- Introduction
- Diagnosis of Key Issues in Diversity and Inclusivity
- Structural and Cultural Barriers to Diversity in Leadership
- Challenges of AI in Hiring and Leadership Progression
- Generational and Workplace Inclusion Issues
- Program Design and Leadership Development Plan
- Gen Z Leadership Development Core Competencies
- Strategies for Creating a Diverse Leadership Environment
- Structured Leadership Development Framework
- Implementation Plan
- Months 1 – 2: Program Launch- Stakeholder engagement
- Foundational Leadership and AI Training (Months 3 – 5)
- Months 6-9: Mentorship, Sponsorship, and Practical Leadership Exposure
- Months 10-12: Leadership Integration and Career Progression
- Ethical Considerations and Risk Management
- Ethical Leadership Training and AI Governance
Introduction
The modern workforce is transformed with the entrance of the new world generation of Gen Z into the leadership pipelines, ushered in by a rapidly evolving AI scenario. Automated by AI, the process is efficient, but that invariably brings up the dark issues of algorithmic bias, job disruption, and shifting skill expectations, to which organisations must be proactive in solving Gen Z leaders.
It is in a very ironic pattern that Gen Z workers have generated a debate around their extreme potential, stereotypical misperceptions of the generation, absence of guidance, and, above all, disjunctions between the company infrastructure without corresponding to their value for inclusion and ethical leadership. Indeed, studies claim that AI would most probably aggravate the prevailing inequalities without fairness and accountability. It, therefore, urges structured affiliation programs on the leaders such that leadership development for Gen Z would thrive in an AI-enabled workplace. In this light, the report proposes a Gen Z Leadership Development Program to the most notable professional services organisation, PwC UK, operating under an extremely AI-driven, duly considered diverse environment.
Diagnosis of Key Issues in Diversity and Inclusivity
Structural and Cultural Barriers to Diversity in Leadership
PwC UK has made considerable progress in diversity and inclusion in recent years. However, leadership roles within the organisation still lack adequate representation of Gen Z employees, women, and ethnic minorities. Slow leadership progression for young professionals is just one of the primary barriers facing attorneys. Another key challenge remains unconscious bias in leadership selection (Innovation, 2023). Whilst PwC has committed to inclusive policies and still has them, bias continues to influence promotion and leadership appointments, favouring those who fit conventional leadership moulds. The lack of tailored mentorship programs for underrepresented groups compounds this.
Challenges of AI in Hiring and Leadership Progression
PwC UK has integrated AI-derived solutions for various steps of talent acquisition, performance evaluation and leadership selection. These technologies make decision-making and efficiency more efficient, but they also create a risk of establishing existing inequalities by accident. One of the most significant issues is algorithmic bias in AI recruitment tools. Currently, AI hiring platforms rely on historical datasets that reflect past inequalities in leadership hiring (Innovation, 2023). Unless these biases receive attention, the AI-based hiring systems will disadvantage diverse Gen Z applicants who do not fit into the classic leadership model.
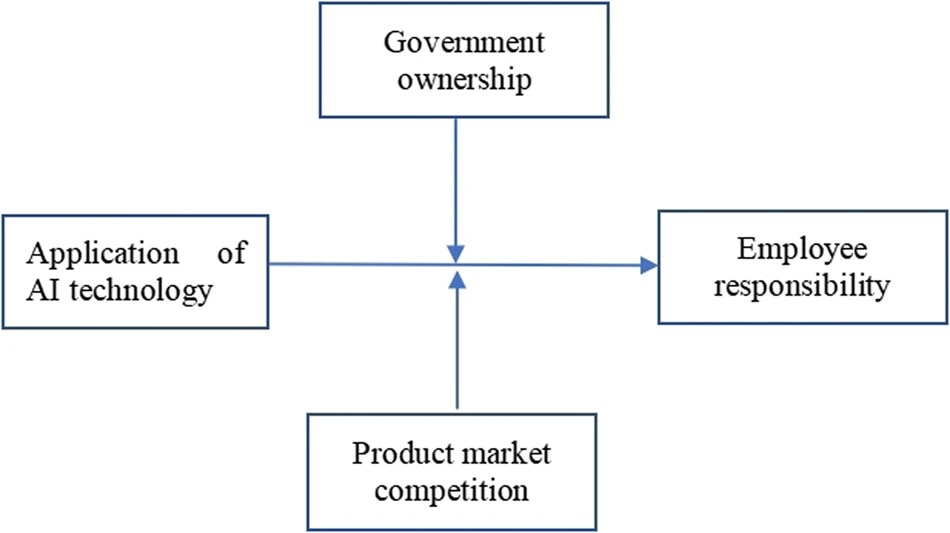
Figure 1: AI technology application and employee responsibility
A big challenge is the increasing variety of leadership competencies brought about by AI-driven automation (Innovation, 2023). With growing dependence on AI, leadership skills are adjusting to become a strategic level of thinking, responsible AI management, and human-led thinking.
Generational and Workplace Inclusion Issues
PwC UK employees of Gen Z bring an excellent drive for workplace inclusivity and proper business ethics. However, traditional corporate structures sometimes vary in their alignment. The main issue concerns workplace conflicts between generations (Westfall, 2023). PwC staff consists of people of different generations, like Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Gen Z, and face communication styles, work expectations, and leadership approaches that do not match, resulting in a lack of collaboration and team coherency.
Gen Z faces another challenge: the issues of mental health and well-being in developing their leadership. PwC's corporate environment still concentrates on long hours and high-pressure performance cultures and is inconsiderate of young professionals' desire for work-life balance and psychological well-being (Westfall, 2023). If a workplace has not developed enough mental health support and is not psychologically safe to talk about mental health, diverse voices may have great difficulty being heard in leadership conversations.
Program Design and Leadership Development Plan
Gen Z Leadership Development Core Competencies
For PwC UK, the leadership development program will hone in on four core competencies that the company deems Gen Z employees must possess to become leaders working at the company (Innovation, 2023). To aid young professionals in navigating through meetings, building strong interpersonal relationships and being direct with empathy, emotional intelligence, and inclusive leadership will be the thematic focus. Gen Z leaders will use digital literacy and AI-applicable techniques to train them to understand AI technologies in business decision-making implementation and analysis. A future of ethical decision-making in AI-driven workplaces will mean that future leaders must recognise AI biases, maintain corporate social responsibility and make ethical business decisions (Varsha, 2023). Further, conflict resolution and cross-generation communication training will assist Gen Z leaders to have successful collaborative relationships with adults from other generations, closing gaps and addressing collaboration.
Strategies for Creating a Diverse Leadership Environment
The program will integrate structured mentorship sponsorship initiatives to create a leadership culture that supports PwC UK’s commitment to promoting diversity and inclusion. To help Gen Z employees gain career-building experience, a reverse mentorship program will be introduced to assist senior leaders with workplace trends, technology, and inclusivity in exchange for their career-building experience (Li et al., 2024). A sponsoring framework will guarantee that GEN Z employees with high potential but are from underrepresented groups get direct career support from senior executives.
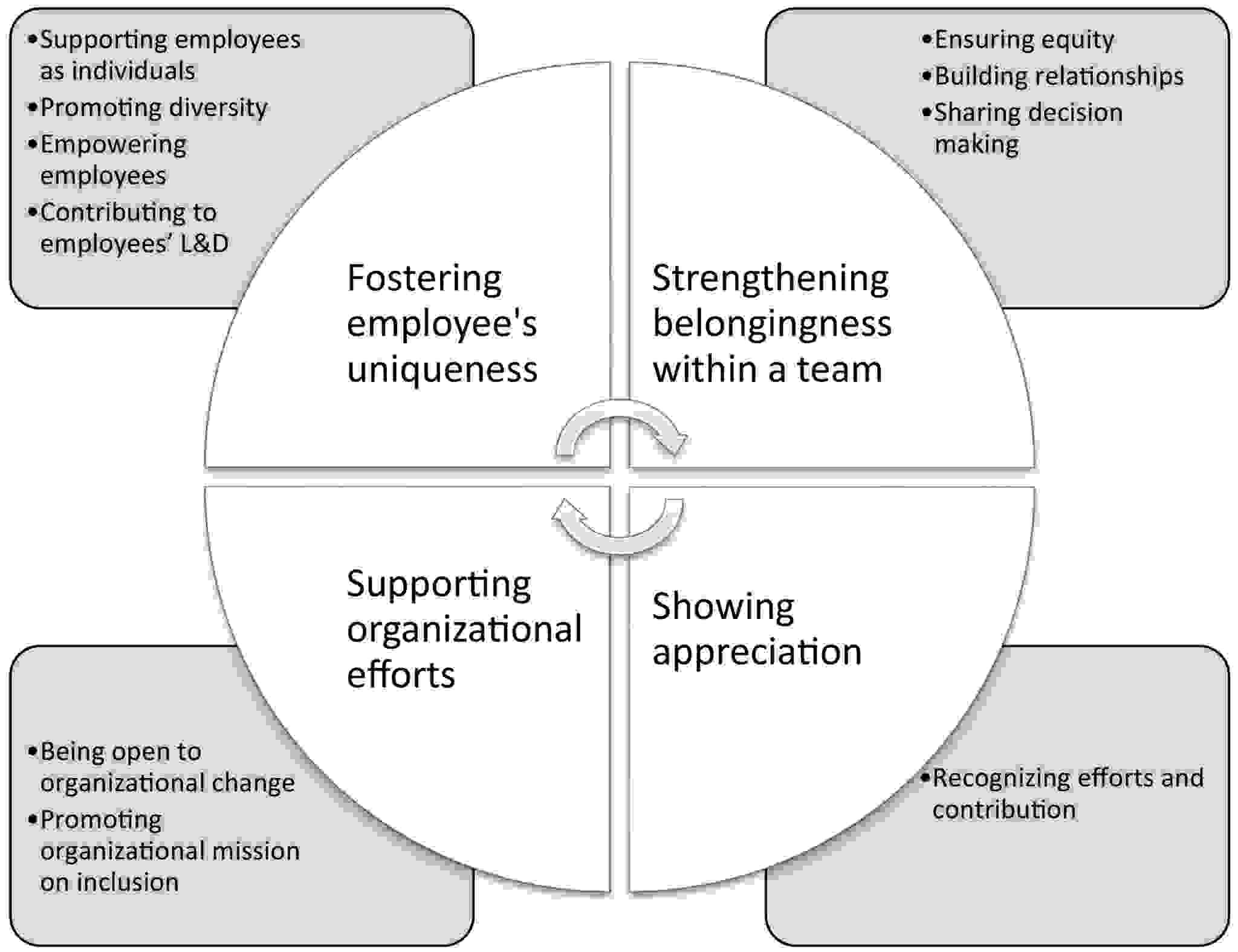
Figure 2: Inclusive leadership multi-level concept
Workshops and practical exercises will be run for GenZ employees to practice AI training for ethical leadership and decision-making, including assessing AI bias, interpreting AI-generated insights, and implementing ethical AI solutions in corporate decision-making. Leadership program to further embed diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in leadership based on DEI frameworks and cultural competency training to help future leaders create inclusive work environments by welcoming diverse perspectives and equitable opportunities for career growth (IMF, 2024).
Collaborative leadership models will be developed to prepare Gen Z employees to lead diverse teams, work in an agile environment, and use inclusive decision-making. Leadership training will focus on distributed leadership, which means that young professionals will be trained to work independently, knowing how to take action and lead projects without constraints from the traditional hierarchical management lines (Wallo, Lundqvist and Coetzer, 2024).
Confused about where to start with your project? Get Assignment Help UK that simplifies your academic journey! Our team provides clear, structured solutions tailored to your requirements.
Structured Leadership Development Framework
Months 1-4 : Phase One: Foundational Leadership and AI Literacy
The workshops for the first phase will be immersive, focus on leadership, discuss AI ethics, and focus on DEI education. As Gen Z employees gain foundational leadership competencies, case studies, interactive simulations, and expert discussions will all be part of the science (Cohen, 2023). PwC UK will give in-depth training on implementing ethical AI and corporate responsibility in partnership with AI ethics researchers and industry practitioners.
Phase Two: Mentorship, Sponsorship, Practical Experience (Months 5-8)
The second phase will be to develop professional networks and put these leadership skills to use in real business settings. They will be matched with senior leaders for mentorship and sponsorship programs so that participants can get individual career guidance. In addition to this, PwC UK will develop reverse mentorship programs that will see Gen Z employees guide senior executives on digital transformation, focusing on new workplace trends and inclusion (Cohen, 2023).
Months 9 – 12: The Leadership Integration and Career Advancement (Phase Three).
The last phase would be career development, leadership assessments and performance-based promotions. Participants will be given leadership responsibilities within the existing projects that PwC UK is committed to during the upcoming years: strategic planning, ethical AI governance, and inclusive team management (Cohen, 2023). Leadership potential, innovation and adaptability will be assessed by senior executives, based on which successful participants will be fast-tracked onto leadership pipelines and into future managerial roles.
Implementation Plan
Months 1 – 2: Program Launch- Stakeholder engagement
PwC UK’s leadership, HR, and DEI teams will establish the program's framework. A steering committee will oversee the initiative comprised of senior executives, AI ethics experts, and members of Gen Z (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2025). Internally, the organisation’s stakeholders will know the program’s goals, expectations, and success metrics through internal webinars, leadership meetings, and digital announcements. Thus, a nomination and application process will help select a pilot cohort from diverse backgrounds.
Foundational Leadership and AI Training (Months 3 – 5)
Leadership skills, AI literacy, and inclusive leadership principles will be developed in the first phase of training. The interactive workshops, AI ethics training, and cultural competency sessions, among others, will be done with Gen Z employees. Together, PwC UK and academic institutions, AI researchers and industry partners will explore real-world case studies of how AI can work in business and make ethical decisions (IMF, 2024). Some e-learning modules will be introduced so that people within that department and those outside can take advantage of flexible learning opportunities.
Months 6-9: Mentorship, Sponsorship, and Practical Leadership Exposure
The second phase will interconnect Gen Z employees with senior mentors and sponsors through a structured career guidance pathway. Gen Z employees will be introduced to reverse mentorship programs where senior executives learn leadership strategies. Gen Z employees will spend 2 cents on digital transformation and inclusivity (Forbes, 2023). In addition, participants will undertake cross-functional leadership projects where they will learn to lead diverse teams, solve problems, and make data-driven decisions first-hand.
Months 10-12: Leadership Integration and Career Progression
First, there will be the application and assessment of authentic world leadership, and then the final phase is to achieve authentic world leadership. PwC UK’s AI-driven projects, DEI initiatives and strategic choices will be led by Generation Z employees who will take on the roles of leaders. Senior leaders will use innovation, adaptability, and inclusive leadership impact to evaluate a follower (Forbes, 2023). Fast-track leadership programs, future managerial roles and global leadership initiatives from within PwC UK may be considered for high-performing participants.
Ethical Considerations and Risk Management
Care must be taken when assessing the bias of AI-driven recruitment or performance assessment tools at PwC UK. Generally, there’s a tendency for AI systems to reproduce historical inequities of their kind, inadvertently leading to discriminatory hiring and promotion procedures. The organisation will conduct AI audits and bias mitigation training, ensuring the AI-powered decision-making tools are transparent and fair (Lacmanovic and Skare, 2025). They ought to be aligned with the DEI goals it is framed. A dedicated AI Ethics Committee reviewing algorithms will handle the fairness and bias correction.
Leadership programs must have equal access to all employees (regardless of ethnicity, gender or socioeconomic background). PwC UK will apply inclusive selection criteria to achieve balanced leadership development representation in underrepresented groups. A diverse hiring panel and anonymised assessment processes will be implemented to combat unconscious bias in participant selection and promotions (Lacmanovic and Skare, 2025).
The top three areas in which Gen Z employees at PwC UK want to work are mental health, work-life balance, and psychological safety. The leadership program will combine mental health support, coaching, and flexible learning opportunities so that employees do not suffer from burnout or excessive pressure (Goldberg, 2023). A confidential feedback and reporting system must deal with discrimination, workplace stress, or inclusivity issues that leave concerns.
Ethical Leadership Training and AI Governance
The program will focus on ethical decision-making about AI-based leadership. Participants will receive training in responsible leadership in technology-driven environments, data privacy, and ethical AI use (Goldberg, 2023). The coursework will include real-world case studies of AI governance, corporate social responsibility, and moral dilemmas in leadership.
On an ongoing basis, PwC UK will develop monitoring frameworks to ensure that ethical leadership remains a critical practice. The program will be overseen by a long-term Leadership Ethics Advisory Board that is concerned with emerging ethical concerns in AI and leadership. Transparency reports and public accountability measures will show a commitment to ethical leadership and inclusivity (Tamayo et al., 2023).
Conclusion
Integrating leaders with AI advancements is the future of leadership at PwC UK and the building block of inclusive and diverse leadership that PwC UK aspires to see. The fact is that Gen Z is entering the workforce with a digital literacy, inclusivity, and ethical leadership mindset, and organisations will have to work hard to support them in becoming future leaders. In addition, the report has laid out a comprehensive leadership development program which could be used to address the impediments to career advancement into leadership roles that are specific to Gen Z, such as structural bias, AI-related issues, and generational differences in the workplace.
Furthermore, PwC UK’s Gen Z Leadership has driven emotional intelligence, AI literacy, ethical decision-making, and cross-generational collaboration as core competencies. The program allows young professionals to interact with business and AI through mentorship, training in AI ethics, and on-the-job leadership experience that will help them develop in this AI environment with diversity and inclusion in mind.
References
- Cohen, M. (2023). Companies are learning that Gen Z isn’t the easiest generation to work with. [online] CNBC. Available at: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/05/26/employers-are-learning-gen-z-isnt-the-easiest-generation-to-work-with.html [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Forbes (2023). 15 Ways Leaders Can More Effectively Manage Gen-Z Workers. [online] Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescoachescouncil/2023/01/17/15-ways-leaders-can-effectively-manage-gen-z-workers/?sh=15e1d5d94172 [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Goldberg, E. (2023). A.I.’s Threat to Jobs Prompts Question of Who Protects Workers. The New York Times. [online] 23 May. Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/05/23/business/jobs-protections-artificial-intelligence.html [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- IMF (2024). Exposure to Artificial Intelligence and Occupational Mobility: A Cross-Country Analysis. [online] IMF. Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2024/06/07/Exposure-to-Artificial-Intelligence-and-Occupational-Mobility-A-Cross-Country-Analysis-549989 [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Innovation (2023). How Gen Z can get ready to face the future of work and the AI landscape. [online] Medium. Available at: https://medium.com/@inclusiveinnovation/how-gen-z-can-get-ready-to-face-the-future-of-work-and-the-ai-landscape-5b829874bc8e [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Korkmaz, A.V., van Engen, M.L., Knappert, L. and Schalk, R. (2022). About and beyond Leading Uniqueness and belongingness: a Systematic Review of Inclusive Leadership Research. Human Resource Management Review, 32(4), p.100894. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2022.100894.
- Lacmanovic, S. and Skare, M. (2025). Artificial intelligence bias auditing – current approaches, challenges and lessons from practice. Review of Accounting and Finance. doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/raf-01-2025-0006.
- Li, M., Guo, J., Zou, C. and Yin, J. (2024). The Impact of Reverse Mentoring on Employees’ Innovative Behavior: Evidence from Chinese Technology Enterprises. Sustainability, 17(1), p.6. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010006.
- PricewaterhouseCoopers (2025). PwC: Building trust for today and tomorrow. [online] PwC. Available at: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/diversity-inclusion/best-practices/assets/the-pwc-diversity-journey.pdf [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Tamayo, J., Doumi, L., Goel, S., Kovács-Ondrejkovic, O. and Sadun, R. (2023). Reskilling in the Age of AI. [online] Harvard Business Review. Available at: https://hbr.org/2023/09/reskilling-in-the-age-of-ai [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].
- Varsha, P.S. (2023). How can we manage biases in artificial intelligence systems – A systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 3(1), p.100165. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2023.100165.
- Wallo, A., Lundqvist, D. and Coetzer, A. (2024). Learning-Oriented Leadership in Organizations: An Integrative Review of Qualitative Studies. Human Resource Development Review, 23(2). doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/15344843241239723.
- Wang, J., Xing, Z. and Zhang, R. (2023). AI technology application and employee responsibility. Humanities & Social Sciences Communications, [online] 10(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01843-3.
- Westfall, C. (2023). How AI Is Hurting Gen Z Careers: 3/4 of Gen Z Workers Fear ChatGPT. [online] Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/chriswestfall/2023/07/17/how-ai-is-hurting-gen-z-careers/?sh=6ed31d6a8947 [Accessed 15 Mar. 2025].

