Price Bubbles
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Analysis of Monetary Policy Limitations
- 3. Conclusion
Question 1: Financial Risk Analysis for Ippo Ltd.
1. Introduction
UK's private equity firm Ippo Ltd. plans to receive $6 million by selling its subsidiary based in the United States by August 2024. Since payment will be made in US dollars, there is foreign exchange risk that the actual amount in USD may reduce when converted to British pounds. This report demonstrates the calculation of fluctuations that could potentially affect the company's financial results if the dollar declines against the pound. The analysis examines various approaches that could be used to address this currency risk and makes recommendations on which approach would help the company maximize the transaction value.
2. Hedging Alternatives and Calculations
a. Do Nothing
The first strategy for Ippo Ltd. is to leave its fate to the market exchange rate and accept the current exchange rate during the August 2024 transaction (Kumar et al. 2024). This means that the company would simply convert $6 million to pounds at the prevailing spot exchange rate at that time.
The major downside with this strategy is that the dollar may decrease in value against the pound, rendering Ippo Ltd. less GBP (Ojukwu et al. 2024). For example, if the rate reduces to $1.2612 to $1.2645 per £1, the firm would receive fewer pounds. Conversely, if the dollar strengthens against the pound, the company would receive more pounds in exchange with no additional effort.
There are no initial investments or operational costs associated with doing nothing. However, it links the income determination directly to the exchange rate, leaving the company vulnerable to the risks associated with exchange rate volatility and hence significant variability of outcomes (Yang et al. 2022). This is the easiest option as minimal action is required, but it represents a very high-risk strategy if market conditions deteriorate.
b. Forward Rate Agreement
Formula: GBP received = (USD Amount) / (Forward Rate)
A forward contract is a method where a company hedges an exchange rate today for a transaction that will occur in the future. For instance, Ippo Ltd. can lock in the rate between $1.2657 and $1.2705 per £1 for $6 million in August 2024 (Demir and Razmi, 2022). Through this mechanism, the company gains certainty about how many pounds it will receive without being vulnerable to future exchange rate fluctuations.
The greatest advantage of a forward contract is transactional certainty. Ippo Ltd. has no concern about the fluctuation of the dollar against the pound since the exchange rate has been predetermined. This makes financial planning considerably easier for the company as it eliminates exposure to unfavorable currency movements.
However, there is a significant downside: if the dollar strengthens and the actual market exchange rate turns out to be superior to the forward rate, Ippo Ltd. cannot benefit from it (Ferreira and Sandner, 2021). The agreed forward rate must be honored regardless of any missed opportunities.
With reference to the forward rates provided, if $6 million is converted at $1.2657 per £1, then Ippo Ltd. will receive approximately £4,740,459.80. However, when using a rate of $1.2705, the amount received would be £4,722,550.20.
Thus, the main drawback of a forward contract is that while insulating the company from adverse exchange rate changes, it simultaneously eliminates the opportunity to gain from favorable changes. This strategy is especially suitable for companies like Ippo Ltd. which prioritize certainty over potential additional profit.
c. Money Market Hedge
A money market hedge is defined as a financial strategy that involves borrowing and placing funds in different currencies with the aim of reducing exchange rate risks. For Ippo Ltd., this implies exercising control over the $6 million receivable by pegging it to USD today using the prevailing market rate in relation to GBP.
To implement this hedge, the company deposits the equivalent USD amount with a US bank that offers interest of 5.5 percent per annum. If the sum is kept for six months, interest is charged for that period. The total deposit in USD including interest amounts to approximately $5,839,416.06.
Subsequently, the USD amount obtained is converted to equivalent GBP using the spot rate of USD against GBP (Barth et al. 2023). The company assesses possible outcomes using both lower and upper spot rates. Using the lower spot rate of $1.2612 yields £4,630,047.62, while using the upper rate of $1.2645 yields £4,617,964.46.
Since the company receives pounds from the beginning, the cost that directly impacts the business is the cost of obtaining a line of pounds for the six-month requirement at an interest rate of 4.7 percent (Croicu et al. 2023). Applying this borrowing cost, after six months GBP would amount to approximately £4,738,853.74 using the lower spot rate and £4,726,486.62 using the higher spot rate.
This approach enables Ippo Ltd. to fix an approximate amount in GBP, thus minimizing exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. The strategy provides predictable cash flow patterns without exposure to currency fluctuation risks.
However, as demonstrated, risks and costs are associated with this approach (Croicu et al. 2023). The strategy depends on careful management of USD and GBP interest rates. In other words, the interest rates for borrowing or depositing may restrict the advantages gained from hedging if such rates are unfavorable.
Therefore, a money market hedge, although it guarantees certainty and protection against exchange rate movements, also requires proper financial planning around interest rate differentials for optimal cost management.
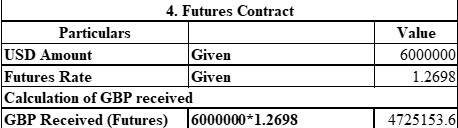
d. Futures Contract
Formula: GBP Received = (USD Amount) / (Future Rates)
A futures contract is a mechanism that enables a firm to lock in current exchange rates for a future foreign currency transaction. For Ippo Ltd., this means establishing a forward rate of $1.2698 per £1 to effect an exchange of $6 million in August 2024. The primary advantage of implementing futures is that there will be no exchange rate risk since the company knows it will receive a specific sum in GBP.
With this approach, the company can secure the rate early enough to avoid being adversely affected by a weak US dollar. The forecast futures rate for GBP/USD is 1.2698. This means that upon exchange, Ippo Ltd. will receive 1.2698 British pounds for every US dollar exchanged at the market (Santoso and Santosa, 2021). By applying this rate to the total USD amount, the company can determine the GBP amount it will receive.
Through this mechanism, the company is assured to receive approximately £4,725,153.57 when converting $6 million in August through the use of a futures contract.
The benefit of this approach is that the company does not experience exchange rate unpredictability (Aslan, 2021). Even if the exchange rate between the US dollar and GBP falls before August, Ippo Ltd. will receive the agreed amount irrespective of market fluctuations. However, if the dollar appreciates, the company cannot benefit from the improved rate.
In general, a futures contract provides certainty of receiving a fixed amount in GBP, which helps Ippo Ltd. organize its finances effectively. Therefore, although futures contracts provide certainty and require no initial investment, they lack flexibility, which may prevent the company from benefiting from favorable foreign exchange rate movements. This strategy is beneficial for companies like Ippo Ltd. that do not seek risky opportunities and are willing to forego potential gains to avoid probable losses.
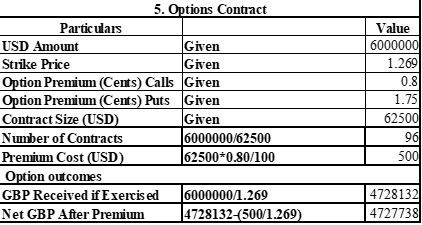
e. Options Contract
An options contract acts as a financial derivative through which Ippo Ltd. has the opportunity, but not the obligation, to trade a currency at a particular exchange rate referred to as the strike rate (Bao et al. 2022). Therefore, the option can be utilized by the company if it is deemed worthwhile based on future exchange rates.
Ippo Ltd. faces a decision to use options contracts concerning fluctuations in the exchange rate for the expected $6 million receivable in August 2024 (Honkapuro et al. 2023). This means that the holder of the option has the right, but not an obligation, to purchase USD at a strike price of 1.269. Should the exchange rate move against the company's interests, it can exercise the option to obtain the specified GBP quantity. However, if the market rate becomes more favorable, the company can choose to abandon the option and employ the better rate on the USD.
To establish this hedge, the company must determine the number of contracts necessary. Since each contract covers $62,500 and provides full coverage area, 96 contracts are needed for complete protection. The premium is offered at 0.8 percent of the dollar amount, meaning each contract costs $500, resulting in a total premium cost. If the option is exercised, then Ippo Ltd. will receive approximately £4,728,132.39. After deducting the adjusted premium cost, this sum comes to approximately £4,727,738.38 as the net figure received (Wang et al. 2024).
One major benefit of an options contract is flexibility. Unlike other hedging strategies, this contract enables the company to speculate on favorable exchange rate movements while simultaneously guarding against adverse movements. This makes options a highly efficient tool in managing currency risk.
- Risks and Benefits: The greatest strength of an options contract can best be described by the word versatility (Ferreira and Sandner, 2021). Ippo Ltd. has insured itself against any exchange rate risk which would otherwise have adverse effects, but at the same time, Ippo Ltd. has positioned itself to gain if exchange rates prove favorable.
3. Recommendation and Conclusion
Each of the strategies discussed comes with different costs, utility, and flexibility compared to the others.
- Do Nothing: This option attracts no cost but exposes Ippo Ltd. to full currency risk, which creates significant uncertainty and imprecision in financial outcomes.
- Forward Rate Agreement: The advantage of this approach is that there is no initial cost and volatility is restricted, but the approach remains inflexible in the event of favorable exchange rate movements.
- Money Market Hedge: Although it provides a protected rate and determines the GBP amount with certainty, it carries interest rate risks and is complex in terms of operational implementation.
- Futures Contract: This strategy provides obvious cash flows and good revenue predictability with no initial investments, but it remains rigid with no ability to benefit from favorable rate movements.
- Options Contract: This is the most flexible and effective form of protection against negative alterations while retaining the potential to utilize positive ones. However, there is a cost in the form of premium payments that must be made upfront before the service is fully operational.
Given the analysis, the Options Contract emerges as the most balanced recommendation for Ippo Ltd. While it requires an upfront premium cost, it provides comprehensive downside protection while preserving upside potential, making it the most prudent choice for managing currency risk in this transaction.
From essays to dissertations, New Assignment Help covers all your academic needs with professional Best Assignment Help services.
Question 2: Monetary Policy and Asset Price Bubbles
1. Introduction
Monetary policy aims to control the inflation rate and maintain stability of financial and credit relations by adjusting interest rates. An asset bubble is a condition that occurs when an asset such as property or shares reaches very high prices, leading to further cycles of fluctuation in asset prices. This section endeavors to justify why it may not be easy to 'pop' these bubbles using solely the tool of monetary policy.
2. Analysis of Monetary Policy Limitations
- Interest Rate Targeting: Interest rates represent a key tool in the central banking arsenal, influencing borrowing, spending, and overall demand in an economy. Although raising rates can control unnecessary credit growth and temper overheated markets, determining an asset price bubble in real-time is challenging since it is difficult to distinguish bubbles from realistic growth (Ajello et al. 2022). This means that changing interest rates solely for purposes of busting bubbles can have distortionary side effects on the rest of the economy, including lower overall output growth or higher unemployment.
- Ineffectiveness against Speculative Behaviour: Speculation, in which investors expect particular prices to escalate, continues to reach unrealistic levels, often encouraging herd behavior (Stephens, 2024). These behaviors frequently do not respond to variations in interest rates. For example, despite higher interest rates, speculative buyers may still purchase assets because they believe prices will continue rising, meaning that monetary policy cannot easily quell bubbles driven by such sentiment.
- Global Capital Flows: Globalization of the world economy represents an important challenge to monetary policy since capital movements across borders are becoming increasingly widespread. Internationalization refers to situations where foreign investors influence national asset prices regardless of domestic interest rates (Ajello et al. 2022). These factors may be beyond the control of central banks because they cannot control the movements of international capital flows.
- Timing Issues: This issue leads to perhaps the biggest hurdle, which is timing. Unfortunately, central banks usually recognize bubbles only after these have reached a very large size. It is costly to intervene early because it threatens economic growth, while intervening late is also problematic in the sense that it may lead to a burst of the bubble, causing severe financial harm. The 2008 financial crisis is an excellent example of when delayed recognition and intervention proved fatal for the economy.
3. Conclusion
Monetary policy as an independent tool has limitations in preventing the building up of asset price bubbles due to timing problems, speculation mechanisms, and international factors. Thus, to provide stabilization of broader economic indicators, an additional set of actions is necessary, including implementation of macroprudential regulation, enhancement of financial control, and creation of early warning signs for bubble identification. A comprehensive approach combining multiple policy tools is essential for effective management of asset price bubbles.
Reference List
Journals
- Ajello, A., Boyarchenko, N., Gourio, F. and Tambalotti, A., 2022. Financial stability considerations for monetary policy: Theoretical mechanisms. FRB of New York Staff Report, (1002).
- Aslan, H., 2021. A review of hedge fund activism: impact on shareholders vs. stakeholders. The Oxford Handbook of Hedge Funds, p.283.
- Bao, T., Nekrasova, E., Neugebauer, T. and Riyanto, Y.E., 2022. Algorithmic trading in experimental markets with human traders: A literature survey. Handbook of Experimental Finance, pp.302-322.
- Barth, D., Kahn, R.J. and Mann, R., 2023. Recent Developments in Hedge Funds' Treasury Futures and Repo Positions: is the Basis Trade "Back"?.
- Croicu, A.E., Iancu, L.A. and Rogojan, L.C., 2023. A Review on the Impact of Shadow Banking on Financial Markets Prudential Regulation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence (Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 1596-1602).
- Demir, F. and Razmi, A., 2022. The real exchange rate and development theory, evidence, issues and challenges. Journal of Economic Surveys, 36(2), pp.386-428.
- Ferreira, A. and Sandner, P., 2021. Eu search for regulatory answers to crypto assets and their place in the financial markets' infrastructure. Computer Law & Security Review, 43, p.105632.
- Honkapuro, S., Jaanto, J. and Annala, S., 2023. A systematic review of European electricity market design options. Energies, 16(9), p.3704.
- Kumar, A., Sharma, S., Vashistha, R., Srivastava, V., Tabash, M.I., Munim, Z.H. and Paltrinieri, A., 2024. International Journal of Emerging Markets: a bibliometric review 2006–2020. International Journal of Emerging Markets, 19(4), pp.1051-1089.
- Ojukwu, P.U., Cadet, E., Osundare, O.S., Fakeyede, O.G., Ige, A.B. and Uzoka, A., 2024. Exploring theoretical constructs of blockchain technology in banking: Applications in African and US financial institutions. International Journal of Frontline Research in Science and Technology, 4(01), pp.035-042.
- Santoso, P.W. and Santosa, P.W., 2021. Risk Management of Agriculture Commodity at Indonesia Futures Market: A Literature Study. SSRG Int. J. Econ. Manage. Stud., 8(7), pp.87-92.
- Stephens, M., 2024. The role of housing in central banks' monetary policy decisions in Australia and the UK. Housing Studies, pp.1-19.
- Wang, C., Li, T., Sensoy, A., Cheng, F. and Fang, Z., 2024. Economic Policy Uncertainty and Options Market Participation: Hedge or Speculation?. Borsa Istanbul Review.
- Yang, Y.T., Yang, T.Y., Chen, S.H. and Tong, C.V., 2022. Exploring the non-linearity of West Texas Intermediate crude oil price from exchange rate of US dollar and West Texas Intermediate crude oil production. Energy Strategy Reviews, 41, p.100854.

