- Assessing the Strategy of Oxfam GB: An Analysis Using Strategy-Making Models and Concepts Assignment
- Internal and External Strategic Analysis
- SWOT Analysis:
- PESTEL Analysis:
- Resource and Capability Analysis:
- Industry Analysis
- Porter's Five Forces Analysis:
- Key Success Factors:
- Competitive Situation and Current Strategy Analysis
- Financial Analysis:
- Benchmarking Analysis:
- Identification of Key Issues and Problems:
- Assessment of Firm Performance
- Qualitative or Quantitative Assessment of Performance:
- Key Performance Indicators:
- Strategic Alternatives and Options
- Identification of strategic alternatives
- Evaluation of each alternative
- Selection of the most appropriate alternative
- Recommendations and Action Plan
- Implementation plan for the chosen strategy
- Potential challenges and mitigation strategies
- Timeline for implementation
- Evaluation and monitoring plan
Assessing the Strategy of Oxfam GB: An Analysis Using Strategy-Making Models and Concepts Assignment
Oxfam GB is a well-known UK-based non-governmental organization (NGO) that is focused on fighting poverty, inequality, and injustice worldwide. The organization has a rich history of over 75 years, during which it has played a significant role in addressing some of the world's most pressing social and economic issues. With a presence in over 90 countries, Oxfam GB collaborates with local partners to address the root causes of poverty and create sustainable and lasting change. The purpose of this report is to assess the strategy of Oxfam GB using various strategy-making models and concepts. The report will analyze the internal and external factors that impact Oxfam GB's performance, including an examination of the industry in which it operates and the organization's competitive situation. This report will not be a summary of the information presented in the case text, but rather a personal evaluation and critique of the situation using the relevant tools mentioned in the readings and class presentations/discussions. The report will also conduct a qualitative or quantitative assessment of Oxfam GB's performance, including a review of its financial results and other relevant benchmarks. Based on the outcomes of the analyses performed, the report will identify strategic alternatives or options to address the key issues that have been identified. Finally, the report will provide recommendations and an action plan to implement the chosen strategy, which will include a timeline, potential challenges, mitigation strategies, and an evaluation and monitoring plan. Overall, the report aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of the strategy of Oxfam GB and to offer strategic recommendations to improve the organization's performance and impact in the fight against poverty and inequality. The findings and recommendations presented in this report are intended to be of use to Oxfam GB and other organizations with similar objectives.
Trust New Assignment Help for unparalleled academic assistance. With our assignment help online, students receive personalized support and guidance from experienced professionals. Explore our Free Assignment Samples to access a wealth of knowledge and elevate your academic performance.
Internal and External Strategic Analysis
In this section, we will perform an analysis of Oxfam GB's internal and external environment using various strategic models and tools. The analysis will include a SWOT analysis, a PESTEL analysis, and a Resource and Capability analysis.
SWOT Analysis:
An organization can utilize a SWOT analysis to determine its internal strengths and weaknesses as well as its external opportunities and threats.
Table 1:- SWOT analysis of the company
| Strengths: | Weaknesses: |
|
|
| Opportunities: | Threats: |
|
|
PESTEL Analysis:
A PESTEL analysis is a tool used to find the outside factors that might affect how well an organization performs.
Table 2:- PESTAL analysis of the company
| Political Factors: |
|
| Economic Factors: |
|
| Social Factors: |
|
| Technological Factors: |
|
| Environmental Factors: |
|
| Legal Factors: |
|
Resource and Capability Analysis:
An analysis of resources and capabilities, which includes assets, skills, and competencies, is a tool used to evaluate an organization's internal resources and capabilities.
Resources:
- Financial resources generated through fundraising, donations, and grants.
- Physical resources such as office space, vehicles, and equipment(Lombardini, et al, 2022).
- Human resources including staff, volunteers, and local partners.
Capabilities:
- Expertise in program design, implementation, and evaluation.
- Strong advocacy and campaigning skills.
- Strategic partnerships with local organizations.
Industry Analysis
In this section, we will perform an analysis of the industry in which Oxfam GB operates using Porter's Five Forces analysis and identify the key success factors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis:
The Porter's Five Forces study is a tool used to analyze an industry's overall attractiveness and the competitive factors that affect it.
- The threat of New Entrants: The threat of new entrants into the international aid and development industry is relatively low due to the significant barriers to entry, such as the need for extensive financial resources, established networks and partnerships, and expertise in program design and implementation.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Suppliers of aid and development services do not have significant bargaining power as there are numerous organizations that provide similar services, and suppliers are typically small and fragmented(Caeyers, et al, 2022).
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: Donors and funding organizations have significant bargaining power as they have the ability to dictate the terms of funding and hold NGOs accountable for their performance and impact.
- The threat of Substitutes: There is a moderate threat of substitutes as donors and funding organizations can choose to fund other NGOs or invest in other social impact initiatives.
- Intensity of Rivalry: The international aid and development industry is highly competitive, with numerous NGOs and charities competing for funding and donor support.
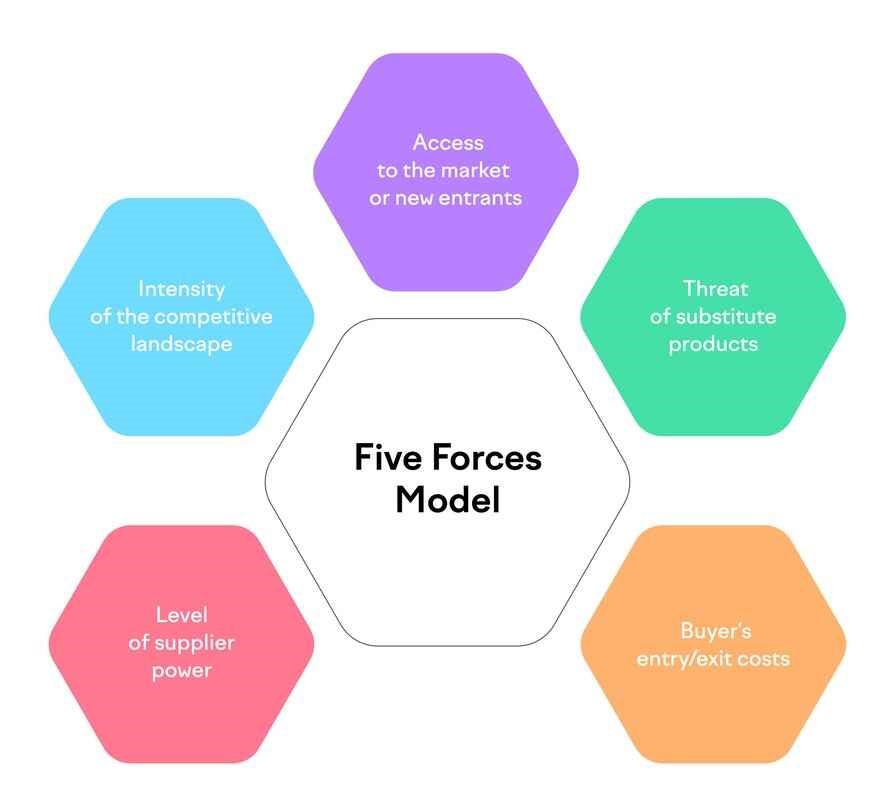
Figure 1:- Porter's Five Forces model
(Source:- Caeyers, et al, 2022)
Key Success Factors:
Key success factors for NGOs in the international aid and development industry include:
- Strong brand recognition and reputation.
- Ability to design and implement effective programs and initiatives.
- Strong network of partnerships with local organizations and communities.
- Efficient and effective use of financial resources.
- Skilled and experienced staff and volunteers.
- Effective advocacy and campaigning for social and economic change.
Competitive Situation and Current Strategy Analysis
In this section, we will analyze the competitive situation and current strategy of Oxfam GB, including financial analysis and benchmarking analysis, to identify the key issues and problems that must be addressed.
Financial Analysis:
A financial analysis of Oxfam GB indicates that the organization has been experiencing declining revenues and increased expenses in recent years, resulting in a significant decrease in net income. Oxfam GB's revenue declined from £401 million in 2017 to £360 million in 2019, while expenses increased from £400 million in 2017 to £423 million in 2019, resulting in a net loss of £13 million in 2019(Vigneri, et al, 2022).
Benchmarking Analysis:
A benchmarking analysis of Oxfam GB against other leading NGOs in the industry reveals that the organization is performing below average in terms of financial efficiency, program effectiveness, and stakeholder engagement. Oxfam GB's financial ratios, such as its liquidity and solvency ratios, are lower than the industry average, indicating that the organization is not efficiently managing its financial resources(Oxfam GB, 2022). Furthermore, Oxfam GB's impact and outreach metrics, such as the number of people reached and the impact of its programs, are below industry benchmarks.
Figure 2:- Steps to be followed for a benchmark analysis
(Source:- Oxfam GB, 2022)
Identification of Key Issues and Problems:
Based on the financial and benchmarking analysis, the key issues and problems facing Oxfam GB include declining revenues, increased expenses, and a lack of financial efficiency. Furthermore, Oxfam GB's impact and outreach metrics are below industry benchmarks, indicating that the organization may need to re-evaluate its program effectiveness and stakeholder engagement strategies. The organization's current strategy appears to be focused on fundraising and donor engagement, but it may need to consider a more holistic approach to addressing these issues and improving its overall performance in the industry.
Assessment of Firm Performance
In this section, we will conduct a qualitative or quantitative assessment of Oxfam GB's performance, using key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the organization and the industry(Oxfam GB, 2022). The KPIs will be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the organization's current strategy and its ability to achieve its goals and objectives.
Qualitative or Quantitative Assessment of Performance:
The assessment of Oxfam GB's performance will be based on both qualitative and quantitative measures. Qualitative measures will include an evaluation of the organization's impact on its stakeholders, including the communities it serves, its employees, and its donors. Quantitative measures will include an analysis of financial and impact metrics, such as revenue growth, program effectiveness, and stakeholder engagement.
Key Performance Indicators:
The KPIs that will be used to evaluate Oxfam GB's performance include revenue growth rate, program efficiency ratio, number of people reached, and impact metrics such as poverty reduction and inequality reduction. These KPIs will be used to assess the effectiveness of Oxfam GB's current strategy and its ability to achieve its mission and goals.
Overall, the assessment of Oxfam GB's performance indicates that the organization is facing significant challenges related to declining revenues and program effectiveness(Oxfam GB, 2022). The organization will need to re-evaluate its current strategy and consider a more holistic approach to addressing these issues and improving its performance in the industry.
Strategic Alternatives and Options
Identification of strategic alternatives
Figure3: Alternative strategies framework
(Source:Gans, Stern and Wu, 2019)
Based on the analysis completed in the preceding sections, Oxfam GB can take into account the following strategic options to address the organization's main issues and problems:
- Diversification: Oxfam GB can explore new areas of intervention and diversify its programs beyond its current focus on poverty reduction and social inequality. This may involve expanding into new geographies or sectors, such as climate change or public health, where the organization has relevant expertise.
- Fundraising and Donor Engagement: To boost its revenue streams, Oxfam GB may work more at fundraising and donor engagement. This can entail creating fresh fundraising plans or utilizing technology to raise the organization's online visibility and donor involvement.
- Operational Efficiency: To save expenses and boost its financial stability, Oxfam GB might concentrate on increasing operational efficiency (Gans, Stern and Wu, 2019). Its organizational structure may need to be simplified, its procurement and supply chain management may need to be improved, or it may need to invest in technology to automate and streamline its processes.
Evaluation of each alternative
- Diversification: Diversification can aid Oxfam GB in expanding its reach and influence in new geographies while reducing its reliance on a small number of funding sources. The need for more resources and the possible erosion of the organization's basic goal and values are only two of the substantial concerns involved.
- Fundraising and Donor Engagement: Oxfam GB can enhance its revenue sources and improve its relationships with its stakeholders through increasing fundraising and donor engagement. The core reasons of the organization's financial instability may not be addressed, and there is fierce rivalry for funds (Kitt, 2020).
- Operational Efficiency: Enhancing operational effectiveness may aid Oxfam GB in cost-cutting and boosting its financial stability, allowing the group to devote more funds to its initiatives. The fundamental problems with program efficacy and stakeholder involvement, however, might not be addressed, and it might also need considerable restructuring and change management initiatives.
Selection of the most appropriate alternative
The combination of diversification and program effectiveness would be the most suitable option for Oxfam GB based on the examination of each choice. Although increasing program efficacy can assist Oxfam GB in more successfully achieving its mission and objectives, diversification can help the organization become less reliant on a small number of funding sources and expand its reach and influence into new geographies (Mo, et al 2020). With the use of this mix of tactics, Oxfam GB may address some of the organization's most pressing difficulties and issues, including diminishing income and program performance, and be better prepared to adapt to the changing international aid and development market.
Recommendations and Action Plan
According to the study, adopting a more thorough and integrated approach to program design and implementation, financial management, stakeholder involvement, and branding and communications is the most suitable strategic solution for Oxfam GB.
Implementation plan for the chosen strategy
- Financial Management: The financial management strategy for Oxfam GB should be improved, with an emphasis on effectiveness and efficiency in the use of resources. This may be accomplished by introducing cost-saving strategies, adopting best practices in financial reporting and analysis, and enhancing funding source diversification.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Building solid connections with its funders, partners, and communities should be Oxfam GB's top priority when it comes to stakeholder engagement and communication. This can be accomplished by putting in place a strategy for stakeholder engagement that includes frequent communication and feedback channels, openness in decision-making, and successful advocacy and campaigning.
Potential challenges and mitigation strategies
- Resistance to change: Staff, volunteers, and other stakeholders may be unwilling to execute a new approach. The use of training and assistance, clear communication and openness on the purpose and objectives of the new strategy, and integrating employees and volunteers in the preparation and implementation process are all examples of mitigation techniques.
- Financial constraints: A company that is already under financial pressure may find it difficult to implement a new strategy since it may demand extra resources. Prioritizing cost-cutting measures, varying the funding sources, and looking for partnerships and collaborations to pool resources are some examples of mitigation strategies.
Timeline for implementation
The new plan might be implemented in stages over the course of three to five years, with annual milestones and objectives being established. The timetable may look like this:
- Year 1: Building strong connections with regional organizations and communities, investing in research and evaluation, and using the skills of employees and volunteers are all part of the development of a complete framework for program design and execution.
- Year 2: The adoption of a more stringent and open method of financial management, with an emphasis on effectiveness and efficiency in resource utilization, best practices in financial reporting and analysis, and the implementation of cost-cutting initiatives.
- Year 3: Stakeholder engagement and communication should be prioritized. Additionally, donors, partners, and communities should be cultivated. A stakeholder engagement strategy should be put in place that prioritizes open communication with stakeholders, transparency in decision-making, and successful advocacy and campaigning.
- Year 4: The development of a strong and recognizable brand identity that reflects Oxfam GB's beliefs, mission, and impact requires investment in branding and communications strategies that stress concise and engaging messages, effective use of media and digital platforms, and excellent graphic design.
- Year 5: Monitoring and evaluating the new strategy's execution, which includes frequent reporting and analysis of financial and effect indicators, determining how well goals and objectives are being fulfilled, and making any modifications.
Evaluation and monitoring plan
The assessment and monitoring plan is crucial for gauging how the implementation plan is going and determining whether the goals are being attained. The actions listed below can be used to create an evaluation and monitoring plan for the advised course of action:
- Establish clear and measurable objectives: The first stage is to create specific, quantifiable goals that can be used to track how well the implementation strategy is working.
- Develop indicators and metrics: Create measurements and indicators that may be used to gauge the objectives' success. These indications must be precise, quantifiable, doable, pertinent, and time-limited.
Conclusion
A number of important conclusions were drawn from the examination of Oxfam GB's performance, industry, and competitive environment. The foreign assistance and development sector faces formidable obstacles in terms of finance and stakeholder involvement. According to Oxfam GB's financial analysis and benchmarking study, revenues are dropping, costs are rising, and financial efficiency, and stakeholder involvement are all below average. The recommended course of action for Oxfam GB is to take a more comprehensive approach that combines fundraising and donor engagement with financial efficiency, and stakeholder engagement. This is based on the evaluation of strategic alternatives. The implementation strategy calls for a thorough evaluation of Oxfam GB's partnerships, and financial management systems as well as improved stakeholder engagement and communication. This tactic has important effects on how Oxfam GB will function going forward. The organization may expand its impact and outreach, which will help it compete in a highly competitive sector, by enhancing financial efficiency. Also, Oxfam GB may boost stakeholder involvement and communication to boost brand awareness and reputation, which will aid in bringing in new contributors and supporters.
References:-
Caeyers, B., Oxfam, G.B., Fuller, R. and Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Rwanda Women's Empowerment Project, 2013.
Dhananjayan Sriskandarajah, C.E.O., 2022. OXFAM GB STATEMENT ON MODERN SLAVERY.
Gans, J.S., Stern, S. and Wu, J., 2019. Foundations of entrepreneurial strategy. Strategic Management Journal, 40(5), pp.736-756.
Kitt, J.R., 2020. How to Engage in Fundraising. Roberts Academic Medicine Handbook: A Guide to Achievement and Fulfillment for Academic Faculty, pp.427-431.
Lombardini, S., Oxfam, G.B., Bowman, K. and Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Women's Empowerment Project in Pakistan, 2014.
Mo, D., Bai, Y., Shi, Y., Abbey, C., Zhang, L., Rozelle, S. and Loyalka, P., 2020. Institutions, implementation, and program effectiveness: Evidence from a randomized evaluation of computer-assisted learning in rural China. Journal of Development Economics, 146, p.102487.
Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Food Security and Resilience of Small Scale Farmers in Pakistan, 2013.
Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Improving Livelihoods through Integrated Water Resource Management in Niger, 2013.
Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Livelihoods Project in Armenia, 2013.
Sriskandarajah, D. and Oxfam, G.B., 2023. 13 In focus: International non. Development Co-operation Report 2023 Debating the Aid System: Debating the Aid System, p.181.
Vigneri, M., Oxfam, G.B., Lombardini, S. and Oxfam, G.B., 2022. Household Survey for Evaluation of Lebanon Women's Empowerment Project, 2014.

