- Chapter:1 Capital Budgeting Risk and Return Capital Structure Assignment
- 1: Implications of Cost of Capital on a Firm’s value and its share price
- 1.1: Implications of Cost of Capital on Firm Value
- 1.2: Implications of Cost of Capital on Share Price
- 2: Limitations of using Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
- 2.1: Dependent on Assumptions
- 2.2: Consideration of Historical Values
- 2.3: A constant capital structure is factored
- 2.4: Sensitivity and Complex Method of Calculation
- 3: Calculation of Cost of Equity for Alibaba
- 3.1: Assumptions
- 3.2: Calculations and Analysis
- 4: Calculation on Estimated WACC for Alibaba
- 4.1: Assumptions
- 4.2: Calculations and Analysis
- 5: Discussion on Investment in Alibaba
- 5.1: Assumptions
- 5.2: Calculations and Analysis
- 6: Impacts on Cost of Capital due to Political Risks
- 6.1: Reduction in Debt Financing
- 6.2: Increased and Lowered Proportions of Risks and Returns
- Part B: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) published in the fiscal year 2024 annual report of Alibaba
- 7: Building Social Trust: A Pillar of Alibaba’s Business Growth
- 7.1: Importance of Social Trust to Alibaba’s Business
- 7.2: Enhancing Privacy Protection and Data Security to Build Social Trust
- 7.2.1: Role of Data Privacy for empowering consumer trust
- 7.2.2: Risk Reduction by Facilitating Cybersecurity
- 7.2.3: Transparent Practices and Accountability
- 7.2.4: Compliance with Legal Frameworks
- 8: Transition to Clean Energy: Long-Term Profitability for Alibaba
- 8.1: Cost Efficiency in Operations
- 8.2: Enhanced Reputation and Customer Loyalty
- 8.3: Regulatory and Tax Incentives
- 8.4: Market Leadership and Innovation
- 8.5: Risk Mitigation and Sustainability
- 9: ECG strategy benefits for Alibaba
- 9.1: Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
- 9.2: Boosting Employee Morale and Engagement
- 9.3: Building a Highly Skilled Workforce
- 9.4: Positive Brand Image and Reputation
Chapter:1 Capital Budgeting Risk and Return Capital Structure Assignment
1: Implications of Cost of Capital on a Firm’s value and its share price
1.1: Implications of Cost of Capital on Firm Value
The cost of capital of a firm contains an inverse relationship with respect to valuation in which a lower cost of capital is expected to generate a higher firm value. However, on the contrary higher cost of capital will generate a lower firm value. Hence, the implications of a higher cost of capital on firm value can affect business decision making facilities of a company due to which organisational dominance in the market could be diluted. The Concept of cost of capital is also alternatively known as the discount rate applicable for appraising investments. Moreover, it is also inclusive of discounted cash flows which are alternatively known as present values when cash flows are converted with respect to applicable discounting factors. The additional implications of a higher cost of capital on firm value is expected to increase financing risks of a company due to which scope of generating progressive Returns are minimal. As per critical narrations of Prasad et al. (2022), an increase in cost of capital can lead to inefficient formation of capital structure due to which overall financial attractiveness reduces drastically.
1.2: Implications of Cost of Capital on Share Price
The implications of cost of capital on share price further involve low investor participation if a higher cost of capital is obtained for a company. This decision making conflict from investors mainly arises due to the possibility of higher financing cost risks available for a company which makes the scope of generating returns less feasible. As critically expressed by Royer and McKee (2021), the increase in cost of capital has a domino effect on organisation leverage in which steep increase can cause catastrophic stock market performances of a company in future. The increase in cost of capital can significantly overvalue share price of a company which might become vindictive in terms of gaming investor confidence and participation for future investment activities. The implications of cost of capital on share price can also contribute to profitability challenges of a company due to which capitalised market growth can become difficult.
Struggling with deadlines? Turn to New Assignment Help for reliable Best Assignment Help that takes the pressure off and boosts your academic success.
2: Limitations of using Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
2.1: Dependent on Assumptions
The first limitation of WACC is associated with the method being dependent on multiple assumptions since it only assumes computations at corporate levels rather than determining financial credibility in terms of individual investments. Zhang et al. (2021) critically idealised that the WACC method also assumes debt and equity as only sources of finance where other sources are often neglected. The dependency on assumptions is also considered to negatively influence values of WACC due to which capital structure decision making is often compromised. The concept of WACC is dependent upon individual weights and cost of financing for debt and equity which is measured in relation to tax free rate applicable.
2.2: Consideration of Historical Values
Consideration of historical values is the second limitation of WACC method in which lack of adequate emphasis on future values is largely absent. The conceptualisation of WACC is mainly dependent upon current and past financial values obtained from financial statements in which the future blueprint or roadmap of financial risks and returns becomes difficult for understanding. As critically explained by Gjergji et al (2021), the lack of incorporation for future values can further lead to difficulties arising for future investment programs due to which investor harmony can be sacrificed. Moreover, the lack of future values can also create difficulties in terms of predicting how a company is expected to perform in the market due to which its abilities of securing additional funding can become a challenge.
2.3: A constant capital structure is factored
The third limitation associated with WACC involves consideration of a constant or fixed capital structure where it is mandatory on part of companies to adopt a fixed or consistent capital structure balance between debt and equity. As critically explained by Zhai et al. (2022), a constant capital structure is often deemed unrealistic since debt and equity values are bound to change every year and hence it can lead to false assessment of future risks and rewards. The constant capital structure of WACC is also implicative in terms of creating difficulties in order to make suitable risk management decisions in the long run. Moreover, a constant capital structure could also fix the tax rate applicable for a company due to which its credibility drops significantly.
2.4: Sensitivity and Complex Method of Calculation
The fourth limitation of WACC is related to sensitivity and complex method of calculation since WACC is highly sensitive or influenced by economic factors including fluctuations in interest rates, inflation and market volatility. Additionally, the WACC is also considered to be a complex method of calculation as figures are usually determined from financial statements which can lead to falsification when numbers are not verified or unaudited. As per critical explanations of Gerged et al. (2021), higher sensitivity and complex method of WACC is expected to present indifferent outcomes for a company in which risk assessment cannot be feasibly measured. The higher sensitivity to economic factors could also contribute to indifferent propositions on part of a company to determine what proportion of returns could be generated if a prospective investment is undertaken in future.
3: Calculation of Cost of Equity for Alibaba
3.1: Assumptions
- Applicable beta chosen for computation of cost of equity is 0.31 which is the US market beta value.
- The risk free rate assumed for computation of cost of equity is 3.72% which is the value of the 10 year US government bond yield as of September 2024.
- The market risk premium is assumed as 13.32% which is the average annual return of S&P for the past 10 years.
3.2: Calculations and Analysis
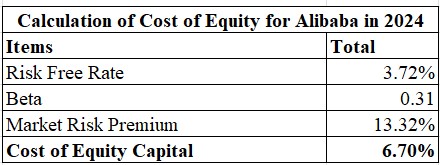
Figure 1: Calculation of Cost of Equity
According to the above figure, the cost of equity for Alibaba is calculated as 6.70% in 2024. In order to calculate the cost of equity, the CAPM approach is being implemented which factors the relationship between risk free rate, beta and market risk premium respectively. The above figures replicate that the market risk premium is higher and can cause challenges for Alibaba to maintain equitable infusion. Zhang and Wang (2024) critically explained that a high cost of equity can also lead to significant company dilation due to which decision making power and authority reduces to make suitable future investments.
4: Calculation on Estimated WACC for Alibaba
4.1: Assumptions
- The risk free rate and market risk premium are assumed as 3.72% and 13.32% which are used to compute the cost of equity capital.
- The proportion of interest expenses on debt will be assumed to obtain the cost of equity.
- The applicable tax rate will be determined by proportioning income tax expenses with income before income taxes.
4.2: Calculations and Analysis
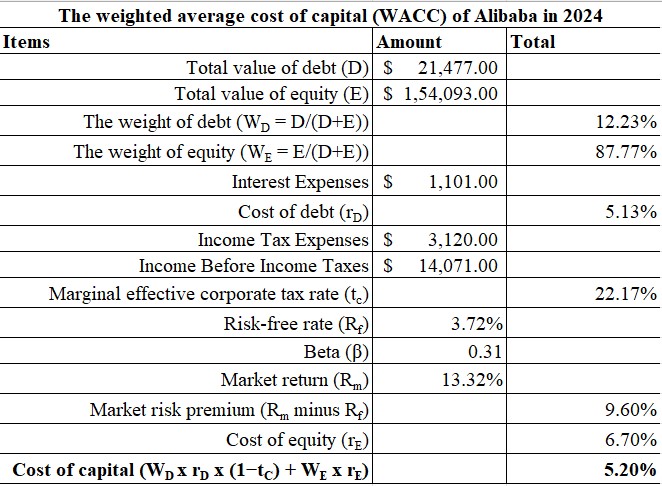
Figure 2: Calculation of Weighted Average Cost of Capital
According to the above figure of weighted average cost of capital, it can be identified that the numerical expression is calculated as 5.20%. The weighted average cost of capital includes debt and equity as key sources of finance in which the cost of debt and cost of equity are identified as 5.13% and 6.70% respectively. The applicable tax rate is identified as 22.17% while the weightage of debt and equity is calculated as 12.23% and 87.77% respectively. On the basis of dissecting the above cost of capital, it is observed that a significant equity proportion is available for the company due to which higher figures are obtained. As critically idealised by Mariani et al. (2021), a high figure of cost of capital is likely to reduce prospects of investment returns due to which future investor participation can become minimal or passive.
The principal concepts associated with implementation and computation of WACC involves consideration of risks and returns that could be extracted in order to substantiate capital structure composition. The above computation of WACC illustrates the fact that the capital structure of Alibaba in 2024 is largely dominated by equity financing in comparison to debt financing. As per opinions and views of Jafar et al. (2024), a higher proportion of equity as the major capital structure is often considered as a less feasible prospect for a company due to which market returns are expected to be lower. The higher proportion of equity is also related to the traditional theory applicable for Alibaba in which a relatively conservative strategy of capital structure composition is being induced. The implementation of traditional theory is also beneficial for a company to reduce financial risks arising from investments and capital structure composition due to which a better stability and streamline of financing sources can be obtained.
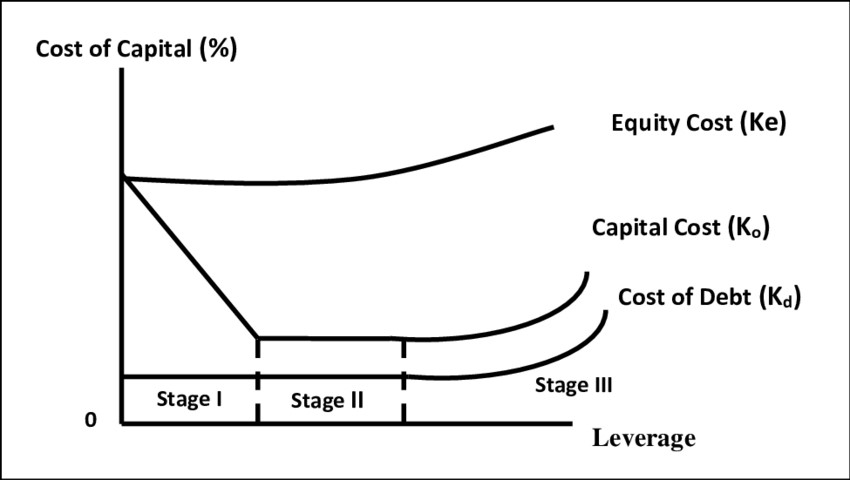
Figure 3: Traditional Theory of Capital Structure
5: Discussion on Investment in Alibaba
5.1: Assumptions
- The usage of “discounted cash flow” (DCF) approach will be executed in order to identify attractiveness of investment for Alibaba.
- The cost of capital worth 5.2% will be used as the discounting factor.
- The initial cost of investment is assumed as $ 25 while the total lifespan of the investment is assumed as 3 years.
- A 5% projected growth rate is assumed in years 2 and 3 when factoring free cash flows of year 1 which are detected by using the free cash flow per share ratio formula.
5.2: Calculations and Analysis
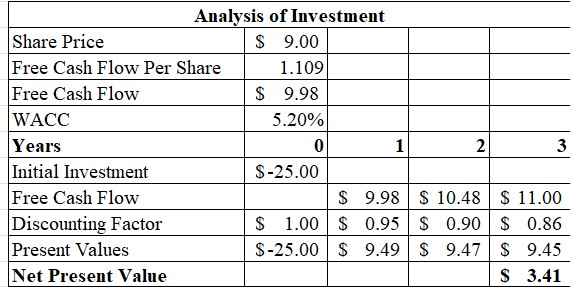
Figure 4: Investment Analysis for Alibaba
According to the above figure, the net present value for Alibaba is identified as $ 3.41. Therefore, the investment in Alibaba should be accepted since positive values of returns are expected through NPV. As per opinions of Abdelhady (2021), positive values as per NPV is considered beneficial for a company due to which better scope of mobilising investment and financial growth can be achieved in the long run.
6: Impacts on Cost of Capital due to Political Risks
6.1: Reduction in Debt Financing
Reduction in debt financing is the primary impact on cost of capital due to political risks potentially arising between China and the US. An increased political risk is expected to make debt financing more volatile due to which investors might back out from offering loans since possibilities of default remain significantly higher. The reduction in debt financing is also subject to risks and cost of capital where a direct relationship is formed between the two factors in which higher cost of capital is responsible for high investment risks.
6.2: Increased and Lowered Proportions of Risks and Returns
Increased and lowered proportion of risks and returns is the second impact on cost of capital where higher market risks and low investment returns are expected due to political tensions between China and the US. Gjergji et al. (2021) critically explained that high risks and low returns could discourage investor harmony and rationale due to which a company can suffer from financing needs and business growth mobility in its markets.
Part B: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) published in the fiscal year 2024 annual report of Alibaba
7: Building Social Trust: A Pillar of Alibaba’s Business Growth
Social trust serves as the foundation of Alibaba’s business policy because digital economy users rely on platform confidence for its expansion alongside innovation and continuous operations. Through social trust Alibaba builds a solid customer base which partners and maintains their long-term market competitiveness in this fast-changing industry.
7.1: Importance of Social Trust to Alibaba’s Business
7.1.1: Enhance User Confidence
Alibaba’s entire ecosystem which encompasses e-commerce logistics and financial services needs millions of customers and merchants for operation. As per critical views of Ye and Du (2020), platform user retention alongside expansion benefits from social trust through activity-driven participation and active engagement.
7.1.2: Reputation of Management
Reputation of management is identified as a key importance of social trust in which availability of a trust framework or concept allows Alibaba to empower better market reliability for attaining global dominance.
7.1.3: Business Sustainability
The business sustainability prospects by Alibaba are mostly determined in terms of its ability to generate and form healthy business partnerships for developing trust with stakeholders.
7.2: Enhancing Privacy Protection and Data Security to Build Social Trust
7.2.1: Role of Data Privacy for empowering consumer trust
The role of data privacy for empowering consumer trust is a key strategy through which Alibaba generates a better prospect of preserving consumer information. The scope of integrating privacy policies and encryptions are also detrimental on part of Alibaba to enhance data protection and privacy standards due to which a better consumer participation on digital platforms are attained.
7.2.2: Risk Reduction by Facilitating Cybersecurity
The company dedicates significant investment into innovative technologies used for both detecting and stopping cyber-attacks in their systems. Open platform security protocols implemented by Alibaba guarantee protected financial transactions while eliminating risks of monetary and identity theft.
7.2.3: Transparent Practices and Accountability
The implementation of transparent practices and accountability is identified as another privacy protection step implemented by Alibaba in which data collection process is developed precisely and responsible individuals or entities are also assigned. The usage of transparent practices and accountability further aids Alibaba to ethically obtain consumer information with consent due to which a favourable trust development is guaranteed with consumers.
7.2.4: Compliance with Legal Frameworks
The compliance with legal frameworks by Alibaba are predominantly applicable with respect to Chinese cybersecurity laws followed to maintain accountability of data with key stakeholders. Sustainable financial performance has persuaded investors to prioritise organisations that show social responsibility because they understand the correlation between responsible behavior and organisational success. The 2018 Sustainability Report from Allianz shows that Americans prefer to invest in companies representing their values yet additionally find ESG investments deliver emotional satisfaction along with monetary gain. Investors who value governance aspects especially executive compensation and transparency rate at 69% (data.alibabagroup.com, 2024). The growing demand for long-term success demands companies to integrate ethical economic, social and environmental considerations within their operations for attracting conscious investors.
8: Transition to Clean Energy: Long-Term Profitability for Alibaba
Moving to clean energy requires upfront funding to support electric operations of lorries and renewable energy system deployment but offers lasting financial advantages beyond spending limits. The sustainability focus of Alibaba serves as a foundation which enhances its market competitiveness.
8.1: Cost Efficiency in Operations
Together with solar power and wind power, renewable technology enables long-term operational cost reductions since energy prices remain more consistent and cheaper than volatile fossil fuel prices. The high upfront cost of electric vehicles results in lower maintenance expenses and reduced energy expenses which produce financial benefits for Alibaba's delivery operations throughout their extended service life (Everman et al. 2021).
8.2: Enhanced Reputation and Customer Loyalty
Sustainability efforts automatically attract environmental-minded customers and investors. The company builds its environmental responsibility reputation through its adoption of clean energy. These efforts appeal to additional customers and maintain loyal clients while attracting investor interest in the company's environmental social governance approaches which ultimately increases profitability.
8.3: Regulatory and Tax Incentives
Clean-up energy implementation benefits from financial support and tax benefits together with subsidies that governments extend to companies. The programs create opportunities for Alibaba to lower its expenses and gain financial benefits (Noked and Wang, 2024).
8.4: Market Leadership and Innovation
Through its clean energy leadership Alibaba establishes itself as an innovation leader in the industry. Alibaba achieves distinction from other competitors through this strategy which enables market share conquest while creating enduring business models that motivate worldwide stakeholders.
8.5: Risk Mitigation and Sustainability
Clean energy use positions Alibaba to minimise both fossil fuel price volatility and future regulatory carbon emissions penalties. Operational stability with long-term sustainability becomes possible through this approach.
Alibaba needs to resolve multiple ethical concerns alongside economic issues and social conditions and environmental problems to sustain long-term profitability. The risk mitigation and sustainability by Alibaba is also dependent in terms of enhancing cost efficiency with ethical business standards implemented due to which a better future investment opportunity could be garnered. Moreover, consideration of meeting regulatory obligations along with framing of efficient leadership strategies are also considered as key risk mitigation steps due to which market sustainability and dominance can be enjoyed by Alibaba.
9: ECG strategy benefits for Alibaba
The ESG strategies applied by Alibaba are mostly applicable for generating higher employee participation in which talent acquisition and training is given utmost importance. The ESG strategies are also inclusive of factoring incentivisation schemes applicable in order to harmonise and develop employee productivity and participation for daily activities. The following benefits could be further determined for Alibaba by implementing proactive ESG strategies for catering high employee encouragement.
9.1: Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
Attracting and retaining top talent is mainly associated with Alibaba adopting employee value growth strategies for achieving better inputs and outcomes on a regular basis. This is mainly carried out through various incentive schemes offered at frequent intervals while emphasis on training and induction is also offered to generate employee skill development.
9.2: Boosting Employee Morale and Engagement
Boosting of employee morale and engagement is largely related to Alibaba appointing managers whose fundamental tasks are linked with motivation of employees both in terms of financial and non-financial aspects. Alibaba achieves better overall performance because employees who demonstrate engagement produce higher productivity and show greater dedication to their work. Employer reputation based on social responsibility continues to increase due to this positive work culture that Benefit Alibaba in public perception and brand loyalty development.
9.3: Building a Highly Skilled Workforce
Building a skilled workforce becomes possible through Alibaba's on-the-job training approach that helps employees adapt to both business and technological market transformations. The systematic employee skill enhancement at Alibaba produces more innovative capabilities and better maintains global market competitiveness for the company (Schmuck and Benke, 2020).
9.4: Positive Brand Image and Reputation
Our employee development strategy matches the social responsibility targets of Alibaba's broader ESG objectives. A company that supports workforce welfare and sustainability interests stakeholders beyond branding but creates a strong reputation that attracts ethical consumers and sustainability-focused investors. Consumers trust businesses which prioritise employee development which leads to better financial outcomes while drawing socially responsible investors.
The long-run advantages of employee empowerment alongside workforce expertise and company reputation improvement and operational efficiency exceed the staffing stability risks which justify Alibaba's market expansion and profitability sustainability.
By implementing sustainable operations Alibaba showcases its knowledge within specific business fields. As per critical views of (Zihan, 2023), critical thinking allows the company to solve problems related to employee talent management and environmental impact reduction. Alibaba maintains its position as market leader and ensures long-term profitability through employee welfare and sustainable practices together with ethical governance measures that build global citizenship.
Reference List
- Abdelhady, S., 2021. Performance and cost evaluation of solar dish power plant: sensitivity analysis of levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) and net present value (NPV). Renewable Energy, 168, pp.332-342.
- data.alibabagroup.com, 2024, Fiscal [online], Available at: https://data.alibabagroup.com/ecms-files/1514443390/9c8490f1-cacf-4a12-bcb6-07adbb38b235/Alibaba%20Group%20Holding%20Limited%20Fiscal%20Year%202024%20Annual%20Report.pdf [Accessed on: 28.01.2025]
- Everman, B., Rajendran, N., Li, X. and Zong, Z., 2021. Improving the cost efficiency of large-scale cloud systems running hybrid workloads-A case study of Alibaba cluster traces. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 30, p.100528.
- Gerged, A.M., Matthews, L. and Elheddad, M., 2021. Mandatory disclosure, greenhouse gas emissions and the cost of equity capital: UK evidence of a U‐shaped relationship. Business Strategy and the Environment, 30(2), pp.908-930.
- Gjergji, R., Vena, L., Sciascia, S. and Cortesi, A., 2021. The effects of environmental, social and governance disclosure on the cost of capital in small and medium enterprises: The role of family business status. Business strategy and the environment, 30(1), pp.683-693.
- Gjergji, R., Vena, L., Sciascia, S. and Cortesi, A., 2021. The effects of environmental, social and governance disclosure on the cost of capital in small and medium enterprises: The role of family business status. Business strategy and the environment, 30(1), pp.683-693.
- Jafar, R., Basuki, B., Windijarto, W., Setiawan, R. and Yaacob, Z., 2024. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) disclosure and cost of equity: the moderating effects of board structures. Cogent Business & Management, 11(1), p.2429794.
- Mariani, M., Pizzutilo, F., Caragnano, A. and Zito, M., 2021. Does it pay to be environmentally responsible? Investigating the effect on the weighted average cost of capital. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 28(6), pp.1854-1869.
- Noked, N. and Wang, J., 2024. Chinese companies in tax havens. Journal of International Economic Law, 27(3), pp.521-537.
- Prasad, K., Kumar, S., Devji, S., Lim, W.M., Prabhu, N. and Moodbidri, S., 2022. Corporate social responsibility and cost of capital: The moderating role of policy intervention. Research in International Business and Finance, 60, p.101620.
- Royer, J. and McKee, G., 2021. Optimal capital structure in agricultural cooperatives and implications for equity retirement. Agricultural Finance Review, 81(2), pp.277-291.
- Schmuck, R. and Benke, M., 2020. An overview of innovation strategies and the case of Alibaba. Procedia Manufacturing, 51, pp.1259-1266.
- Ye, G. and Du, L., 2020. The entrepreneurship of Alibaba. 城西国際大学大学院紀要= The bulletin of the Graduate School of Josai International University, (23), pp.209-229.
- Zhai, Y., Cai, Z., Lin, H., Yuan, M., Mao, Y. and Yu, M., 2022. Does better environmental, social, and governance induce better corporate green innovation: The mediating role of financing constraints. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29(5), pp.1513-1526.
- Zhang, C. and Wang, Y., 2024. Is enterprise digital transformation beneficial to shareholders? Insights from the cost of equity capital. International Review of Financial Analysis, 92, p.103104.
- Zhang, R., Li, Y. and Liu, Y., 2021. Green bond issuance and corporate cost of capital. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 69, p.101626.
- Zihan, L., 2023. Analysis of Brand Image Building of Chinese and US Agricultural Enterprises on Alibaba Based on a Corpus from the Multimodal Perspective. International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology, 5(4).

