- Entrepreneurship And Small Business Management Assignment sample
- 1. Introduction Of Entrepreneurship And Small Business Management Assignment Sample
- 2. Investigation and demonstration of the variety of business endeavors
- 3. Assessment of the impact of small business on the economy
- 4. Identification and evaluation of the critical characteristics of an entrepreneurship mentality
- 5. Examining the many circumstances that promote or stifle entrepreneurialism
- 6. Conclusion
Entrepreneurship And Small Business Management Assignment sample
Get free written samples by our Top-Notch subject experts and Online Assignment Help team.
1. Introduction Of Entrepreneurship And Small Business Management Assignment Sample
In the context of the competitive global world, it is necessary to cater to the ideas of the different types of business and policies that will help to enhance the business profile in the international platform (Tabares et al., 2021). Regarding this matter, in this report, a consultancy service has provided some knowledge about the types and characteristics of the businesses that would help the selected organization “Trading Scents” to generate the notions of business through the deepest path. Regarding this matter, this particular report has shown the differences among the business and also shown the impact of small businesses on the economy of the United Kingdom.
2. Investigation and demonstration of the variety of business endeavors
2.1 An analysis of the many kinds of running a business and a description of how they connect to the entrepreneurial classification
- Small Scale Business Entrepreneurship: A tiny company is one that operates on a limited scale and requires less public investment, fewer employees, and less equipment to run. The owner either makes a one-time investment in equipment, businesses, and facilities or leases or hires them (Neumeyer and Santos, 2018). These businesses invest a maximum of one crore.
- Large Corporations: This business type is intended to promote sustainable learning and growth via the incorporation of new goods. They are subject to significant competition on the market and have a unique service life. Its success depends on the creation of the system.
- Scalable Business Start-ups: A growing business is one that increases revenues and expenditures at the same rate. Not only increases income but also lowers spending by a scalable business (Wallmeroth, Wirtz, and Groh, 2018).
- Social Entrepreneurship: Social enterprise is a method by people, organizations, start-ups, or enterprises in which remedies to social, economic, or environmental problems are developed, funded, and implemented.
2.2 Exploration of the similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures
|
Type of business |
Purpose |
Responsibility |
Features |
|
“Large Corporations” |
The main objectives of this program are massive investment returns, profits, and incomes (Kwon, Choi and Hwang, 2021). |
It was a competitive task given to them. To this end, consistency and delivery are rewarded by these efforts. |
This is lifetime-long and the subject of strong rivalry in the marketplace. Their success is the technological development delegate. |
|
“Scalable Entrepreneurship” |
The main goal is the creation of dominance and the maximum volume of revenue. |
These kinds of companies are led by the leadership. They evaluate the advantages and disadvantages in and out of. These companies have established a brand recognition approach (Bendickson, 2021). |
Because companies manage, regulate, and influence these kinds of start-ups, they are primarily responsible. It aims to disrupt the current economy and boost profits. |
|
“Small Business Entrepreneurship |
Use of the world’s current and semi marketplaces. |
These businesses offer employees the chance to gain technical knowledge and abilities. These departments are responsible for the involvement of employees (Kwon, Choi and Hwang, 2021). |
They typically work at the regional and local levels and have less than 10 employees. Limited room for the production process. No more than 15 to 50 workers are employed. |
|
“Social Entrepreneurship” |
Development of high-quality goods and services that enhance mankind. |
The activities must impact people, the ecosystem, and the community as simply a sustainable initiative (Neumeyer and Santos, 2018). |
This may be expensive, but it helps humanity. |
2.3 Demonstrated knowledge of innovation in both the public and private sectors
In both the government and the trading sectors, corporate strategy plans are being developed in the UK. These completely developed models assist the country’s economic development. In order to measure its effect, the cultural growth and achievements of the nation should be examined. Increasing the economic growth of the region and creating new employment are also important to private companies (Halaskova, Gavurova, and Kocisova, 2020).
Public and private enterprises help to support the development of entrepreneurship via technical and economic aid. Concerning developing nations, innovative and efficient ways are needed to achieve and stimulate economic growth, while making use of these prospective streams (Halaskova, Gavurova and Kocisova, 2020). The economic outlook of a nation is influenced by both industry and government policy. Business standards establish rules, assess the business climate, and foster private production via the World Bank. The characteristics of the Treasury Department Index are founded on government and business tactics in underdeveloped countries, with unclear outcomes.
2.4 Entrepreneurship endeavors are critically examined in terms of requirements, growth, and expansion
Innovation is the promotion of value via the discovery of economic opportunities. Planning and management are simple problems in producing company funds and resources. It has been stated that small and medium enterprises are capable of promoting the entrepreneurial paradigms of the country (Kiani et al., 2021). Instead of manufacturing them, they may promote and sell several goods. Largely creative or successful micro-container companies are generating comparatively modest incomes.
There is a broad range of marketing techniques in industry, service, and agriculture. The service sector was among the three most competitive. There are also many additional problems. The industry, for instance, is constantly changing and more intense. Entrepreneurs must attempt to evaluate their procedures to preserve their strategic performance and growth. The shortfall of finance is another problem, especially for SMEs and micro-enterprises. The primary problem is the lack of technical and management capabilities.
3. Assessment of the impact of small business on the economy
3.1 Collection and analysis of pertinent statistical data to demonstrate the financial impact of small and medium enterprises
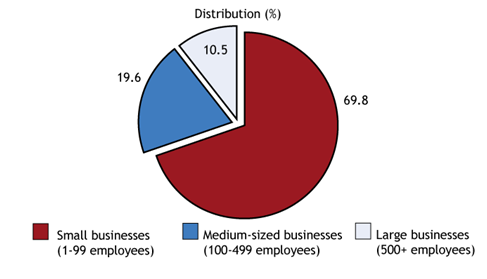
Figure 1: Ratio of the contributed economy of small businesses in the UK
(Source: Williams Jr et al., 2020)
Firms constitute more than fifty percent of the world’s workers, as per the OECD. As stated in this study, many business companies in both emerging and advanced nations operate independently (Williams Jr et al., 2020). These help underdeveloped nations to create wealth and employment. In addition, large company concepts draw domestic foreign investment. Small-scale model approaches to certain key significant issues are successful on a provincial size. For instance, such SMEs may offer access to clean drinking water, power, and training.
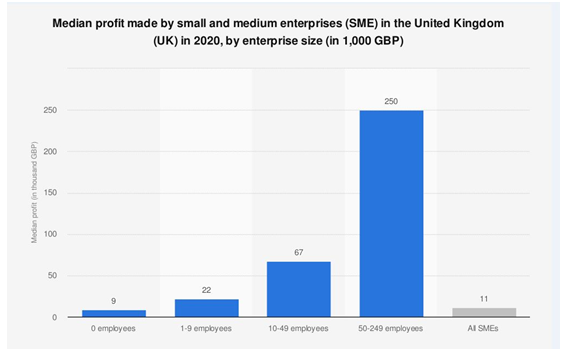
Figure 2: Profit gained by the small and medium businesses in the UK
(Source: Rahman et al., 2020)
Allowing for private sector growth enables small businesses in impoverished countries to contribute to the commonwealth. Because small companies create local prosperity, they play a critical role in resolving youth development problems. Small enterprises contribute to the development of skills in big corporations in a variety of fields, such as information technology, green tech, and market research (Rahman et al., 2020).
Around 32 million individuals in the United Kingdom work for small companies. Small business growth is also increasing. It is noteworthy. The number of small companies in the United Kingdom has exceeded the number of large firms. Additionally, the industry as a whole is endangered by the use of smart, inventive, and unique commercial techniques. Small companies generate 41% of the UK’s income.
3.2 Description of the critical role of small companies and new ventures in the development of the social-economic
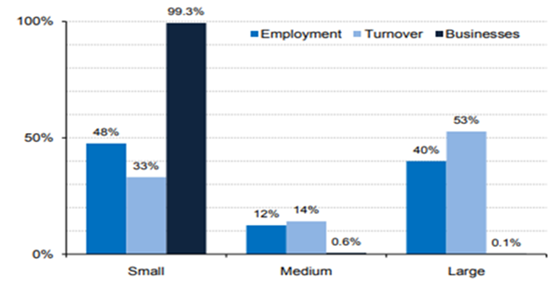
Figure 3: Ratio of Business in UK economy
(Source: Lenoël and Young, 2020 )
From the above chart, it has been seen that in the overall social economy the small businesses have a massive impact. It has enhanced social business in the United Kingdom.
In the 1980s, the British government recognized the critical role of SMEs in tackling social challenges such as unemployment, employment, and socioeconomic inequalities. According to the latest studies, the UK’s “lengthy wealth” and “labor productivity” need the active participation of SMEs. The government thinks that supporting small businesses is an effective strategy for reviving the economy (Lenoël and Young, 2020). Small businesses, which provide a growing number of employment opportunities, may contribute to the achievement of local, national, and worldwide health goals. Simply stated, small and medium-sized businesses are the engine that propels the world industry ahead.
Small businesses contribute to the growth and creativity of local economies by offering growth prospects in the regions in which they operate. Additionally, small companies earn money by employing individuals who would otherwise be unemployed due to larger enterprises. Numerous small businesses are also adaptive to changing economic circumstances. Including this idea, smaller businesses are likely to be consumer-oriented and sensitive to community needs. Despite the recession, many residents of the region continue to patronize their favorite small businesses.
3.3 Assessment of the contributions of the small, medium, and big companies to the economy via the use of pertinent facts and figures
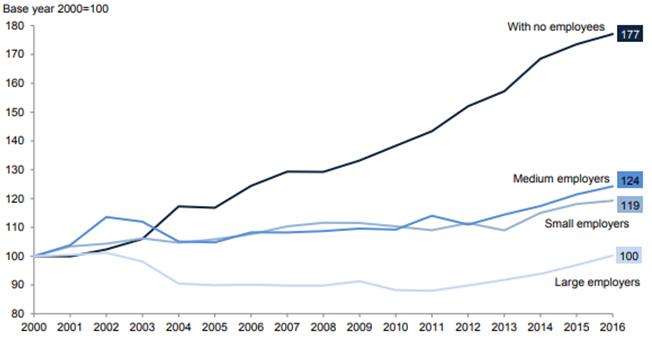
Figure 4: Employment scale from the different business context
(Source: Kozlinska, Rebmann and Mets, 2020)
Numerous analysts say that innovation stimulates economic growth. It may contribute to unlocking the benefits of both large investments by promoting the most suitable company model.
There are some data on small business marketing in the United Kingdom (Babalola et al., 2020).
- Expansion of a company and the adoption of a large-scale microenterprise model may impede economic progress, particularly in developing nations.
- The expansion of “medium-sized businesses” inside a country, particularly in developed nations, may have a beneficial effect on inflation.
On this basis, industry, and government must collaborate to foster a diverse mix of small, medium, and large companies at the municipal, provincial, and national levels.
3.4 A critical study of the effect of small companies on the economy at various levels (local, regional, and national) and in an increasingly globalized world
The United Kingdom’s small & mid businesses are encouraged to invest. They are well recognized for their achievements in the national, regional, and local economies. Due to their little size, they have had a major influence on the UK market. In the United Kingdom, almost 26 million small organizations employ 70% of the population. Small businesses may profit from factors such as an intelligent tax structure and regulations (Dilli, Elert and Herrmann, 2018). In the United Kingdom, money constraints and incentives are contributing to the death of SMEs.
In terms of business size, two distinct elements were found. For start, business expansion and a widespread micro-business structure may have a detrimental effect on a country’s economy, especially in emerging economies (Molino et al., 2018). Second, growth in small businesses, especially in industrialized nations, may contribute to economic progress.
4. Identification and evaluation of the critical characteristics of an entrepreneurship mentality
4.1 Determine the distinctive characteristics and abilities of successful businessmen that set them apart from other top management
|
Entrepreneurs |
Business Managers |
|
· Successful entrepreneurs possess an inquisitive mind that drives them to seek out new possibilities (Stephan, 2018). Rather than accepting what they believe they already know, inquisitive entrepreneurs pose critical questions and pursue novel paths. · Entrepreneurs are also enthusiastic and ready to spend long days with their businesses. They excellently connect and build industry experience for the goods and services of their companies. |
· Good managers are excited about the management team of the company and transmit their direct reports favorably on company structure or the basis of its distinctiveness. · The supervisors are looking for managers with honesty, transparency, and the ability to take their acts into account and to assume accountability for all of them and others (Gielnik, Zacher and Schmitt, 2017). |
4.2 Evaluation of the extent to which certain facets of the entrepreneurial personality represent market potential and attitude
Entrepreneurship is a certain mentality that governs human behavior towards entrepreneurship and results. Individuals with such thoughts are frequently attracted to chances, new values, and breakthroughs (Young et al., 2020). This type of character helps businesses build trust and take chances fearlessly.
Non-monetary stimulus: Certain semi resources are given to meet selfishness and update requirements.
Leadership: employees have a “hierarchy of needs” and a feeling of responsibility that leads to a good engagement with their “line director” and other group members.
The environment of the workplace: workers have cultural aspirations and ambitions matched with professionals.
4.3 Examining and evaluating various lines of reasoning about staff appraisal
A competent contractor is a person who maintains and runs a worn-out business instead of seeking a job somewhere. To be a good company owner, it is important to respect and follow the unique qualities and characteristics of the organization (Young et al., 2020). Employers have certain abilities or qualities to be able to communicate successfully. It is difficult to maintain business connections when language skills are used to cope with issues. He must be very innovative to obtain the needed outcomes to bring new commercial profits to the table and to integrate them into its processes.
4.5 An examination of the distinguishing characteristics, abilities, and motivating drives of successful entrepreneurs, illustrated with particular instances
Motivation: The individuals’ wishes and ambitions will be fulfilled by workers and other employees of the company (Rheinbergm and Engeser, 2018). Trained workers are more effective and efficient than others who contribute to the development and success of the company.
Flexibility and open-mindedness: These are important characteristics of a healthy businessman who requires new ideas and the capacity to deal with obstacles and difficulties in any positive or negative scenario (Michna and Kmieciak, 2020). To be accepted, new market developments and the culture of the workplace must be enjoyable and ambition is needed in order to reach the objectives and unique character of the business.
5. Examining the many circumstances that promote or stifle entrepreneurialism
5.1 Examine how one’s background and experience may either stifle or promote entrepreneurialism via the use of pertinent examples
Education: In entrepreneurship training plays an essential role. If an employer is skillful, he or she has entrepreneurship and applies complicated innovative ideas, facilities, processes, and business processes.
National Culture: Businessmen are affected by their environment. In this scenario, companies may enhance their service, if the atmosphere is pleasant and supportive (Şahin, Karadağ and Tuncer, 2019).
Economic Factors: Economic variables are all shown through government legislation and other national agency with corporations, currency exchange, tax rates, and levels of inflation.
Traits: One needs a broad variety of characteristics to become the most successful business owner. For instance, he has to be personality and motivated in his actions and processes.
5.2 An examination of the relationship between entrepreneurial qualities and the impact of personal background and traditions on the performance of particular entrepreneurs
Motivation and inspiration: A successful entrepreneur’s key element is an owner that inspires supports and is enthusiastic about achieving objectives.
Credit management: Money is a vital commodity, and the corporation’s functionality and activities are determined by the business person how it is utilized (Vallaster et al., 2019).
An effective schedule: A timeline is created to ensure timely decisions, effective time management, and effective use of funding and support in the organization’s functions and processes.
Risk: Entrepreneurs are often known as a risk because they are willing to take time and cash big risks to predict future unpredictability.
5.3 Critical assessment of how businessmen have a good and bad impact on their history and experience by comparing and contrasting instances
Entrepreneurial qualities must be implemented correctly; otherwise, they will have a detrimental impact on the company’s name and brand. For instance, Bill Gates is one of the world’s most successful entrepreneurs, yet he earned his success through hard work and perseverance. He faces many problems and deceptions throughout his life, but never considers his future growth and wealth, and so continues to face hurdles (Roomi, Rehman and Henry, 2018). According to all estimations, he is the fourth wealthiest man on the planet and the “Founder of the Microsoft Company.”
6. Conclusion
The current research counsels the leadership of “Trading Scents” on various entrepreneurial initiatives and assesses the proposed business’s impact on the local and national economy. Additionally, after a comprehensive examination, the article emphasizes the essential components of an entrepreneur. To add to the report’s depth, many relevant instances of established entrepreneurs were mentioned and the character of their entrepreneurial attitude was analyzed.
References
Babalola, M.T., Greenbaum, R.L., Amarnani, R.K., Shoss, M.K., Deng, Y., Garba, O.A. and Guo, L., 2020. A business frame perspective on why perceptions of top management's bottom‐line mentality result in employees’ good and bad behaviors. Personnel Psychology, 73(1), pp.19-41.
Bendickson, J., 2021. Building entrepreneurship research for impact: Scope, phenomenon, and translation.
Dilli, S., Elert, N. and Herrmann, A.M., 2018. Varieties of entrepreneurship: exploring the institutional foundations of different entrepreneurship types through ‘Varieties-of-Capitalism’arguments. Small Business Economics, 51(2), pp.293-320.
Gielnik, M.M., Zacher, H. and Schmitt, A., 2017. How small business managers’ age and focus on opportunities affect business growth: a mediated moderation growth model. Journal of Small Business Management, 55(3), pp.460-483.
Halaskova, M., Gavurova, B. and Kocisova, K., 2020. Research and development efficiency in public and private sectors: An empirical analysis of EU countries by using DEA methodology. Sustainability, 12(17), p.7050.
Kiani, A., Yang, D., Ghani, U. and Hughes, M., 2021. Entrepreneurial passion and technological innovation: the mediating effect of entrepreneurial orientation. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, pp.1-14.
Kozlinska, I., Rebmann, A. and Mets, T., 2020. Entrepreneurial competencies and employment status of business graduates: the role of experiential entrepreneurship pedagogy. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, pp.1-38.
Kwon, J., Choi, Y. and Hwang, Y., 2021. Enterprise Design Thinking: An Investigation on User-Centered Design Processes in Large Corporations. Designs, 5(3), p.43.
Lenoël, C. and Young, G., 2020. Prospects for the UK economy. National Institute Economic Review, 252, pp.F10-F43.
Michna, A. and Kmieciak, R., 2020. Open-mindedness culture, knowledge-sharing, financial performance, and industry 4.0 in SMEs. Sustainability, 12(21), p.9041.
Molino, M., Dolce, V., Cortese, C.G. and Ghislieri, C., 2018. Personality and social support as determinants of entrepreneurial intention. Gender differences in Italy. PloS one, 13(6), p.e0199924.
Neumeyer, X. and Santos, S.C., 2018. Sustainable business models, venture typologies, and entrepreneurial ecosystems: A social network perspective. Journal of cleaner production, 172, pp.4565-4579.
Rahman, M., Akter, M., Odunukan, K. and Haque, S.E., 2020. Examining economic and technology‐related barriers of small‐and medium‐sized enterprises internationalisation: An emerging economy context. Business Strategy & Development, 3(1), pp.16-27.
Rheinberg, F. and Engeser, S., 2018. Intrinsic motivation and flow. In Motivation and action (pp. 579-622). Springer, Cham.
Roomi, M.A., Rehman, S. and Henry, C., 2018. Exploring the normative context for women’s entrepreneurship in Pakistan: a critical analysis. International Journal of Gender and Entrepreneurship.
Şahin, F., Karadağ, H. and Tuncer, B., 2019. Big five personality traits, entrepreneurial self-efficacy and entrepreneurial intention: A configurational approach. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research.
Stephan, U., 2018. Entrepreneurs’ mental health and well-being: A review and research agenda. Academy of Management Perspectives, 32(3), pp.290-322.
Tabares, A., Chandra, Y., Alvarez, C. and Escobar-Sierra, M., 2021. Opportunity-related behaviors in international entrepreneurship research: a multilevel analysis of antecedents, processes, and outcomes. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 17(1), pp.321-368.
Vallaster, C., Kraus, S., Lindahl, J.M.M. and Nielsen, A., 2019. Ethics and entrepreneurship: A bibliometric study and literature review. Journal of Business Research, 99, pp.226-237.
Wallmeroth, J., Wirtz, P. and Groh, A.P., 2018. Venture capital, angel financing, and crowdfunding of entrepreneurial ventures: A literature review. Foundations and Trends® in Entrepreneurship, 14(1), pp.1-129.
Williams Jr, R.I., Smith, A., R Aaron, J., C Manley, S. and C McDowell, W., 2020. Small business strategic management practices and performance: A configurational approach. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja, 33(1), pp.0-0.
Young, R., Wahlberg, L., Davis, E. and Abhari, K., 2020. Towards a Theory of Digital Entrepreneurship Mindset: The Role of Digital Learning Aptitude and Digital Literacy. In Americas Conference on Information Systems (pp. 1-10).

