- Business Law Assignment: Ensuring Fair Business Practices, Resolving Disputes, and Exploring Alternative Solutions
- Section 1 - Understanding the English Legal System and Its Impact on Business
- P1- Explain the hierarchy of courts in UK and discuss the different sources of laws that organisations must comply with.
- P2- Explain the role of government in law-making and how statutory and common law are applied in the justice courts
- How statutory and common laws are applied in the justice courts?
- M1- Evaluate the effectiveness of the legal system in terms of recent reforms and developments.
- D1- Provide a coherent and critical evaluation of the English legal system and law, with evidence drawn from a range of different relevant examples to support your judgement.
- Section 2 - Employers' Legal Obligations: Ensuring Workplace Safety and Fairness
- P3 (a) - Briefly explain employers’ legal obligations in relation to;
- P3 (b) - Explain how the relevant employment and contract law will have a potential impact on the business in this scenario.
- M2 - You will differentiate and analyse the potential impacts of regulations, legislation and standards with regards the above scenario.
- Section 3- Legal Solutions for Business Problems: Strategies and Impact
- P-4 Suggest appropriate legal solutions for each of the above business problems
- M3- You will assess the positive and negative impacts of legal solutions to the business problems.
- Section 4 - Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): A Path to Efficient Conflict Resolution
- P6 (a) - Explain the concept and benefits of using Alternative Dispute Resolution process
- P6 (b) - Recommend alternative legal solutions to the following business problem. You can consider another country’s legal system or a different legal framework.
- M4- Compare and contrast the effectiveness of two different recommendations
Business Law Assignment: Ensuring Fair Business Practices, Resolving Disputes, and Exploring Alternative Solutions
Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking assignment help services.
The rule of law in the professional world is crucial in order to keep business fair, just and orderly. By the rule of law, it is meant that there are clear, easy-to-understand rules that everyone in the business world has to follow. This report elucidates how business laws and legislation are essential to run the organization and impact the decision-making process and other organizational tasks. The overall report is divided into four different sections and each section highlights some differentiating issues. First section explain about the English legal system and different laws that organisations must follow. In addition, the role of government in law-making is also discussed. To deepen the understanding, the effectiveness of the legal system and reforms in it are explained. On moving further, the key points of different business laws have been elucidated along with their applicability in different case studies. In the end, the comparison of legal systems and alternative legal advices have been done.
Section 1 - Understanding the English Legal System and Its Impact on Business
P1- Explain the hierarchy of courts in UK and discuss the different sources of laws that organisations must comply with.
The English legal system follows a hierarchy of courts in UK, on top of which is the Supreme Court, formally called ‘the House of Lords’. Verdicts given by this judicial body are binding on all the judicial bodies in the hierarchy. The hierarchy is shown in Figure 1. Even though the Supreme Court is given the status of the highest English court, decisions of the European Court of Justice must be followed by every court in the UK under sub-sections 2 and 3 of the European Communities Act 1972.
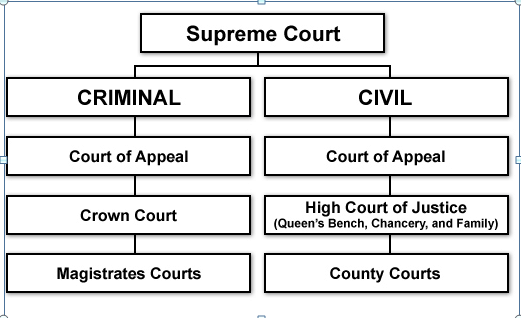
The Court of Appeal falls below the SC in the UK court hierarchy and which is divided into Civil and Criminal courts. The lower courts have to abide by the decision made by both of these courts, but the Civil division has been given some powers that make it an exception to this rule as given in Young v Bristol Aeroplane Co. Ltd (1944)(CA).
The Divisional Courts fall under the three High Court divisions, the verdicts of which are appellate. These judicial bodies abide by the ‘doctrine of stare decisis’ following decisions from the Supreme Court and the UK Court of Appeal (Siemsand Deakin, 2014). Then comes the Crown Court which falls under Criminal Division. It is not bound to follow the verdicts given by it previously. Below Crown Court, Magistrates Courts is present which is not bound by any other courts and is not liable to follow its previous decision.
Different Sources of Law: There are basically two sources of law- 1.) Primary Source 2.) Secondary Source
Primary Source: It includes the sources, such as legislation and the European Laws that are explained below.
- Legislation: These are those laws that are passed by the parliament and are binding on every citizen of the country and nobody has the right to challenge them.
- European Law: These laws are applicable to those countries that are a part of the European Union and are kept above the laws of the UK (Garoup & G ´omez Lig ¨uerre, 2014).
Secondary Sources: The following sources are considered in this- Textboks, Legal Encyclopedia
P2- Explain the role of government in law-making and how statutory and common law are applied in the justice courts
In UK, the parliament is the greatest legislative authority that examines and check the work of the government. This legislature is responsible for making laws from the part of the government, and debate upon their impact (Cotterrell, 2017). In UK, the parliament comprises the House of Commons and the House of Lords. Before making a law, a bill is passed which is up voted by both the bodies. Know More about Business Law Assignment Help in UK.
How statutory and common laws are applied in the justice courts?
A complete procedure is described below briefly:
- A challenge emerges on the agendas formulated by government.
- Ideas for the same issue is considered.
- Interested experts and people are contacted.
- Cabinet ministers take forward the proposal
- Proposals are made into bills.
- Parliament debates upon the bill
- Parliamentary stages- First reading, Second Reading, Committee stage, Report Stage, Third Reading.
- A bill is approved
- A bill is turned into an act
- The judicial laws are made under the act.
M1- Evaluate the effectiveness of the legal system in terms of recent reforms and developments.
By law reforms, number of meanings can be interpreted. In the context of English legal system, the Education Act of 1944, has gone through law reform. The Consumer Rights Act 2015, was criticized severely by the business communities of UK, but it was mandatory to protect the consumer from illegal practices followed by the business owner. In phase 1, various institutional changes were made, such as establishment of Ministry of Justice (2007), replacement of Department for Constitutional Affairs. Phase 2 consists of creation of National Crime Agency (2013) and Family Court (2014).
An effective legal system is crucial for the sustainability of rule of law in the UK. Not only the rich people, but poor should also have the access to the legal system. In business world, an effective legal system is important to protect the rights of employees and employers and to maintain the healthy relationship among them (Barkan, et. al., 2015).
D1- Provide a coherent and critical evaluation of the English legal system and law, with evidence drawn from a range of different relevant examples to support your judgement.
The English legal system comprises three legal systems: one each for Scotland, England and Wales, and Northern Ireland. The Constitution has given the supreme law-making power to the parliament which is responsible for formulating laws and reform them in the future. The doctrine of supremacy of parliament means the all the courts accept the legislation passed by the parliament (Hutchinsonand Duncan, 2012). The constitution of UK does not allow the division of powers, even though there is hierarchy in the system. The English legal system is not rigid, therefore certain reforms have been made in the past, for example the creation of fast-track courts and family courts for resolving minor issues.
Conclusion
In this report, the English legal system had been discussed thoroughly and its impacts on businesses were also assessed. In the first section, the law-making process had been discussed and structure of the judicial system was talked about. On moving further, different laws that are essential for business organization were elucidated along with some case studies. Later on, the importance of legal system in resolving business problems had been explained with some examples. To end this report, a comparison between the legal solutions and alternatives legal advice is done and importance of these two options in different scenarios had been explained.
References
- Barkan, S.M., Bintliff, B. and Whisner, M., 2015. Fundamentals of legal research.
- Cotterrell, R., 2017. Law, culture and society: Legal ideas in the mirror of social theory. Routledge.
- Hutchinson, T. and Duncan, N., 2012. Defining and describing what we do: Doctrinal legal research. Deakin L. Rev., 17, p.83.
- Siems, M. and Deakin, S., 2014. Comparative law and finance: Past, present, and future research. Journal of Institutional and Theoretical Economics (JITE)/Zeitschrift für die gesamte Staatswissenschaft, pp.120-140.
Section 2 - Employers' Legal Obligations: Ensuring Workplace Safety and Fairness
P3 (a) - Briefly explain employers’ legal obligations in relation to;
- Occupational Health and Safety
The employer’s obligations include the following:-
- The provisions of maintenance of machineries and plant or systems that are reasonably safe, practicable, and risk-free.
- The provisions for a safe and risk-free handling, storing, and transporting substances.
- Provisions for providing educations, training, guidance, setting a benchmark, essential for the safety of workers (Russ, 2012).
- Provisions of providing arrangements for the welfare at work for employees.
- Workers Compensation
Workerscompensation is a reimbursement provided by the employer to those employees who incurred certain injuries while working on the site. The obligations includes:-
- Providing immediate medical aid to the injured person.
- Formulating a report of the whole incidence and submitting it in the nearby worker’s compensation board office.
- Comply with the changes suggested by the worker’s compensation board or the insurance company.
- Harassment
According to the Protection from Harassment Act 1997, it is the key responsibility of the employer to make sure that any type of harassment, such as physical, mental or verbal does not occur in the workplace as employees’ safety and welfare are his/her sole responsibility. And, if any of such unethical event occurred in the future, then he/she will be held responsible for such events.
- Equal Opportunities
Equality Act 2010, obligates the employer to give similar or equal opportunities to the workers irrespective of their caste, race, religion, gender, age, origin, or disability. In case of disabled person, the employer are required to make some adjustments to jobs which place disabled worker at a lower place compared to non-disabled people.
P3 (b) - Explain how the relevant employment and contract law will have a potential impact on the business in this scenario.
Employment law and contract law talks about all the obligations and rights that are within the employer-employee relationship. It is very complex relationship and involves various legal issues, such as wrongful discrimination, termination, employment rights and laws, workplace safety. And, almost all of these are governed by federal laws(HSL, 2014).
Right to safe workplace is the most essential employee right that talks about a workplace which is free of toxic or hazardous substance and other potential safety hazards (Ball and BallKing, 2013).
So in this case, the employer is liable to pay compensation under the Workers Compensation Act 1943, as the fault is from the employer’s side.
M2 - You will differentiate and analyse the potential impacts of regulations, legislation and standards with regards the above scenario.
In the above scenario, the two laws- Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1974 and Workers Compensation Act 1943 played a crucial role together to provide a justified compensation to the girl. Every employee has some basic rights in the work place. Differentiating the two is a bit perplexing, still a brief of the two is given below:
Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1974:
It is one of the crucial part of legislation that covers occupation health and safety in the UK. This act defines various duties of contractors, employers, and employees. It also defines the substances to be used at work, set safety guidelines at work premises. A Health and Safety Commission is established for the regulations and enforcement of this law. If anyone found guilty of not following it, then he/she is liable to fine and imprisonment (King, 2016).
Workers Compensation Act 1943:
This law is applicable to every employer and employee working in British Columbia excluding those who are living cross the border. It says that if in an industry or within its scope, a personal injury or death occurs in and out of the employment to a worker, then compensation is provided to him/her out of the accident fund (Chaklader, 2015).
Section 3- Legal Solutions for Business Problems: Strategies and Impact
P-4 Suggest appropriate legal solutions for each of the above business problems
Case 1-As given in the case study that Calvin had offered his services to Donna for more than 4 years, therefore he has right to 4 weeks prior notice before his employer terminates his contract under the section 86 of Employment Right Acts 1996. The section 94 empowers the employees against the unfair dismissal (Barak, 2016). Calvin can file a suit at an employment tribunal claiming that his rights have been breached. He can seek compensation for the challenges he had faced.
Case 2- According to the Limitation Act 1980, insurance company can deny the repayment of insurance claim on same property that got damage in last 2 years (Robsonand McCartan, 2016). And Dan had already got the payment for his earlier store. But, the new store for which he is seeking claim has a new contract and has nothing to do with the old store and its insurance contract. So his demand for insurance claim is legit and judicially right. The insurance company is trying to combine the two mutually exclusive contracts in order to find a way out of paying the claim amount to Dan.
P5 - Provide justifications for your solutions by either referring to a relevant statute or using an appropriate case.
- To support the suggestions provided in the case 1, a similar case study is given below:
Here, Mrs. B was working for a firm since last 3 years and got dismissed by the employer stating her gross misconduct to be the main reason for her dismissal. By gross behavior, her employer meant the following actions:
- Leaving lights before leaving the office at the end of the day.
- Incomplete building check
- Leaving the office keys at a place which is quite unsecure.
After looking into this case, her Employment Solicitors claimed that the dismissal was unfair and they seek the intervention of Employment Tribunal.
This case gone through a 3 stage test as given below:
- Was the employer sure about the misconduct have occurred?
- Was accusation based on some relevant or reasonable grounds?
- Had the employer ordered a probe into the matter?
The employer failed in all the test and Employment Tribunal felt the dismissal to be outside the reasonable actions. The Tribunal ordered the employer to offer a settlement and Mrs. B received a financial compensation.
So Calvin can also do the same in his case.
- Talking about the second case study, the Limitation Act 1980 and Enterprise Act 2016 empower Mr. Dan to ask for the damages caused by the fire incident in his new store. The company is seeking a way out of paying any insurance claim amount, so Mr. Dan can file a suit against the wrongful reasons given by the insurance company.
M3- You will assess the positive and negative impacts of legal solutions to the business problems.
Challenges are more often in businesses and sometimes they create a negative image of an organization on a global stage that further leads to a loss to revenue or customer base. Even the top organizations, such as Google, Facebook, etc. have gone through some serious legal issues. Since such litigations consume organization’s resources, money, time, and energy, they need to be curbed as soon as possible.
Legal solutions to business is important to solve critical situation efficiently and effectively in the minimal time and help in the preservation of crucial business relations. The skilled counsel is considered to be one of the essential asset of an organization to face such challenges. Legal solutions have served as a helping hand for almost all the high-performing businesses and resolve business issues.
Legal solutions can also have a negative impact on an organization as they sometimes lead the organization in some irrelevant suit battles that dent the image of the organization and waste funds of the firm. Many a time, organizations have formed certain regulatory measures suggested by their counsel that later on affects the rights of employees and smooth functioning of the organizational operations. Moreover, if an enterprise is fighting a law suit and if it lose that case, then it sends a negative message to the rest of the world and affects the goodwill of the firm.
D2- You will critically review and evaluate the use of appropriate legal solutions in comparison with alternative legal advice.
In this section, a comparison between the appropriate legal solutions and alternative legal advice, such as ADR, negotiation, settlement conferences, collaborative family law, etc., has been done. Legal proceedings in court may take time to reach to a solutions sometimes decades and it is usually not good option from the cost-effectiveness point. While ADR provides both the party an opportunity to sit together and find a way out of a problem with an external neutral third party. Organization nowadays, seek ADR as a major instrument which provides fast and less expensive solutions. ADR assists the parties to find a flexible and creative option that safeguards the benefits of both the parties. ADR provides access to justice to those people who cannot afford to fight a suit in the court due to financial problems. Also, it keeps the disputes private, unlike the court proceedings where everything is on public record.
For cases that involve public interest, legal solutions is the better option than ADR. In addition to this, cases where some binding agreements have to be made, legal solutions can serve the purpose.
Section 4 - Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): A Path to Efficient Conflict Resolution
P6 (a) - Explain the concept and benefits of using Alternative Dispute Resolution process
The term ‘ADR’ (Assisted Dispute Resolution) sometimes termed as ‘conciliation’. In this process, the disputes are settled without the court proceedings, usually through arbitration, negotiation or mediation. It is the cost-effective solution that is often more expeditious (Leeand Cheung, 2016) . Issues, such as divorce, labor disputes, and insurance claims can easily be resolved using ADR. The procedures involve in ADR are usually collaborative and bring parties on a common solutions that satisfy both the parties and safeguard their interest. The major advantages of ADR include: Speedy process and cost-effective. To increase the understanding of people, methods involved in ADR are explained below:-
- Arbitration:This method involves an arbitrator or a neutral third party who individually listens to both the party involved in an issue and later on give his/her decision.Here, appealing rights are very limited. Used in disputes, such as labor wage issues or domestic disputes or else defined under Arbitration Act 1996.
- Negotiation: It is the most common method of settling the disputes. Parties can directly or by any third medium can negotiate and there is no define procedure of settling an issue.
- Mediation: This is a voluntary method of settling out a dispute between two partiesusing mediator who not only carries out communication but it also promotes the mutual deal between the parties. It is suggested to go for mediation at the early stage of disputes.
P6 (b) - Recommend alternative legal solutions to the following business problem. You can consider another country’s legal system or a different legal framework.
Since both Antwon and Tyrell wish to burry down the hatches and resolve their issues together, nothing can be as good as negotiation and arbitration. Former method is more apt than the latter. The reason being that the negotiation approach is voluntary and keep the dispute under the cover. In addition, the parties controls the process, make their own guidelines keeping in mind the interests that do not hinder the progress of other. Being informal and unstructured, negotiation method make the settlement process to be flexible. In other words, the final outcome of the dispute is often a win-win situation for both sides.
Apart from this, arbitration can also be a second option where both of them can hire a common arbitrator to resolve the issues without favoring one over the other. The arbitrator can be attorneys or any private professionals hired for a fee.
M4- Compare and contrast the effectiveness of two different recommendations
Both arbitration and negotiation are two litigations of ADR. Both offer speedy and cost-effective measures and make sure that confidentiality should not breach.
- Both recommendations differ in their functionality and means of resolving disputes. In arbitration, both parties appoint an arbitrator, whereas a facilitator supervise a negotiation approach.
- In arbitration, the arbitrator give his/her decision after hearing both parties. The resolution is termed as ‘award’, which is legally binding. In negotiation, the facilitator gives opportunities to talk among themselves to solve the disputes and helps in making settlement. The final verdict is called a memorandum of agreement. This is not legally binding.
- The arbitrator is the only one to decide on the final outcome of an issue, whereas the facilitator allows both the parties to come on to a common decision.
- An award can never be appealed in the judicial court. On the other hand, the court has the power to question the memorandum of agreement.
D2- Critically review and evaluate the use of appropriate legal solutions in comparison with alternative legal advice
Legal solutions revolve around the adversarial system. The primary goal is either punishment or deterrence. Many people choose the judicial system to punish the opposite party and get justice. The purpose of ADR is to lessen the overall burden of the judicial system of a nation. Courts have millions of pending cases and ADR aids in minimizing them. Businesses seek a speedy solution to their problems and disputes. So instead of waiting for months or years, they opt an approach that takes only a week or two to resolve issues. The best part of ADR is that it offers the flexibility of challenging the solutions given by ADR methods in court. Need to know more about the law? then check Law Assignment Help from top UK Writers.
References
- Russ, K., 2012. Risk assessment in the UK health and safety system: theory and practice. Safety and health at work, 1(1), pp.11-18.
- HSL, H., 2014. RR262-Health and Safety of Homeworkers: Good Practice Case Studies.
- Ball, D.J. and BallaKing, L., 2013. Safety management and public spaces: restoring balance. Risk analysis, 33(5), pp.763-771.
- Chaklader, A., 2015. History of Workers’ Compensation in BC. A report to the Royal Commission on Workers' Compensation in BC.
- King, M., 2016. Does the Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 Apply to Roads. Victoria U. Wellington L. Rev., 47, p.617.
- Barak, M.E.M., 2016. Managing diversity: Toward a globally inclusive workplace. Sage Publications.
- Robson, C. and McCartan, K., 2016. Real world research. John Wiley & Sons.
- Lee, C.K., Yiu, T.W. and Cheung, S.O., 2016. Selection and use of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) in construction projects—Past and future research. International Journal of Project Management, 34(3), pp.494-507.

