- Introduction - FND3003 research method in social science Assignment Sample
- Aim and Objectives:
- Research Questions
- The rationale for the Research
- Literature Review
- The Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Young Adults
- Core Mental Health Support Services Categories
- Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Support Services
- Effectiveness of Mental Health Support Services in Recovery
- Methods and Methodologies
- Research Methodology
- Data Collection
- Ethical Issues
- Data Analysis
- Expected Results/Findings
Introduction - FND3003 research method in social science Assignment Sample
Depression and anxiety are among the most prevalent mental health disorders that have attracted a lot of attention from the global community. According to the World Health Organization (WHO,) more than 280 million people worldwide experience depression, including young adults. Everyone in the UK has a one in four chance of experiencing a mental health problem this year, and anxiety and depression are the two common disorders (Mental Health Foundation, 2023).
Nonetheless, as more youth suffer from mental health disorders, most young adults remain untreated because of prejudices or inadequate health literacy, financial difficulties, or low availability of mental health care services. There are numerous mental health support: cognitive behavioural therapy, online counselling, peer support groups, helplines, etc. In the meantime, it is unclear which types of intervention are most beneficial for enhancing well-being and promoting recovery-oriented practice, specifically amongst young adults. This study aims at determining the efficacy of various mental health related service provisions for enhancing the lives of young adults living with anxiety and or depression.
Experience stress-free academics with our reliable Assignment Helper team! We combine expertise, dedication, and timely delivery to ensure your complete satisfaction and academic growth.
Aim and Objectives:
To investigate the impact of mental health support services on the well-being and recovery of young adults (18-30) suffering from anxiety and depression.
Objectives:
- To identify the most commonly used mental health support services among young adults with anxiety and depression.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of various support services (e.g., therapy, online interventions, peer support) in improving mental well-being and recovery.
- To explore the barriers that prevent young adults from accessing mental health support services.
- To provide recommendations on improving mental health service accessibility and effectiveness for young adults.
Research Questions
- What are the most commonly used mental health support services among young adults with anxiety and depression?
- How effective are different mental health support services in improving the well-being and recovery of young adults?
- What are the key challenges that prevent young adults from accessing mental health support services?
- What improvements can be made to mental health services to enhance accessibility and effectiveness for young adults?
The rationale for the Research
Rates of mental disorders among young adults are rising, but many people cannot get the help they need because of the stigma, cost, or lack of available care. Multiple intervention strategies are already known; however, studies comparing how effective these interventions are in enhancing well-being and recovery outcomes for this particular age group are scarce.
This study will help in identifying which mental health support services are most effective for young adults with anxiety and depression. Thus, the findings can be useful for healthcare providers, policy makers and mental health agencies to understand how they could enhance services and decrease the gaps in access. This study will help add to the discourse on mental health reform, accessibility and the new support systems for the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review
The Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Young Adults
Mental health issues of anxiety and depression appear most frequently in young adult populations. Young adults face a high risk for depression and anxiety because they deal with major life changes, including college studies, jobs, and money management. College students and working youth struggle with academic workload, job instability, and community expectations. Research indicates that social media harms mental health because users experience harmful actions like unfair comparison and online harassment (Varma et al., 2021).
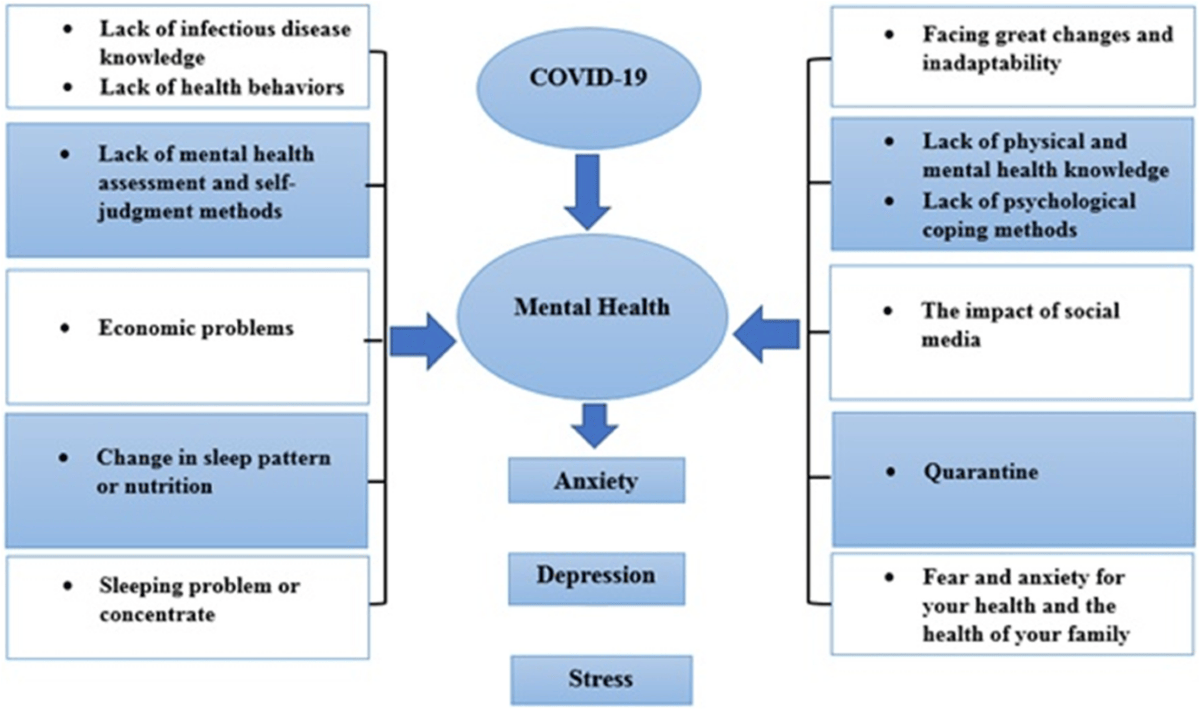
Figure 1: Prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression among the general population
(Source: Salari et al., 2020)
The spread of COVID-19 made mental health problems worse for young adults. The pandemic created a mix of feelings from young adults who faced isolation requirements and job stability concerns, which resulted in higher levels of depression and anxiety. Many young adults struggle to access sufficient mental health care services because of money problems and negative social views about mental health problems.
Core Mental Health Support Services Categories
Mental health support services for young adults can be divided into three main approaches: traditional therapy, digital interventions, and peer support. Each type provides distinct outcomes and barriers determining its effectiveness for young adults seeking help. People with anxiety and depression often benefit from face-to-face counselling, while traditional therapy includes psychotherapy and cognitive-behavioural methods. Trained therapists provide professional treatment to help people handle their feelings and thoughts better while breaking the destructive ones.
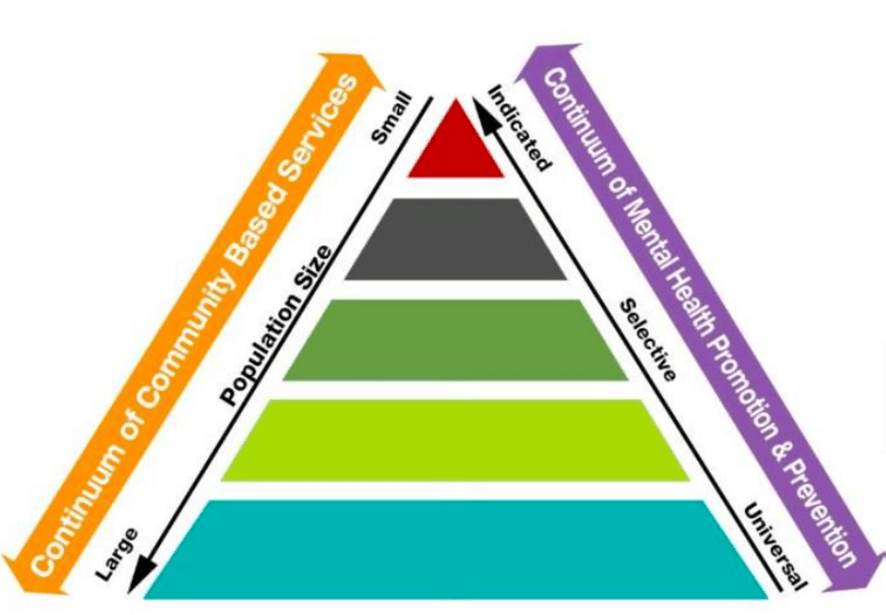
Figure 2: The Community Mental Health Care Model
(Source: Centre for Suicide Prevention, 2024)
Modern technology improvements led people to adopt digital mental health treatment options (Balcombe and De Leo, 2021). Technology-based mental health programs like web therapy and smartphone apps let people get professional help whenever needed. Young people select online therapy because it provides secure treatment at an affordable price while meeting their desire for convenience.
Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Support Services
Though mental health help is out there, young adults cannot get the support they desperately need. When mentally healthy young people feel judged by their community and fear their judgmental neighbours, they do not look for help to fix their problems. Because others judge and shame them for mental health difficulties, young adults often keep their emotional problems to themselves.
Cheap access to mental health treatment is difficult for young adults who can't cover expenses, whether they have insurance or receive a stable income. Many young adults can't afford mental health care, so they find help by themselves or lean on family and friends instead of seeing specialists.
Young people find it hard to get mental health care when there are not enough therapists available, and they must wait too long to see one.
Effectiveness of Mental Health Support Services in Recovery
Mental health support comes in different forms that work better for certain people based on their needs, how severe their symptoms are, and how accessible the services are. Traditional therapy keeps proving itself as the most reliable and scientifically proven way to treat anxiety and depression. Research shows that when mental health experts use "cognitive-behavioural therapy," patients feel better and have fewer symptoms. Young adults often can't access therapy since they lack enough money and great places to get there (Berg et al., 2023).
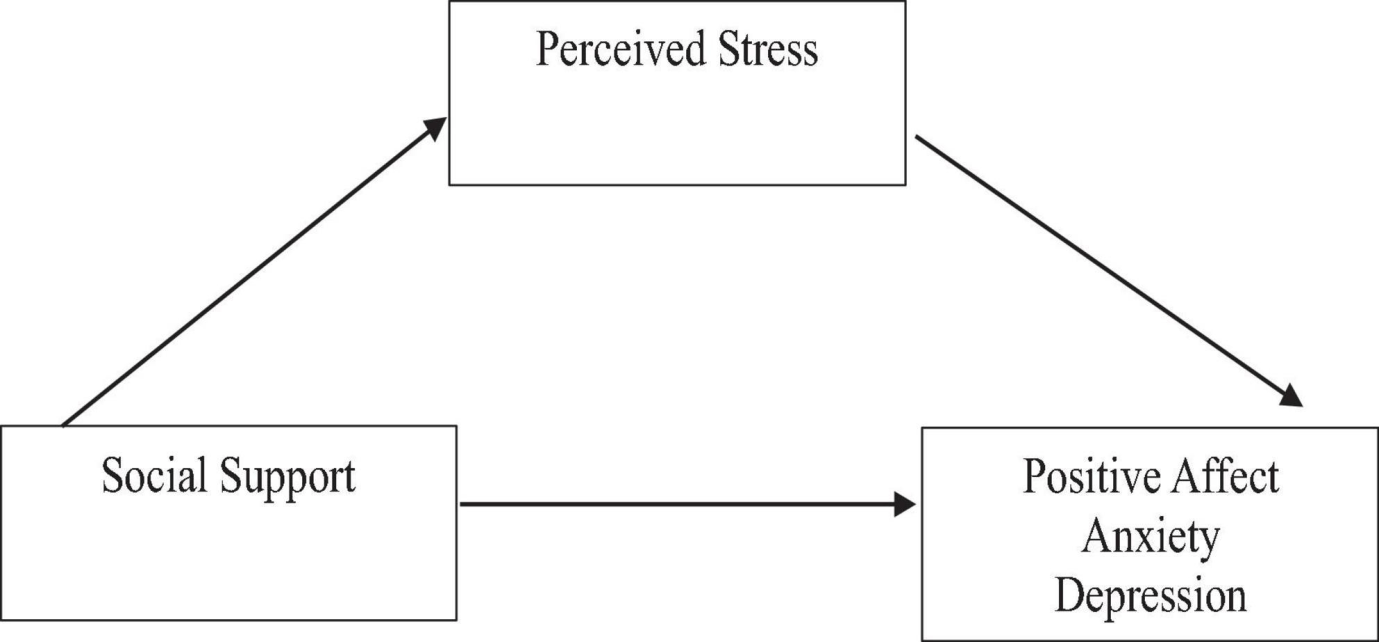
Figure 3: Social support and mental health
(Source: Acoba, 2024)
Online programs have become a good choice for people who want to handle things on their own. Research shows that combining digital tools for mental health (such as online therapy, apps, and groups) with expert support from professionals helps people better manage their symptoms. The modern tools make it easier for young people to find mental health help when regular options aren't available.
Methods and Methodologies
Research Methodology
This study uses numbers and statistics to show how well and easily mental health services are available to young adults. The focus is on math-based data because it want to know precisely how many people use these services, how well they rate them, and what gets in their way. Through a survey method, it intends to create standardized questionnaires with limited-response questions to collect participant responses.
Data Collection
The primary data for this study will be collected through an online survey. The survey will consist of multiple-choice and Likert-scale questions designed to measure the effectiveness, accessibility, and barriers associated with mental health support services (Özlem Coşkun, Yavuz Selim Kıyak and Işıl İrem Budakoğlu, 2024).
It will investigate what medical or psychological services each participant turns to when dealing with mental health issues. Participants will rate how well services helped their mental health. Furthermore, many people avoid mental health services because of negative social views, high costs, and insufficient access to treatment.
Sample
This project focuses on collecting information from young people between 18 and 30 who have treated anxiety or depression through mental health support services at least once. The project plans to obtain replies from at least 150 participants to meet the necessary requirements for effective statistical evaluation. Purposive sampling will serve as the selection method to obtain participants who fulfil the study criteria. This approach selects people who received mental health services, putting the research findings into practice.
Ethical Issues
Due to its importance, ethical research protects participants' rights and keeps their personal information private while maintaining their wellbeing during the research period. Studies based on Almossa and Alzahrani (2022) will use different protective measures to ensure ethical practice. Participants will receive a written letter that explains the study all steps and data usage plus withdrawal options and confidentiality protection. All researchers must receive agreement from each participant prior to the survey completion.
Data Analysis
Using correlational analysis, it will examine if mental health service usage patterns connect to user satisfaction ratings as described by Aggarwal et al (2020). Chi-square tests help show if mental health service usage patterns differ between groups of people with different genders, education levels, or income backgrounds. Statistical software programs like SPSS and Microsoft Excel will process the data to help us understand results accurately (Aggarwal et al., 2020). The findings will become more understandable when it shows them as graphs, charts and tables.
Expected Results/Findings
It seeks to understand which mental health solutions serve young patients best in treating anxiety and depression while exploring ways they can obtain them. Based on existing research and preliminary assumptions, the following key findings are anticipated: Cognitive-behavioural therapy and professional counselling are likely to get high marks as the best mental health care.
Conclusion
This study looks at mental health services for young adults with anxiety and depression, specifically focusing on how useful these services are and what difficulties they encounter. This research gathers numbers through survey questionnaires to show which mental health programs work best for young adults and what stops them from using them. Despite proven therapeutic success, traditional treatment is challenging for young adults to access, especially those facing location and financial hurdles, prompting them to explore digital alternatives or reach out to peers for support.
References
- Acoba, E.F. (2024). Social support and mental health: The mediating role of perceived stress. Frontiers in Psychology, 15(15), pp.1–12. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1330720.
- Aggarwal, R., Farag, S., Martin, G., Ashrafian, H. and Darzi, A. (2020). Patient Perceptions on Data Sharing and Applying Artificial Intelligence to Healthcare data: a Cross Sectional Survey (Preprint). Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(8). doi:https://doi.org/10.2196/26162.
- Almossa, S.Y. and Alzahrani, S.M. (2022). Lessons on maintaining assessment integrity during COVID-19. International Journal for Educational Integrity, 18(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40979-022-00112-1.
- Balcombe, L. and De Leo, D. (2021). Digital Mental Health Challenges and the Horizon Ahead for Solutions. JMIR Mental Health, 8(3), p.e26811. doi:https://doi.org/10.2196/26811.
- Berg, K.A., Ishler, K.J., Lytle, S., Kaplan, R., Wang, F., Tugba Olgac, Miner, S., Edguer, M.N. and Biegel, D.E. (2023). ‘Don’t Promise Something You can’t Deliver:’ Caregivers’ Advice for Improving Services to Adolescents and Young Adults with Autism. Springer, 2023(13), pp.1–13. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6597554.
- Centre for Suicide Prevention. (2024). The Community Mental Health Care Model - Centre for Suicide Prevention. [online] Available at: https://www.suicideinfo.ca/local_resource/the-community-mental-health-care-model/ [Accessed 21 Jan. 2025].
- Özlem Coşkun, Yavuz Selim Kıyak and Işıl İrem Budakoğlu (2024). ChatGPT to generate clinical vignettes for teaching and multiple-choice questions for assessment: A randomized controlled experiment. Medical Teacher, 2, pp.1–7. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159x.2024.2327477.
- Salari, N., Hosseinian-Far, A., Jalali, R., Vaisi-Raygani, A., Rasoulpoor, S., Mohammadi, M., Rasoulpoor, S. and Khaledi-Paveh, B. (2020). Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Globalization and Health, [online] 16(1), pp.1–11. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w.

