- 1.1: Top five cyber security best practice
- 1. Strong Password Management
- 2. Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- 3. Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
- 4. Data Encryption
- 5. Employee Security Awareness Training
- 1.2: Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) cards
- 1.3: DoS attack
- 1.4: Cloud vs local
- 1.5: WannaCry
- 1.6: Backup
- 1.7: Password recovery
1.1: Top five cyber security best practice
The main focus of cyber security continues to be on the trending threat and therefore it is a field that has to be evolving continuously. Five of the many best practices are effective in mitigating risk and ensuring the security of digital systems. Mixed methods are any practices that involve strong password management, multi-factor authentication, (MFA), up-to-date software, data encryption, and employee security awareness.
1. Strong Password Management
It is the first line of defense against unauthorized access and passwords. Cyber-attacks such as brute force and credential-stuffing attacks are more likely against your system if you use a weak or reused password. Reducing the likelihood of breaches includes implementing complex passwords, avoiding reuse, and using a password manager (Berkley, 2020). A good password policy makes it hard to crack credentials and so contributes to increased security.
2. Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Phishing or data breaches may give cyber criminals access to do so unless they have strong passwords. MFA is an extra layer of security in which an extra method of authentication is required, e.g. one-time password (OTP), biometric authentication, or security token. It’s a lot harder for attackers to exploit accounts if they manage to get their hands on login credentials.
3. Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Cyber-attacks often start from unpatched software. Malware, ransomware, and remote code are deployed on outdated systems by exploiting vulnerabilities to do so. According to the organization’s security strategy, the organization should make automatic updates, vulnerability assessments, etc (CIS, 2020).
Figure 1: Top Practices of cyber security
(Source: www.psmpartners.com)
Assignment Help Online in the UK helps students achieve academic success with expert-written, plagiarism-free assignments delivered on time.
4. Data Encryption
In different scenarios, encrypting data ensures both confidentiality and integrity for data at rest and in transit respectively. With robust security like strong encryption algorithms like AES for data storage and TLS for online communications, there is better protection for stolen data in the cloud and remote work environments.
5. Employee Security Awareness Training
Security breaches continue to be a result of human error. Phishing, social engineering, and other deceptive tactics make cyber criminals exploit unsuspecting employees. Regular cyber security training helps your employees recognize threats, avoid malicious links, and follow good security practices (CNBC, 2016). A well-informed workforce is a very powerful shield to fight cyber threats.
Resources:
- CNBC (2016) Security Experts Talk Future of Cyber Security, YouTube. [Online]. [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- CIS (2020), Cybersecurity Best Practices, [Online]. Available at: https://www.cisecurity.org/cybersecurity-best-practices [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Berkley (2020), Top 10 Secure Computing Tips, Berkley Information Security Office, [Online]. Available at: https://security.berkeley.edu/resources/best-practices-how-to-articles/top-10-secure-computingtips [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- com (2025). Top Practices of cyber security, Retrieved from:https://www.psmpartners.com/blog/cybersecurity-best-practices-for-small-businesses/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.2: Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) cards
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are generally aimed at making services unavailable for consumers. This threat is brutally worse in the case of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks which amplify these threats by making use of multiple compromised devices. Such attacks are possible in critical infrastructures like power grids, communication networks, nuclear plants, etc., and are carried out through remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) (Naveen et al., 2013). An overloaded RTU can cause an operation to stop and that failure is catastrophic. Attack methods include brute force attacks, continuous staring of a system in the face until it surrenders, buffer overflow or system crashing due to an unwelcome load of data, and rootkits that exploit application vulnerabilities to break in.
Figure 2: Radio Frequency Identification Device
However, such attacks are protected by intrusion detection systems (IDS), rate-limiting mechanisms, firewalls, and other AI-driven monitoring tools that can recognize malicious traffic. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, which is ubiquitous for access control and payment systems, is also vulnerable to cloning, skimming, and eavesdropping (Siani Pearson and George, 2013). Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is strongly suited for low-power RFID tags, leading to the use of ECC for identity verification and similar RFC decks. Secrete requirements, power constraints, and application sensitivity determine which encryption method to select.
Resources:
- Siani Pearson and George Yee (2013), Privacy and security for cloud computing -. London, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Naveen Chilamkurti, Sherali Zeadally, and Hakima Chaouchi (2013), Next -generation wireless technologies . London: Springer, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- com (2024). Radio Frequency Identification Device, Retrieved from: https://cyberhoot.com/cybrary/radio-frequency-identification-rfid/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.3: DoS attack
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks threaten digital systems greatly, leaving the services unavailable to legitimate users. Because these attacks can distort system integrity and reliability, they can support unauthorized access, financial loss, and operational failures. The different ways that cyber attackers get control over targeted systems involve methods like phishing, SQL injection, and web cross-site scripting.
Example: Mirai Botnet Attack
In 2016 the Mirai botnet launched a large-scale DDoS against Dyn, one of the largest DNS providers. IoT devices harboring malware were used in an attack that created a botnet of malware vehicles all to flood Dyn’s servers with traffic, making a majority of their websites inaccessible across the internet (Prajapati et al., 2014). The flashpoint here lies in the fact that the attack took advantage of weak passwords in IoT devices which shows how sloppy and dangerous positively insecure security practices can be in connected systems.
Threats Associated with DoS and DDoS Attacks
DoS and DDoS attacks exploit system vulnerabilities using various techniques:
- By sending extra data to an application, attackers make it crash, this is called Buffer Overflow.
- Unauthorized Duplication of Credentials (RFID tags) – Cloning and Replication can compromise the use of secure access due to duplication of credentials.
- Attackers: Backdoor Exploitation – Backdoor Exploitation is when attackers put in the backdoors bypassing authentication.
- A network of compromised devices (bots) used to spew out massive amounts of traffic to take down a target system is called the botnet.
Impact on Critical Infrastructure
Remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are excellent targets for denial of service (DoS) attacks and can have devastating consequences for power grids, communication networks, and nuclear plants. Preventing access to RTUs may result in physical damage, and interruption to critical services, as dangerous to public safety (Puri and Dukatz, 2015). An attack against financial institutions could also cause unauthorized use of bank transfers, data breaches, or compromise of financial integrity.
Preventive Measures and Solutions
| Security Measure | Description |
| Strong Access Controls and Authentication |
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) prevents brute-force attacks. Strong password policies reduce unauthorized access risks (Omotunde and Ahmed, 2023). |
| Traffic Filtering and Rate Limiting | Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) and firewalls block malicious traffic. Rate limiting restricts excessive requests from a single IP (El et al., 2022). |
| Secure Software Development Practices | Regular updates fix vulnerabilities. Input validation prevents SQL injection and buffer overflow (Rindell et al., 2021). |
| DDoS Mitigation Services | Cloud-based services (Cloudflare, AWS Shield) absorb attacks. Load balancing distributes traffic to reduce impact (Karnani and Shakya, 2023). |
| IoT Security Enhancements | Changing default IoT credentials prevents botnet attacks. RFID encryption secures access control systems (Pandey et al., 2022). |
Table 1: Preventive Measures and Solutions
Specifically, the table describes five essential security measures that can help prevent and mitigate cyber-attacks, including Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS). Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies along with strong access controls (that prevent unauthorized access) are strong controls. Cloudflare and AWS Shield are DDoS mitigation services that take on attack traffic, and IoT security enhancements include changing default credentials and encrypting RFID-based systems so that no one can gain unauthorized access or infect the system with a botnet.
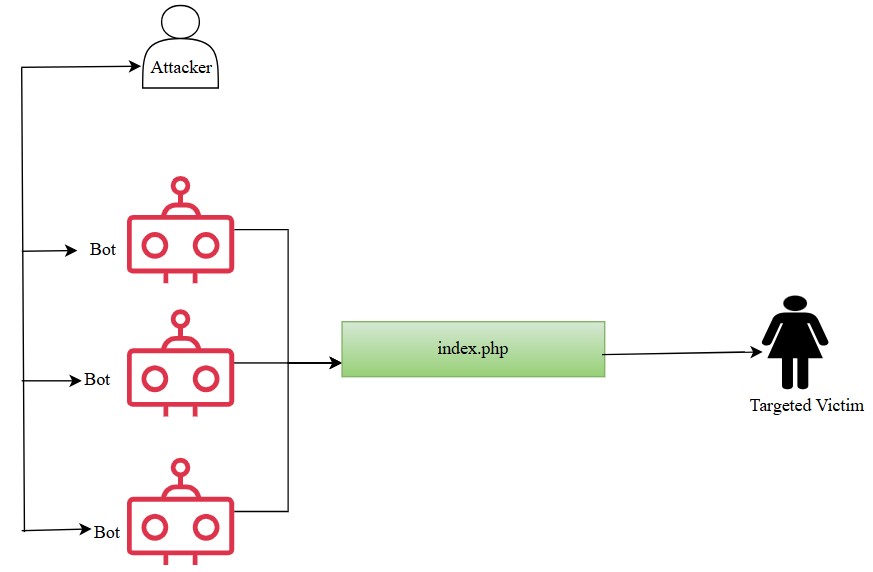
Figure 3: DDos Attack
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is shown in the above figure which uses many bot-controlled devices against a web application or service. The attack starts at the top, an entity we call 'Attacker' does not directly interact with the target. Instead, the attacker directs a network of compromised bots, displayed as red robotic icons, to regularly and repeatedly make malicious requests at a central target, pictured as 'index.php'. It was likely a script running a web app on a server that started overflowing with incoming traffic and overloading it, causing the performance to drop or the app to be inaccessible entirely.
The result of this attack was a legitimate user, a human figure labeled Targeted Victim could not access a web service (Mittal et al., 2023). The botnet generates an excessive number of requests which effectively block or slow legitimate access to online services, causing disruptions to the online services. The above image well illustrates how DDoS attacks typically operate to attack a company, websites, and all other online platforms. There are traffic filtering, rate limiting, botnet detection, and DDoS protection services such as Cloudflare or AWS Shield which help absorb and distribute attack traffic, but keep service available for legitimate users.
Resources:
- Prajapati, N.M., & Mishra, A. and, Bhanodia, P. (2014) Literature survey - ids for ddos attacks . Available from: IT in Business, Industry and Government (CSIBIG) online. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7056943?arnumber=7056943[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Puri, C. and& Dukatz, C. (2015) Analyzing and Predicting Security Event Anomalies: Lessons Learned from a Large Enterprise Big Data Streaming Analytics Deployment, pp. 152-158. Ain Proceedings of IEEE 26th International Workshop on Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA), [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Omotunde, H. and Ahmed, M., 2023. A comprehensive review of security measures in database systems: Assessing authentication, access control, and beyond. Mesopotamian Journal of CySecurity, 2023, pp.115-133.https://www.iasj.net/iasj/download/9ac0ae2ed78bc24c [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- El Kamel, A., Eltaief, H. and Youssef, H., 2022. On-the-fly (D) DoS attack mitigation in SDN using Deep Neural Network-based rate limiting. Computer Communications, 182, pp.153-169.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140366421004308[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Karnani, S. and Shakya, H.K., 2023. Mitigation strategies for distributed denial of service (DDoS) in SDN: A survey and taxonomy. Information Security Journal: A Global Perspective, 32(6), pp.444-468.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19393555.2022.2111004[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Pandey, J.K., Jain, R., Dilip, R., Kumbhkar, M., Jaiswal, S., Pandey, B.K., Gupta, A. and Pandey, D., 2022. Investigating role of iot in the development of smart application for security enhancement. In IoT Based Smart Applications (pp. 219-243). Cham: Springer International Publishing.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-04524-0_13[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Mittal, M., Kumar, K. and Behal, S., 2023. Deep learning approaches for detecting DDoS attacks: A systematic review. Soft computing, 27(18), pp.13039-13075.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00500-021-06608-1[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Rindell, K., Ruohonen, J., Holvitie, J., Hyrynsalmi, S. and Leppänen, V., 2021. Security in agile software development: A practitioner survey. Information and Software Technology, 131, p.106488.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950584920302305 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.4: Cloud vs local
At this time, cloud storage vs local storage is a choice that we have to consider especially about the issue of cybersecurity. Scalability, ease of use, and remote accessibility are all things that cloud platforms provide, whereas local storage also has more control and security advantages. Recent cyber-attacks on cloud-based services, however, have raised fears over their reliability and security. In this discussion, we discuss the pros and cons of cloud storage versus local storage and the cybersecurity implications.
Advantages of Cloud Storage in Cybersecurity
Scalability and Accessibility
Cloud services also enable people to view or use their data from anywhere and at any time. This is ideal for working with remote people and a global team. Yet, cloud platforms are a lot better than local storage as they allow seamless integration with several devices that do not necessarily need physical access or network-dependent solutions.
Security Measures by Cloud Providers
Cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure put a lot of work into security infrastructure like encryption, firewalls, AI-driven threat detection, and multi-factor authentication (MFA). The latest in advanced defences offers a level of security that may prove challenging to replicate from non-premises local storage solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness
It saves money on hardware maintenance, power consumption, and IT personnel. For organizations using solutions on the cloud, they can adjust their storage needs on the fly, paying only for what they use, instead of investing in large infrastructure (Wheeler, 2015).
Security Risks of Cloud Storage
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Being Internet-accessible, cloud storage is a favourite target for cybercriminals, hackers, and insider threats. Even a major cloud provider can’t be invincible, as evidenced by high-profile cloud breaches, such as the Capital One data breach in 2019, where even a major cloud provider can’t be invincible (Siciliano, 2019).
Dependence on Third-Party Security
Organizations that place trusted data in the hands of cloud providers require additional security on the external side. One example is a massive data leak in the cloud through a small misconfiguration in cloud settings (e.g., publicly exposed S3 buckets) of which the organization might not even be aware.
Regulatory Compliance Issues
Finances, healthcare, legal, government agencies … the industries that deal with sensitive data have to abide by rules such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. For such sectors that have to deal with specific regulations, cloud storage might not always be the best choice, and local storage remains a preferable choice (Wu and Irwin, 2013).
Downtime and Service Outages
So, from time to time, the outages at cloud providers make data temporarily inaccessible. Cloud platforms are dependent upon internet connectivity, and the uptime of their provider, and unlike local storage, are not always operational unless physically damaged.
Resources:
- Wheeler, A. (2015), Cloud storage security: a practical guide . Amsterdam: Elsevier, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Wu, C. and& Irwin, D. (2013) Introduction to Computer Networks and Cybersecurity : CRC Press, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Siciliano, Robert (2019), Cybersecurity Best Practices for Protecting Your Company's Data, Small Business, [Online]. Available at: https://www.thebalancesmb.com/best-cyber-security-practices-for-your-company-4158800 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.5: WannaCry
In 2017 the WannaCry ransomware attack exploited vulnerabilities in outdated Windows systems which encrypted files and demanded ransom. To prevent such attacks, the following security measures should be taken:
With Software Updates Available:
- You should update and patch OS as required and applications regularly.
- Keep your network updated automatically for any security fixes as they happen.
Without Software Updates Available:
- Don’t enable SMBv1 protocol which was exploited by WannaCry.
- Separate the network and isolate the vulnerable systems (Algarni,2021).
- Perform offline backups to restore data should an attacker attack your server.
- Remove admin privileges and limit internet exposure.
These strategies are combined and mitigate ransomware risks greatly.
Resources:
- Algarni, S., 2021. Cybersecurity attacks: Analysis of “wannacry” attack and proposing methods for reducing or preventing such attacks in future. In ICT Systems and Sustainability: Proceedings of ICT4SD 2020, Volume 1 (pp. 763-770). Springer Singapore.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-15-8289-9_73
at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lftSPF7bQOI [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.6: Backup
The Importance of Backup Systems in Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, the backup system is the things which are important to cyber threats of ransomware, failure of hardware, and accidental deletion which is the availability, integrity, and recovery of it in this situation. As part of risk management and disaster recovery planning, all cybersecurity frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27001, and CIS Controls include a backup strategy (Little, 2007). A good backup system reduces downtime, keeps your data safe, and guarantees your business goes on during a cyber incident.
For a large organization with multiple offices, an enterprise-level backup strategy should include:
- 3-2-1 Backup Rule Maintain three copies of data one on each of two different storage types and two offsite/cloud-based.
- Geo Redundant Cloud Storage is storing backups in multiple locations for you in case of a disaster in the region.
- Isolated Backups cannot encrypt these isolated backups, called Air-Gapped Backups.
- Immediate recovery options within cybersecurity response plans: Incident response integration.
Integrating backup strategies with cybersecurity frameworks allows organizations to reduce cyber threats, regain from attacks quickly, and safeguard critical business operations as a way to be resilient against the changing cyber risks.
Resources:
- Little, D.B. (2007) Digital data integrity: the evolution from passive protection to active
management - . Chichester: John Wiley [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
1.7: Password recovery
| Online Service | Password Reset Procedure | Potential Attack Vectors |
| Microsoft Outlook | Verification via email, SMS, or authenticator app; may require previous passwords or security questions; 2FA adds extra security. | Phishing for verification codes, SIM swapping to intercept SMS OTPs, and email hijacking for recovery email access (Sethuraman et al., 2024). |
| Amazon | Password reset via email or SMS; additional verification may include billing details or security questions; 2FA is required for high-risk logins. | Email/phone compromise, social engineering to manipulate customer support, brute force on security questions. |
| Reset via email, SMS, or linked Facebook account; may require photo verification for unusual logins; trusted devices may skip steps. | SIM hijacking to intercept SMS codes, credential stuffing using leaked passwords, and fake recovery requests targeting Facebook accounts (Faircloth et al., 2022). |
Table 2: Comparison of Password Recovery Procedures and Security Risks
Comparison of password recovery methods as well as safety risks of Microsoft Outlook, Amazon, and Instagram are made on the table and the way each platform deals with password resets as well as conceivable dangers for extortionists are explained. Password resets via email, SMS, an authenticator app, or questions/successful password verification will be supported via Microsoft Outlook with additional security layers like security questions or previous password verification. Where Two Factor Authentication (2FA) has been enabled, users need to add an OTP for added security. But, as with SIM swapping and email hijacking, this process is susceptible to being attacked using phishing (Zhao et al., 2021). The high-risk accounts need additional verification like their billing information, which means that Amazon uses email or SMS verification for password resets.
This makes security stronger but is still susceptible to email, phone, social engineering, or brute force attacks on security questions. There are also attempts to trick customer support into resetting passwords. There are various reset options available, including email, SMS, and Facebook links. Photo verification is used for suspicious logins as well. With these measures, Instagram remains susceptible to SIM hijacking where attackers intercept SMS codes credential stuffing, where passwords are reused from leaked accounts, and fake recovery requests are sent to your linked accounts. Both 2FA and strong passwords, and secured recovery email add substantially to the protection afforded by the multi-layered authentication employed by all three services.
Resources:
- Sethuraman, S.C., VS, D.P., Reddi, T., Reddy, M.S.T. and Khan, M.K., 2024. A comprehensive examination of email spoofing: Issues and prospects for email security. Computers & Security, 137, p.103600.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404823005102
Springer, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Faircloth, C., Hartzell, G., Callahan, N. and Bhunia, S., 2022, June. A study on brute force attack on T-mobile leading to SIM-hijacking and identity-theft. In 2022 IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT) (pp. 501-507). IEEE.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9817175/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Zhao, J., Ding, B., Guo, Y., Tan, Z. and Lu, S., 2021, October. SecureSIM: rethinking authentication and access control for SIM/eSIM. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (pp. 451-464).https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3447993.3483254 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
References
- Algarni, S., 2021. Cybersecurity attacks: Analysis of “wannacry” attack and proposing methods for reducing or preventing such attacks in future. In ICT Systems and Sustainability: Proceedings of ICT4SD 2020, Volume 1 (pp. 763-770). Springer Singapore.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-15-8289-9_73 Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lftSPF7bQOI [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Berkley (2020), Top 10 Secure Computing Tips, Berkley Information Security Office, [Online]. Available at: https://security.berkeley.edu/resources/best-practices-how-to-articles/top-10-secure-computingtips [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- CIS (2020), Cybersecurity Best Practices, [Online]. Available at: https://www.cisecurity.org/cybersecurity-best-practices , [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- CNBC (2016) Security Experts Talk Future of Cyber Security, YouTube. [Online]. Available
- cyberhoot.com (2024). Radio Frequency Identification Device, Retrieved from: https://cyberhoot.com/cybrary/radio-frequency-identification-rfid/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- El Kamel, A., Eltaief, H. and Youssef, H., 2022. On-the-fly (D) DoS attack mitigation in SDN using Deep Neural Network-based rate limiting. Computer Communications, 182, pp.153-169.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140366421004308, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Faircloth, C., Hartzell, G., Callahan, N. and Bhunia, S., 2022, June. A study on brute force attack on T-mobile leading to SIM-hijacking and identity-theft. In 2022 IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT) (pp. 501-507). IEEE.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9817175/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Karnani, S. and Shakya, H.K., 2023. Mitigation strategies for distributed denial of service (DDoS) in SDN: A survey and taxonomy. Information Security Journal: A Global Perspective, 32(6), pp.444-468.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19393555.2022.2111004 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Little, D.B. (2007) Digital data integrity: the evolution from passive protection to active
- management - . Chichester: John Wiley, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Mittal, M., Kumar, K. and Behal, S., 2023. Deep learning approaches for detecting DDoS attacks: A systematic review. Soft computing, 27(18), pp.13039-13075.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00500-021-06608-1 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Naveen Chilamkurti, Sherali Zeadally, and Hakima Chaouchi (2013), Next -generation wireless technologies . London: Springer, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Omotunde, H. and Ahmed, M., 2023. A comprehensive review of security measures in database systems: Assessing authentication, access control, and beyond. Mesopotamian Journal of CyberSecurity, 2023, pp.115-133.https://www.iasj.net/iasj/download/9ac0ae2ed78bc24c [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Pandey, J.K., Jain, R., Dilip, R., Kumbhkar, M., Jaiswal, S., Pandey, B.K., Gupta, A. and Pandey, D., 2022. Investigating role of iot in the development of smart application for security enhancement. In IoT Based Smart Applications (pp. 219-243). Cham: Springer International Publishing.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-04524-0_13 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Prajapati, N.M., & Mishra, A. and, Bhanodia, P. (2014) Literature survey - ids for ddos attacks . Available from: IT in Business, Industry and Government (CSIBIG) online. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7056943?arnumber=7056943[Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- psmpartners.com (2025). Top Practices of cyber security, Retrieved from:https://www.psmpartners.com/blog/cybersecurity-best-practices-for-small-businesses/ [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Puri, C. and& Dukatz, C. (2015) Analyzing and Predicting Security Event Anomalies: Lessons Learned from a Large Enterprise Big Data Streaming Analytics Deployment, pp. 152-158. Ain Proceedings of IEEE 26th International Workshop on Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA), [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Rindell, K., Ruohonen, J., Holvitie, J., Hyrynsalmi, S. and Leppänen, V., 2021. Security in agile software development: A practitioner survey. Information and Software Technology, 131, p.106488.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950584920302305 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- RSA Conference (2019), A View from the Front Lines of Cybersecurity, YouTube [Online]. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7EH7ehAY3_w [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Sethuraman, S.C., VS, D.P., Reddi, T., Reddy, M.S.T. and Khan, M.K., 2024. A comprehensive examination of email spoofing: Issues and prospects for email security. Computers & Security, 137, p.103600.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404823005102 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Siani Pearson and George Yee (2013), Privacy and security for cloud computing -. London, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Siciliano, Robert (2019), Cybersecurity Best Practices for Protecting Your Company's Data, Small Business, [Online]. Available at: https://www.thebalancesmb.com/best-cyber-security-practices-for-your-company-4158800 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Wheeler, A. (2015), Cloud storage security: a practical guide . Amsterdam: Elsevier, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Wu, C. and& Irwin, D. (2013) Introduction to Computer Networks and Cybersecurity : CRC Press, [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Zhao, J., Ding, B., Guo, Y., Tan, Z. and Lu, S., 2021, October. SecureSIM: rethinking authentication and access control for SIM/eSIM. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (pp. 451-464).https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3447993.3483254 [Retrieved on 29.01.2025].
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, nonumes voluptatum mel ea, cu case ceteros cum. Novum commodo malorum vix ut. Dolores consequuntur in ius, sale electram dissentiunt quo te. Cu duo omnes invidunt, eos eu mucius fabellas. Stet facilis ius te, quando voluptatibus eos in. Ad vix mundi alterum, integre urbanitas intellegam vix in.
- Eum facete intellegat ei, ut mazim melius usu. Has elit simul primis ne, regione minimum id cum. Sea deleniti dissentiet ea. Illud mollis moderatius ut per, at qui ubique populo. Eum ad cibo legimus, vim ei quidam fastidii.
- Quo debet vivendo ex. Qui ut admodum senserit partiendo. Id adipiscing disputando eam, sea id magna pertinax concludaturque. Ex ignota epicurei quo, his ex doctus delenit fabellas, erat timeam cotidieque sit in. Vel eu soleat voluptatibus, cum cu exerci mediocritatem. Malis legere at per, has brute putant animal et, in consul utamur usu.
- Te has amet modo perfecto, te eum mucius conclusionemque, mel te erat deterruisset. Duo ceteros phaedrum id, ornatus postulant in sea. His at autem inani volutpat. Tollit possit in pri, platonem persecuti ad vix, vel nisl albucius gloriatur no.
- Ea duo atqui incorrupte, sed rebum regione suscipit ex, mea ex dicant percipit referrentur. Dicat luptatum constituam vix ut. His vide platonem omittantur id, vel quis vocent an. Ad pro inani zril omnesque. Mollis forensibus sea an, vim habeo adipisci contentiones ad, tale autem graecis ne sit.
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, nonumes voluptatum mel ea, cu case ceteros cum. Novum commodo malorum vix ut. Dolores consequuntur in ius, sale electram dissentiunt quo te. Cu duo omnes invidunt, eos eu mucius fabellas. Stet facilis ius te, quando voluptatibus eos in. Ad vix mundi alterum, integre urbanitas intellegam vix in.
- Eum facete intellegat ei, ut mazim melius usu. Has elit simul primis ne, regione minimum id cum. Sea deleniti dissentiet ea. Illud mollis moderatius ut per, at qui ubique populo. Eum ad cibo legimus, vim ei quidam fastidii.
- Quo debet vivendo ex. Qui ut admodum senserit partiendo. Id adipiscing disputando eam, sea id magna pertinax concludaturque. Ex ignota epicurei quo, his ex doctus delenit fabellas, erat timeam cotidieque sit in. Vel eu soleat voluptatibus, cum cu exerci mediocritatem. Malis legere at per, has brute putant animal et, in consul utamur usu.
- Te has amet modo perfecto, te eum mucius conclusionemque, mel te erat deterruisset. Duo ceteros phaedrum id, ornatus postulant in sea. His at autem inani volutpat. Tollit possit in pri, platonem persecuti ad vix, vel nisl albucius gloriatur no.
- Ea duo atqui incorrupte, sed rebum regione suscipit ex, mea ex dicant percipit referrentur. Dicat luptatum constituam vix ut. His vide platonem omittantur id, vel quis vocent an. Ad pro inani zril omnesque. Mollis forensibus sea an, vim habeo adipisci contentiones ad, tale autem graecis ne sit.

