- Methods Of Advancements Design Materials Lower Prosthetic Limbs
- Eligibility criteria
- Information sources
- Search strategy
- Data collection
- Quantitative Data Collection
- Validity and Reliability
- Ethical Considerations
- Data analysis
- Thematic Analysis
- Theme development and interpretation.
- Validity and Reliability
- Results
- Theme 1: Clinical Innovations and Mechanisms in Osseointegration for Amputees
- Theme 2: “Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites” in Lower-Limb Prosthetic
- Theme 3: Multifunctional Role of Composite Materials
- Theme 4: Innovative Prosthetic Interfaces
- Theme 5: Advancements and Challenges in Robotic Rehabilitation
- Discussion
- Interpretation of Results
- Context and Significance
- Unexpected Findings and Challenges
- Evaluating the Future Prospects
- Communication approach for research outcomes
- Evaluation of the Communication Approach
- Exploration of Established Communication Methods
- Identifying the Target Audience
- Communication approach
- Conclusion
- Brief Report
- Introduction
- Key Technological Innovations
- Transcutaneous Osseointegration (TOI)
- Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites (NFRCs)
- Interface and Suspension Systems
- Robotic Rehabilitation Developments
- Challenges and Future Directions
- Recommendations
Methods Of Advancements Design Materials Lower Prosthetic Limbs
Eligibility criteria
Table 1: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
| Population | Prosthesis users with lower limb prosthetics | The studies on upper limb prosthetics |
| Intervention | The developments in prosthetic material and structures from 1960 to 2024. | Papers that are nevertheless not directly connected to the field of prosthetics technology |
| Comparison | Older prosthetic designs and/or material | Non-comparative studies |
| Outcomes | Comfort, functionality, durability | Used studies that do not demonstrate clearly defined goals |
| Study Design | Qualitative method | Editorials, opinions, or reviews |
| Language | English | Non-English publications |
| Publication Status | Medical and scientific peer-reviewed and non-peer reviewed, grey literature | Unpublished data |
Information sources
The sources of info will be research databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science for research articles. Also, the International grey literature from institutional reports, technical publications, and conference papers will also be considered. Published materials will also be reviewed from trial registers including ClinicalTrials.gov. We may request the authors of pivotal studies in cases where unpublished information is needed. These include materials published between 1960 and 2024 to match the research interest of prosthetic development. Language is limited to English to make the process more manageable and to have uniformity in all the sources used.
Search strategy
As for the search strategy for this study, we will consider all the sources published from 1960 to 2024 concerning developments in lower limb prosthetics (Peters et al. 2020). To that end, the primary electronic databases to be employed shall be, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science since they provide a comprehensive database of biomedical and engineering fields. A secondary search will be done in Google Scholar, ProQuest, and grey literature and technical reports from government, and institutional repositories. The current approach will use keywords and Boolean operators to improve on the kind of results obtained. The main keywords will consist: Table 2: Key words and Boolean Operators
| Key Words | Boolean Operators |
| “lower limb prosthetics”, “user satisfaction”, “prosthetic design”, “prosthetic materials”, “comfort”, “durability,” and “technological advancements”. | AND, OR, NOT |
There will be additional sorting criteria to allow only peer-reviewed articles, technical papers, and studies in English only. Specifically, there will be no searches in upper limb prosthetics and no non-comparative studies of human topics will be included (Tibúrcio‐Machado et al. 2021). For a thorough review of citation tracking and reference lists, the search of the identified articles will be done. Furthermore, trial registries and author contact will provide additional information sources and form a source of backup information about the topic.
Academic success starts here. New Assignment Help offers personalized Assignment Help in UK that fits your requirements perfectly.
Data collection
The process of data collection will be organised to guarantee that the information to be gathered comprehensively covers the developments in prosthetic limb technology from the year 1960-2024. Both qualitative and quantitative data will also be used in the study and thus, the mixed-method design will be adopted.
Quantitative Data Collection
Qualitative data will concern with prosthetic materials and designs results of effectiveness performance. Information will be lodged in peer-reviewed journals, clinical trials, as well as technical reports. Essential parameters like the strength of materials, flexibility, durability and comfort to the user will be derived (Peel 2020). Internet sources such as PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar especially peer reviewed articles and research papers will be consulted extensively. An advanced search approach will use a set of relevant terms and connecting words to filter the outcomes.
Validity and Reliability
It can be made to recognized that the process of data collection used in this study does not have the problem of selection bias due to the use of several databases and information sources. Using articles that passed the peer reviewing process allows obtaining the data of high quality. Grey literature augments from the fact that it provides information that may not be obtainable from discover refereed journals. Reliability is maintained through the usage and standardization of a data extraction form, and distinct eligibility or exclusion criteria. All the inconsistencies that may arise between the extracted data shall be rectified through consultation so that the reliability is boosted.
Ethical Considerations
The quality data shall be collected from participants and informed consent given by each of the participants. Pertaining to anonymity and confidentiality, it will be employed from the beginning of the study up to the end.
Data analysis
This account will incorporate qualitative data analysis outcomes in as much as the study will offer an elaborate account of new technologies in prosthetics for data Analysis Process. The research data analysis procedure will be based on the qualitative analysis of secondary data sources crucial to thematic analysis (Hamel et al. 2021). This is also a quantitative work approach that we will undertake, where we will collect and examine papers that enthused on specifically selected key advancement in lower limb prosthetics over the reviewed period from 1960 to 2024 and look for paucity.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis will be conducted in three main phases: descriptive analysis is about data familiarization, development of themes, and in-depth analysis of those themes. The next step is to take the necessary steps in order and read through having gathered pertinent qualitative data. On this account, coding will be focused on excerpts that describe prosthetic material innovations, design enhancements, and the overall findings of the users (Lochmiller 2021). As a result of the prevalence of these areas of interest in the data and the research objectives, a coding framework will be generated.
- Material Advancements: Material composite alterations on prosthetics mainly with regard to weight, durability, and flexibility.
- Design Innovations: Modifications in the locations and shapes of the prosthetic members to facilitate the comfort of the individual.
- User-Centered Outcomes: Information concerning customers’ satisfaction, comfort, and the enhancements on the functionality of the screens and other interfaces.
Theme development and interpretation.
After generating the themes, triangulation will be used to create the themes. These themes will reflect the general directions of the prosthetic development (Christou 2022). An additional qualitative method of synthesis will be narrative synthesis, which will illustrate how disparate advancements have developed over time and, with them, the user experience.
Validity and Reliability
Interpretation of study themes will be done by triangulation by comparing the results of different studies to establish coherence. Self-generated code checks and themes were created through group discussion will improve reliability, as the coder will not be proven bias in the development of the theme.
Results
Theme 1: Clinical Innovations and Mechanisms in Osseointegration for Amputees
In the present study by Hoellwarth et al.,2021, the section dealing with the results explains enhancement done on transcutaneous osseointegration (TOI) and its basics. Osseointegration as the direct contact between bone and implant was developed from dental implants by Brånemark who used titanium material because of its favorable interaction with the body tissues and mechanical compatibility (Hoellwarth et al. 2021). That is why an important direction of this work is the consideration of principles of this concept and their application in the field of limb prosthetics, with reference to a decrease in prosthetic complications and an increase in load transfer. Important findings is related to the cellular and tissue reactions to titanium implants. Imaging also shows that there at mature lamellar bone formation around the implants which are necessary for the longevity of the implant. Cultures also show that living osteoblasts adhere perfectly to titanium surfaces, hence, the material is biocompatible. Moreover, own prior application of Malgaigne clamps and early limb implants as well as of the further developed TOI methods indicate continuous improvement (Hoellwarth et al. 2021). The clinical implications support TOI’s ability to dramatically improve amputees’ prosthetic control and to do away with problematic sockets. Nevertheless, infection risks are another essential concern with which researchers have not yet been able to overcome specific difficulties when it comes to implant design and surface treatments. In a broad perspective, TOI has become a major innovation and improvement in prosthetics that distinguish the clinical demand with biomechanical development.
Theme 2: “Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites” in Lower-Limb Prosthetic
The development of “natural fiber-reinforced composites (NFRCs)” make them poised to be used for sustainable lower-limb prosthesis designs. These composites provide supreme advantages such as improved biocompatibility, low density and comparatively improved environmental concern than CFRP and other metal alloys.
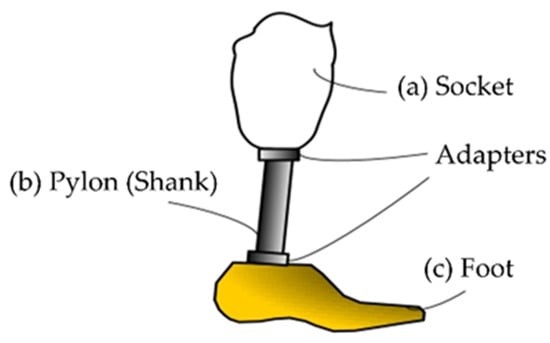
Figure 1: Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites
In their study, the authors relate prosthetic applications to the characteristics of the material used which includes stiffness, flexibility and impact strength. Natural reinforcements are preferred and normally used ones include flax, jute and hemp because of their impressive mechanical characteristics and accessibility. Furthermore, it is possible to design NFRCs according to the applicable load-bearing and the flexural flexibility necessary to constantly fit lower limb prostheses for the users (Castro-Franco et al. 2024). Issues remain a matter of lasting strength and uniformity in resistance to such conditions as moisture and variations in temperature. To the researchers, there is a discursive call for the development of improved manufacturing and surface technologies to transform the durability and mechanical properties of these composites. Moreover, the inclusion of NFRCs in prosthetic devices has implications for testing and certification for the relevant prosthetics. Therefore, using NFRCs in prosthetic applications shows a great potential for further development of sustainable patient-oriented solutions in the field of medical device.
Theme 3: Multifunctional Role of Composite Materials
The findings of the review point to the need for the use of composite materials in order to provide boost to the performance, support, and flexibility of exercise equipment. They have low density and high stiffness, which makes it easier to design articles that are light and b and which can be adapted to different fitness uses. This comprises racquets, tennis, squash, badminton and golfing equipment, and strength training equipment, in which optimum stiffness and fatigue strength are critical to performance improvement. In rehabilitation and recovery habitats, composites are used in braces and padding, as well as in prosthetics to support joints as well as to allow for activity. That is partly because the materials used have good shock absorption characteristics, minimizing the strain that muscles feel and making workouts more comfortable (Fan et al. 2024). These gains must be noted to stem from careful material choices and the drive for more advanced design, according to the study. New area of research is aimed at creating new multifunctional high-performance polymer composites with increased lifetimes and the smart material applications. They are expected to change the entire face of the exercise fraternity by providing equipment that enhances strength and flexibility as well as offers client-specific training and injury management.
Theme 4: Innovative Prosthetic Interfaces
New developments and enhancements in lower limb prosthetic interfaces have concerned socket design, suspension systems and manufacturing materials with aiming to provide comfort, function and mobility for the users. The Total Surface Bearing (TSB) socket and Vacuum-Assisted Suspension Systems (VASS) are among the improvements experienced. TSB sockets provide pressure distribution on the residual limb painless and comfortable particularly when combined with viscoelastic liners. VASS enhances this a notch higher by using controlled vacuum pressure, enhanced suspension stability and improved residual limb health is realized (Safari 2020). Sub-ischial sockets do not touch the pelvis and offer users great mobility and comfort. These designs decrease the value of the trim line and yet increases the flexibility and stability of use. Other relatively recent designs, such as the High Fidelity socket, consider the squeezing of soft tissues as means to keep the femur steady and more comfortable for the patient.
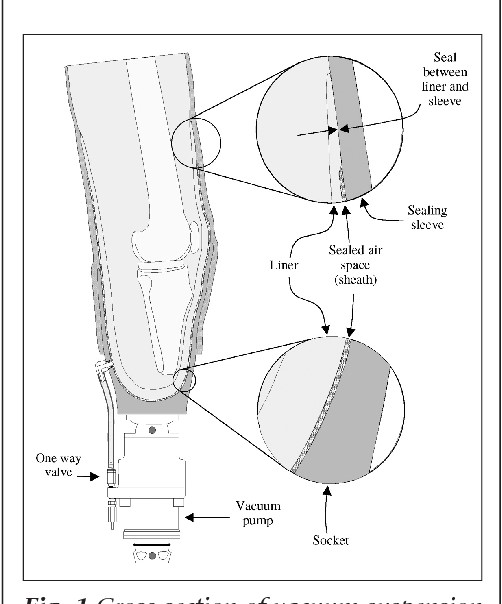
Figure 2: Vacuum-Assisted Suspension Systems (VASS)
However, there are some issues that exist to date. Most clinic based trials are methodologically less robust, thus it becomes doubtfully feasible to evaluate the sustained efficacy of these systems. Therefore, future research which should be more extensive and including systematic single blinded or double blinded randomized controlled trials will be useful to determine their actual effect on the quality of lives of the users and their worth from the financial standpoint. Other possibilities of future developments are smart materials and smart sensors needed for monitoring the use of prostheses and enhancing its effectiveness.
Theme 5: Advancements and Challenges in Robotic Rehabilitation
In this section, the authors outline new technological advancements to the robotic rehabilitation devices for lower limb function recovery. These developments are partially focused on the areas of mobility and strength, as well as functional independence in disabled patients with diseases like stroke, spinal cord trauma, and other neurologic disorders (Bhardwaj et al. 2021). The paper also focuses on several forms of robotic exoskeletons, prostheses, and assistive or interventional therapeutic robots that have been designed in an attempt to support the rehabilitation process by providing individualized assistance and motion profiles. They have cut down the amount of physical demands on therapist and also improved the quality of treatment offered to patients.

Figure 3: robotic rehabilitation devices
However, the findings show that there is still much to be done in the areas of cost, availability and usage and acceptance. Most robotic systems are still costly, therefore making scalability of the robotic systems in clinical setup especially in the developing countries a challenge. However, extensive issues on patient acceptance and subsequent adoption of robotic systems in daily rehabilitation further remain concerning discomfort and ease of use (Bhardwaj et al. 2021). The authors recommend carrying out more research to develop on the subsequent systems to lower costs, comprise better patient-robot interaction and overall, to augment the systems’ versatility for rehabilitation purposes.
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
This study has demonstrated improvement in robot assist and robotic rehabilitation in the lower limb impaired persons as well as advances in prosthetic technology for the improvement of mobility of the affected persons. As shown by the current research, the development of new solutions include TOI technique, insertion and application of the NFRCs in prosthetics, and the construction of robotic rehabilitation equipment (Roy et al. 2024). All of these innovations are equally important to contribute an improvement in functional recovery for the patients with different disabling conditions especially for the stroke, traumatic brain or spinal cord injuries, Neuromuscular disorders, or any other neurological disorders. Direct bone-implant contact known as TOI has been developed from dental implant technologies and may provide better prosthetic control and fewer complications with sockets. In limb prosthetics, the application of this technology enable better load distribution and the overall loading is minimized among the users (Choudhari et al. 2024). From the results of the present study concerning to biocompatibility reactions of titanium plates such as lamellar bone formation and osteoblast adhesion, it is assumed that the TOI can has an important responsibility on limb prosthetics’ success. Also, the use of natural fiber reinforced composites (NFRCs) has similar economic benefits to CFRPs and has environmental advantages and better biocompatibility than traditional carbon fiber reinforced polymers. Flax, jute and other fabrics possess mechanical characteristics that make them suitable for use in prosthetic limb appliances. However, issues to do with resistance to moisture and other forms or durability still persist (Han and Harnett 2024). The need to advance the pressing manufacturing technologies illustrated by the NFRCs mascots implies that the future of sustainable prosthetic materials is in advanced strength, moisture resistance and consistency.
Context and Significance
The significance of these developments cannot be overemphasized, particularly because most of the problems that affect the users of lower-limb prosthetics are squarely addressed here. Most of the conventional prosthetic designs affect the comfort and foremost, skin complications, and poor mobility. TOI and NFRCs are the solutions that make the difference and help to have more durable, comfortable, and effective innovations. We provide promising solutions to these persistent problems in prosthetics, patients will therefore gain more flexibility and therefore a higher quality life. Robotic rehabilitation technologies also have a great importance with potential utilization. Friendly technological occupational therapeutic tools like robotic exoskeletons, prostheses, and therapeutic robots are helpful tools in the rehabilitation of clients who suffer from neurological problems, stroke, or spinal cord injuries (Mohammadi et al. 2024). It is optional to such systems to facilitate functional recovery because these systems are supposed to address functional needs of individual patients depending on their uniqueness. They can alleviate the amount of physical pressure that is felt by a therapist and increase the level of the provided rehabilitation services. But the problem of cost relegates this form of transport to the background while its implementation remains a major dream due to its high costs in the developing world. Further optimization of these technologies and their subsequent cost-effectiveness will be crucial to their utilization in the clinical practice worldwide.
Unexpected Findings and Challenges
As with the case of prosthetics and rehabilitation, several interesting and somewhat unexpected results were revealed in this study that require further investigation. Another important question to be raised is the possibility of infections in transcutaneous osseointegration (TOI). Nevertheless, Kosmac’s work has shown that infection, which is a severe drawback of such constructs, does not seriously hinder the osseointegration and biomechanical compatibility outcomes (Chatterjee et al. 2024). This emphasises the importance of future studies into the implant design aspect, the surface finishes together with sterilisation processes that can reduce infection chances, and enhance the general efficacy of TOI. Another surprising aspect relates to application of natural fiber-reinforced composites (NFRCs) to prosthetics. Although these materials have relative advantages on the sustainability and, biocompatibility aspects, these composites present some issues in the moisture resistance and the longer term strength. Due to the fact that mechanical properties of natural fibers, particularly their responses towards environmental factors such as temperature alterations are inconsistent, durability becomes an issue of concern. The continuous improvement of manufacturing technology must be able to look into these issues but practical application of these composite material in prosthetic devices still needs more research and development. The use of robotic rehabilitation has been seen to have many advantages in rehabilitation, but the major drawback has been the high price of the devices, which make it expensive for many patients. However, there is the problem of patient compliance and adjustment to the robotic systems and the patients complained of discomfort and challenges with the devices (Parente et al. 2024). These results suggest that additional research is needed to optimize the interaction between a patient and the robot as well as the overall design of the robotic system. They suggest that the availability of cheaper robotic rehabilitation technologies would indeed revolutionize limited access to rehabilitation, but this is made possible only when these technical and social barriers are addressed.
Evaluating the Future Prospects
The results of this research emphasize the successfully of these achievements in prosthetics and rehabilitation robotics. It is the future work that should pursue the goal of increasing the availability and efficacy of these technologies (Sanjarnia et al. 2024). An analysis of potential future developments in NFRC/implant technologies indicates that future advancements in this area would be achieved through research in the following directions, Biocompatibility and improved surface characteristics of implants, Durability of NFRCs, Cost and ergonomics of robotic rehabilitation systems. The increased focus on the individual approach in rehabilitation also speaks for this kind of solutions. The self-learning robotic systems that can provide personalized patient care specially for the patients with neural injury or trauma are the area of opportunity with regard to enhancing the rehabilitative process (Li et al. 2024). Further, incorporating such advanced materials as NFRCs with sophisticated prosthetic solutions can promote producing even lighter yet ber and more durable prostheses which will fulfill the needs of patients. Finally, this will require further cooperation of engineers, healthcare professionals and researchers to answer them and to advance these technologies to the cutting edge of clinical applicability (Jiang et al. 2024). With regards to cost reduction, the overall interaction between the robot and the patient, as well as the improvement of material technologies in the future, the field of lower-limb rehabilitation robotics is viewed with positive potential to change rather the prosthetic and rehabilitation services across the world.
Communication approach for research outcomes
Evaluation of the Communication Approach
The use of the communication approach in disseminating the findings and analysis of the research was critically assessed. Both the concurrent explanatory text and data sources included tables, figures and summaries of thematic analyses that provided the overall context of the study. This meant that the content was easily understood by the common person, as was necessary for this type of publication. The findings on the underdeveloped prosthetic limbs are presented systematically thus streamlining topics such as, material developments, design enhancements, and future developments (Kulkarni et al. 2024). This system enabled the chronological progression of the data and in some way could satisfy the professionals as well as those who are not so well familiar with narrow specialization. However, some challenges were noted. This is particularly due to the technical terms used when naming some of tools and methodologies such as Transcutaneous Osseointegration or Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites. However, to enhance understanding there was need for additional clarification of some terms even as definitions were extended. This is indicative of a desire to tailor both visual (graphic) and linguistic appeals more suitably according to the target audience.
Exploration of Established Communication Methods
The researcher disseminates the results in different communication through writing results in a journal, presenting his findings in conferences and through publishing on the internet. These modes make sure that the findings reached the various stakeholders in academic, clinical, and industrial contexts. The identified peer-reviewed journals were highlighted because credit and reliability of the results obtained were provided. Reporting of the results in the two approaches with the theme of analysis and the quantitative form has also been common for quite a long period (Marinelli et al. 2023). These themes represented the main modes of communication that are actively used in science-oriented domains and that stress explicitness, cohesiveness, and accuracy of language. Graphs and other images were a second method which was considered, these are commonly employed to present data information particularly in material and engineering analysis. However, the performance of these, the research figured out, is best optimised whenever they are made simpler in order to understand by people of lesser educative background.
Identifying the Target Audience
The target population for this research mainly included medical personnel, engineers, prosthetics producers, and scholars. This audience defined not only the medium of the message but also these content because of its selection. They spoke in the specialized language familiar to academics and supplied their technical demands with an account of the advancements made in materials like carbon fiber and titanium (Xu & Qin, 2023). It included the other users that may be interested with knowledge of the studies’ implications in the life of patients who suffer from limb loss and their cares. For this audience, efforts were made to try and explain how these advances could lead to prosthetics that are less uncomfortable to wear and which are more long-lasting. Less problematic terms, and easier examples might have been helpful to use for communicating with this group.
Communication approach
In the chosen communication approach the use of written and visual media were employed. One suitable strategy of communication for this research could be the type “Interactive Infographic-Based Storytelling” with the use of exciting graphics and infographics. The detailed written report was created, and tables that presented details of inclusion criteria, keywords used and study design were prepared. They said there were specific sections given on the topics like robotic rehabilitation, new material and future developments (Raspopovic et al. 2021). To make results applicable, clarified quick briefs were used in the discussion and conclusion segment where easy and intense interaction of the study propositions can occur without overwhelming the audience with complex technicalities. Descriptions of prosthetic designs, and tabulated summaries of the research findings as supplementary figures readily explained in text are also employed throughout. The approach was effective for the primary audience, but might have been further implemented for the secondary audience. Other means of passing information such as through graphics, or animations might have been more appealing to non-experts. Assessing the communication strategy, it can be noted that the research successfully translated the discovered improvements in the design and materiality of lower limb prosthetics to the audience. Organization of the presentation by themes, thematic analysis and the incorporation of visuals were well in line with research communication literature. Apart from that, some alterations are necessarily to demystify the terms and visualizations for the broader no specialist audience. It will be necessary for future studies to apply various modes of communication including the interactive media in an effort to increase the representativeness of the research. This would enhance dissemination of the research findings to other people, and hence enhance the usage of the research findings.
Conclusion
Thus, the findings of this study help to elucidate the major breakthrough and progress in the design of the modern prosthetics and robotic rehabilitation. There are forecasts of future in transcutaneous osseointegration, natural fiber-reinforced composites, and robotic exoskeletons where rehabilitation and prosthetic care is concerned. Remaining objectives include issues pertaining to infection risks, material’s ability to withstand wear and tear, its cost, and patient acceptance. The improvements of design & material in lower prosthetic limbs from 1960 to 2024 are revolutionary for those with limb loss, as allowing the users greater mobility and comfort. Prosthetics in the 1960s were based mainly on elementary mechanical designs and used massive materials in their construction. New materials such as carbon fibre, and novel polymer composites that made their way into prosthetics, enhanced both the durability as well as comfort. The addition of robotic systems and neural interfaces in the recent year is also an innovation which has allowed users more direct control and added to rehabilitation. In future, there are efforts and concern for enhancing the cost, availability and satisfaction with these enhanced technologies so as to make them available and applicable to the clients with lower-limb amputation.
Brief Report
Introduction
In the field of lower limb prosthetics in the last six decades with regard to materials, design and technology. The presented studies suggest that the advancements concerning osseointegration, natural fiber composites and robotic rehabilitation systems have been recently achieved.
Key Technological Innovations
Transcutaneous Osseointegration (TOI)
TOI is one of the progressive enhancements in prosthetic attachment, which provides direct implant support by using titanium. It has been shown that with this technology the prosthetic control is better enhanced and many complications regarding the sockets are prevented (Joshi and Badola 2024). Titanium materials have provided impressive biocompatibility with successful lamellar bone formation and osteoblast adhesion but infection factors are an area that needs additional investigation.
Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites (NFRCs)
NFRCs are thought to represent one of those sustainable options to compete with the CFRP where biocompatibility and density is concerned. Flax fiber, jute fiber, and hemp fiber can be considered a good candidate for development as prosthetic materials due to their good mechanical behavior (Sanjarnia et al. 2024). But they still have drawbacks in moisture resistance and long-term materials and durability, therefore, requiring manufacturing development.
Interface and Suspension Systems
Some of them include, Total Surface Bearing (TSB) sockets and Vacuum-Assisted Suspension Systems (VASS). These innovation give an improved pressure distribution and greater stability for the users. Sub-ischial sockets have also been presented being able to provide better slippage and comfort excluding contact with the pelvis.
Robotic Rehabilitation Developments
Technologically advanced rehabilitation equipment have brought a major change in the processes of treatment among those with various diseases, such as a stroke or spinal cord injuries. These systems are: Exoskeletons, Smart prostheses, Therapeutic robots. Lack of high costs of this equipment and accessibility continue to be a major challenge despite the fact that innovations cut down on the amount of stress on the therapist and enhances the quality of treatment given to the patients.
Challenges and Future Directions
Current Challenges
- With regard to infection threats for TOI implementations, clearly the use of gloves and other healthcare equipment increases the risk for infection.
- Resistance to wear and tear, as well as resistance to moisture contents in NFRCs
- Expensive or costly robotic rehabilitation systems
- Perceived usefulness and ease of use of the new technologies
- However, promising innovations that have demonstrated significant clinical trial yields are not exotic or new.
Future Prospects
- Improvement of the manufacturing processes of NFRC
- The institution must look into enhancing the effectiveness of the robotic options in its operation at a minimum cost
- Developing unique rehabilitation processes
- Applying smart material and sensors
- The author calls for more spending in research about infection prevention in the context of TOI.
Recommendations
- Since there are numerous opportunities in robotic rehabilitation systems, the emphasis should be placed on cost containment measures.
- Pursue more Clinical studies
- Thus, encourage engineers, healthcare professionals, and researchers work cooperatively.
Conclusion
Significant trends in materials, design, and rehabilitation technologies have characterized the progress of lower limb prosthetics from 1960 to 2024. Although there remains much work to be done, the profile of further improvements and research as well as closer interaction between disciplines indicate future improvements. Achieving success in these current limitations can greatly enhance access and functionality of prosthetic products globally.
Reference List
Journals
- Bhardwaj, S., Khan, A. A., and Muzammil, M. 2021. Lower limb rehabilitation robotics: The current understanding and technology. Work, 69(3), 775-793.
- Castro-Franco, A. D., Siqueiros-Hernández, M., García-Angel, V., Mendoza-Muñoz, I., Vargas-Osuna, L. E., and Magaña-Almaguer, H. D. 2024. A Review of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites for Lower-Limb Prosthetic Designs. Polymers, 16(9), 1293.
- Chatterjee, S., Das, S., Ganguly, K. and Mandal, D., 2024. Advancements in robotic surgery: innovations, challenges and future prospects. Journal of Robotic Surgery, 18(1), p.28.
- Choudhari, A., Gupta, A.K., Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Gupta, A., Chowdhury, N. and Kumar, A., 2024. Wear and friction mechanism study in knee and hip rehabilitation: A comprehensive review. Applications of biotribology in biomedical systems, pp.345-432.
- Christou, P.A., 2022. How to use thematic analysis in qualitative research. Journal of Qualitative Research in Tourism, 3(2), pp.79-95.
- Fan, Q., Duan, H., and Xing, X. 2024. A review of composite materials for enhancing support, flexibility and strength in exercise. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 94, 90-103.
- Hamel, C., Michaud, A., Thuku, M., Skidmore, B., Stevens, A., Nussbaumer-Streit, B. and Garritty, C., 2021. Defining rapid reviews: a systematic scoping review and thematic analysis of definitions and defining characteristics of rapid reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 129, pp.74-85.
- Han, M.S. and Harnett, C.K., 2024. Journey from human hands to robot hands: biological inspiration of anthropomorphic robotic manipulators. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 19(2), p.021001.
- Hoellwarth, J. S., Tetsworth, K., Akhtar, M. A., and Muderis, M. A. 2021. The Clinical History and Basic Science Origins of Transcutaneous Osseointegration for Amputees. Advances in Orthopedics, 2022(1), 7960559.
- Jiang, M., Deng, W. and Lin, H., 2024. Sustainability through Biomimicry: A Comprehensive Review of Bionic Design Applications. Biomimetics, 9(9), p.507.
- Joshi, R. and Badola, R., 2024. Feasibility of AI and Robotics in Indian Healthcare: A Narrative Analysis. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Drug Design and Development, pp.563-603.
- Kulkarni, P.G., Paudel, N., Magar, S., Santilli, M.F., Kashyap, S., Baranwal, A.K., Zamboni, P., Vasavada, P., Katiyar, A. and Singh, A.V., 2024. Overcoming challenges and innovations in orthopedic prosthesis design: an interdisciplinary perspective. Biomedical Materials & Devices, 2(1), pp.58-69.
- Li, J., Zhang, F., Lyu, H., Yin, P., Shi, L., Li, Z., Zhang, L., Di, C.A. and Tang, P., 2024. Evolution of Musculoskeletal Electronics. Advanced Materials, p.2303311.
- Lochmiller, C.R., 2021. Conducting thematic analysis with qualitative data. The Qualitative Report, 26(6), pp.2029-2044.
- Marinelli, A., Boccardo, N., Tessari, F., Di Domenico, D., Caserta, G., Canepa, M., Gini, G., Barresi, G., Laffranchi, M., De Michieli, L. and Semprini, M., 2023. Active upper limb prostheses: A review on current state and upcoming breakthroughs. Progress in Biomedical Engineering, 5(1), p.012001.
- Mohammadi, A.T., mohammad Taheri, S.A., Karamouz, M. and Sarhaddi, R., 2024. Rising Innovations: Revolutionary Medical and Dental Breakthroughs Revolutionizing the Healthcare Field. Nobel Sciences.
- Parente, M.A., Geil, M. and Monroe, B., 2024. In the future: prosthetic advances and challenges. Prosthetics and Patient Management, pp.215-231.
- Peel, K.L., 2020. A beginner’s guide to applied educational research using thematic analysis. Practical Assessment Research and Evaluation, 25(1).
- Peters, M. D., Marnie, C., Tricco, A. C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., ... and Khalil, H. 2020. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI evidence synthesis, 18(10), 2119-2126.
- Raspopovic, S., Valle, G. and Petrini, F.M., 2021. Sensory feedback for limb prostheses in amputees. Nature Materials, 20(7), pp.925-939.
- Roy, S., Ahuja, D. and Kumar, V., 2024. Research and Advancements. Chest Wall Tumors: A Comprehensive Review Book, p.93.
- Safari, R. 2020. Lower limb prosthetic interfaces: Clinical and technological advancement and potential future direction. Prosthetics and Orthotics International.
- Sanjarnia, P., Picchio, M.L., Solis, A.N.P., Schuhladen, K., Fliss, P.M., Politakos, N., Metterhausen, L., Calderón, M. and Osorio-Blanco, E.R., 2024. Bringing innovative wound care polymer materials to the market: Challenges, developments, and new trends. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, p.115217.
- Tibúrcio‐Machado, C.S., Michelon, C., Zanatta, F.B., Gomes, M.S., Marin, J.A. and Bier, C.A., 2021. The global prevalence of apical periodontitis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. International endodontic journal, 54(5), pp.712-735.
- Xu, K. and Qin, S., 2023, May. An Interdisciplinary approach and advanced techniques for enhanced 3D-printed upper limb prosthetic socket design: A literature review. In Actuators (Vol. 12, No. 6, p. 223). MDPI.

