Introduction Of Computer Architecture and Systems Software Assignment
In Boolean algebra, there are two forms namely Sum-of-Products (SOP) and Product-of-Sums (POS) to express the logical functions. SOP can be defined as a means of representing a function in terms of minterms or Product of Literals, where each of the minterms is a case in which an output is true. On the other hand, POS defines the function in terms of maxterms, which is more analytical in nature, focusing on the cases when the output is false, which adds to the logical completeness of a circuit.
Sum-of-products
Y = (Ā B̅ C̅ D̄ +Ā B̅ C D̄) + (Ā B C̅ D, + Ā B C D̄ ) + ( A B̅ C̅ D̄ + A B̅ C D̄)+( A B C̅ D̄ + A B C D̄) D̄
The given Boolean expression incorporates many terms that may seem complicated at first sight. Nevertheless, in analyzing the above terms, fundamental structures of similarity can be noted and searched for in order to apply such a concept of simplification. The first step is to combine the terms which differ in one variable only, thus allowing one to factor expressions that are common to both terms. In this case the variable C is both complemented and uncomplemented hence does not influence the logic characteristic in any way. All the above terms can be expressed in a shorter and more concise form thus minimizing redundancy and thereby enhancing the interpretation of the expression when used to develop logical circuits.
When factors are taken from the pairs: Y = Ā B̅ D̄ (C̅ + C )+ Ā B D̄ (C̅ + C ) + A B̅ D̄ (C̅ + C ) + A B D̄ (C̅ +C )
This reduces the considerations in arriving at the result to only variables A, B, and D (GeeksforGeeks 2024). The result also shows that the presence of C hardly impacts the final result and as such the expression could be rewritten without C in it at all (Storr, W 2023). Substituting further brings about the conclusion that output is an indication of D, which should be zero. This means that no matter the values assigned to the variables A and B in forming the logic function, the function is valid only if the variable D is omitted thereby increasing the ease in the design of the circuit.
Assignment deadlines piling up? Let New Assignment Help ease your burden with expert Assignment Help UK tailored for student success.
As, C = C̅ + C = 1, it is found that,
Y=Ā B̅ D̄ + Ā B D̄ + A B̅ D̄ +A B D̄
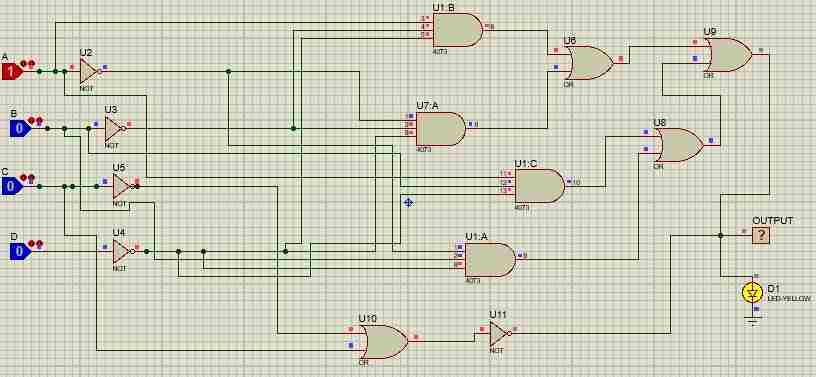
Figure 1: Sum-of-products
The desired relative performances are achieved using principles of steady state circuit theory, and the fact that the circuit implementation becomes greatly simplified with the simplified expression. Contrary to expecting to observe several instances of the logic gates functioning, the final function can be obtained simply utilizing one NOT gate (Bowler Hat LLC 2024). This optimization greatly helps in minimizing hardware complexity thereby making the construction of the circuit simpler and affordable. In such a case, such approximations are inevitable in the course of implementing digital logic designs since they enhance low power consumption and performance. Simplification of expressions is an important function of circuit design: translations that allow Boolean expressions to be performed with as few components as possible, but with the same functionality.
Product-of-sums
The Product-of-Sums (POS) is used here for implementing logical functions such that the output is at zero. It applies this type of cases where the function is equal to 1; POS explains the function in terms of conditions that give a false outcome. This is done by finding the rows of the truth table with the output value of zero, and then resulting in the formation of logical sum terms for each of the sets (Robert, F.J., et al. 2021). That is, each sum term contains all the input variables in their complemented or complemented forms depending on whether they are 1 or 0 in the respective row. Using AND operation to multiply these sum terms, functional description of the POS is complete up to the level needed.
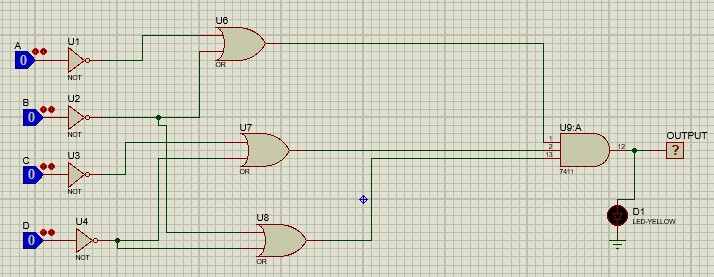
Figure 2: Product-of-sums
Y = (A + B + C + D) (A + B + C̅ + D) (A + B̅ + C + D) (A + B̅ + C̅ + D) (A̅ + B + C + D) (A̅ + B + C̅ + D) (A̅ + B̅ + C + D) (A̅ + B̅ + C̅ + D)
The process of converting the given function includes a determination of the input conditions that result in the output of 0 and then representing such conditions in the form of maxterms. This operation is performed in such a manner that the set of inputs is taken and then through the OR operation it is ensured that all false conditions are covered to arrive at the maxterm. The POS form records the exact oppositeness—when the function is false. This serves to make the function expressed in a logically equivalent way but from a different angle. The POS form is frequently useful in a circuit design in which both NOR and NAND gates are favorable; moreover, it is convenient in some varieties of logic families (Virtual Labs 2025).
Thus, by applying the POS representation, it is possible to build up logic circuits which consist of only universal circuits, for example, the NOR and NAND circuits which seem to be more effective in the circuit designing in hardware. Following the conventional structure of the POS form, all the false conditions are taken into consideration making it possible to systematically cover all the aspects of Boolean functions (Teja, R 2024). This approach is widely used in combinational circuit design because it offers less possible logic minimization in implementing circuits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sum-of-Products (SOP) and Product-of-Sums (POS) forms are fundamental methods for expressing Boolean functions in digital logic design. SOP is useful for directly implementing combinational circuits using AND and OR gates, ensuring that all conditions producing a high output are covered. POS, on the other hand, simplifies circuit design by focusing on conditions where the output is low. Both forms play a crucial role in optimizing and constructing efficient logic circuits.
Reference List
Journals
- Bowler Hat LLC 2024. NOT gate — logicly documentation, [Online] Accessed from: https://logic.ly/lessons/not-gate/ Accessed on: [20.3.2025]
- GeeksforGeeks 2024, NOT gate, [Online] Accessed from: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/not-gate/ Accessed on: [20.3.2025]
- Robert, F.J., Jordana, J. and Casanella, R. 2021, Problems on digital circuits and systems (CSD).
- Storr, W 2023, Sum of product expression in Boolean algebra, [Online] Accessed from: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/boolean/sum-of-product.html Accessed on: [20.3.2025]
- Teja, R 2024, Implementation of Boolean Functions using Logic Gates, [Online] Accessed from: https://www.electronicshub.org/implementation-of-boolean-functions-using-logic-gates/ Accessed on: [20.3.2025]
- Virtual Labs 2025. Realization of logic functions with the help of universal gates NAND and NOR Gate, [Online] Accessed from: https://de-iitr.vlabs.ac.in/exp/realization-of-logic-functions/theory.html Accessed on: [20.3.2025]

