- Introduction - HC4005-Social Science Perspective Assignment Sample
- Theoretical frameworks
- Sociological perspective
- Systems theory and exploring its application to the understanding of families and service users
- Psychological perspective
- Discrimination
- Systems theory and exploring its application to the understanding of families and service users
- Primary Socialisation Theory
- Secondary socialisation theory
- Concept of discrimination and its impact on families and service users
Introduction - HC4005-Social Science Perspective Assignment Sample
The study tends to elevate the sociological and psychological perspectives to the human behaviour. Basically, different sociological theory and psychological theory will be discussed in the further section of this study. The psychological perspective on discrimination examines the underlying psychological factors that contribute to discrimination and prejudice. These factors include biases, stereotypes, and attitudes. Various forms of discrimination, such as sexism, homophobia, and racism, adversely affect individuals who encounter them, both in public settings and in their everyday lives. The human tendency to generalize and the economic motivations can lead to discriminatory behaviors, which are often exacerbated by the development of hostile attitudes towards individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
Experience stress-free academics with our reliable Assignment Helper team! We combine expertise, dedication, and timely delivery to ensure your complete satisfaction and academic growth.
Theoretical frameworks
The sociological and psychological perspectives of human behaviour will be discussed on the basis of two of the topics such as discrimination and systems theory and exploring its application to the understanding of families and service users (Guhin et al., 2021).
Sociological perspective
Systems theory and exploring its application to the understanding of families and service users
Socialization theory assists in analyzing families by demonstrating the ways in which families shape the social development of a child. Socialization is considered to be the procedure of learning ways to have into society and families are considered to be the primary social organizations which teach this. The theory states that socialization is a lifelong procedure and it starts at birth and endures across life (Pak et al., 2024). Furthermore, families are considered to be the first and most powerful social institution into a child’s life. Along with this, children learn ways to behave, what to believe and ways to communicate with others. Moreover, children learn ways to negotiate with others, manage conflicts along with emotions. It has been evaluated that children learn ways to analyze themselves along with the place into the world. The theory demonstrates that families learn regarding the society’s material norms, values, philosophy along with culture. The factors which create an impact on socialization are family structure, socioeconomic status, ethnicity along with time period. At the time of the process of socialization, children learn regarding their family traditions through their elders and protect them and get ahead of them on to the next generation as they produce older. Along with this, socialisation assists children to learn as well as perform diverse roles and responsibilities that they have learnt through their elders (Allen and Henderson, 2022). With the help of socialization, a child will learn to promote understanding, grow more confident, find the concepts of teamwork and sharing and enhance language skills. Furthermore, practicing these concepts via socialization would assist family members in generating friendships and thus learn ways to admire others. It is considered to be the process via which a person learns their society’s customs, beliefs, values and norms. It is considered to be a versatile and complex procedure which includes numerous agents and phases of socialization. Socialization plays a major role in shaping the social, behaviour and personality interactions.
It has been evaluated that service users have not been engaged into social work theorizing systematically. The theory determines the fact that disabled individual movements, other service users and mental health services have built their own knowledge on the basis of direct experience. Furthermore, they have created their own bodies of theory as well as conceptual frameworks (Harrison et al., 2021). It is seen that their interpretation along with developments need the straight engagement of service users as well as their organization into socialization. There possess robust political, philosophical along with practical arguments for including the theories and knowledge’s of service users along with their organizations into the procedure of social-work theory-building. It has been observed that group socialization is determined to be the theory which a person’s peer groups, instead of parental figures create an impact on their behaviour and personality into adulthood.
Psychological perspective
A psychological perspective is regarded as a manner of looking at human thought and behaviour.
Discrimination
Psychological perspective on discrimination determines the psychological factors which lead towards discrimination and prejudice. These factors involve biases, stereotypes and attitudes. Types of discrimination like sexism, homophobia and racism are creating a negative impact on the people which are being exposed to these both in public aspect and daily life. The generalizing and economic tendency of the human mind could result into discrimination among others and use along with the growth of hostile attitudes towards people through diverse cultures. Attachment theory is a psychological explanation for the relationships and emotional bonds among individuals (Stern et al., 2022). The theory states that individuals with insecure attachment styles possess more chances to be discriminated and prejudiced against others, while individuals with protected attachment styles possess fewer chances to do so. It has been analyzed that apprehensively attached individuals might possess more chances to discriminate and stereotype against others. Along with this, they might be more likely to consider others as a danger that could result into prejudice and fear. The theory determines the act that secure attachment is positively and significantly associated with the discriminatory attitudes towards women and adversely associated to the overseas discrimination.
In most of the studies it has been found that sexism scores were greater among people having insecure attachment styles. Moreover, disgrace tendencies of individuals with the protected attachment style are inferior for the discrimination, psychological health dimensions, prejudgment and exclusion and are greater for individuals with the fearful attachment style for the discrimination, psychological health dimensions, labelling along with exclusion (Stern et al., 2022). Furthermore, it has been noticed that disgrace tendencies of males possess more chances to be greater as compared to females for the exclusion and discrimination. As per World Health Organizations (WHO), discrimination is the major topics across the world in enhancing the quality of mental health practices. Most of the research has monitored the manner in which people with stigmatizable personalities react to and cope with discrimination. However, prior to reacting with effectual coping approaches, people must identify as well as attribute such events to discrimination. It has been analyzed that attachment style directs the viewpoint of women regarding sex discrimination (Causadias et al., 2022). Even though its role in being a goal of discrimination remains indefinite, attachment style consistently anticipates being a performer of discrimination. Current experimental work has set a causal association, focused towards attachment insecurity which could result into greater levels of discriminatory choices. Moreover, research determines the fact that attachment style is significantly associated with discrimination instead of the targets of discrimination. Nevertheless, as stigmatizing group membership holds the possible threat of discrimination, apprehensive attachment plausibly affects observation towards and reacting to prejudice.
Systems theory and exploring its application to the understanding of families and service users
Systems theory is considered to be a framework which studies the manner in which systems are build-up of interconnected portions which communicate and adapt to their setting. The theory helps in understanding families by monitoring the ways in which families communicate and functions together as a whole (Murry et al., 2022). According to the theory, family members sense and respond to each other’s emotions which in turn generate an interdependency which creates an impact on all members. Along with this, families are self-organizing and adapt to their members as well as the external setting. As per the theory, families could recognize dysfunctional patterns as well as set objectives to enhance. Furthermore, families could draw the origins of emotional and behavioural patterns via generations. With this, families could learn to reframe their communications and also resolve conflicts. Furthermore, the attachment theory could help in promoting secure attachment among the family members like children and parents (Choate and Tortorelli, 2022). This in turn could assist children in feeling safe and secure and build healthy expectations for upcoming relationships. Moreover, attachment theory could assist in explaining how family dynamics could create an impact on the psychological and emotional development. It could also in demonstrating the ways in which these dynamics might be converted across generations.
Furthermore, systems theory assists social workers in analyzing service users by determining how they are impacted by various influences and factors. It could assist in recognizing the resources and strengths and the ways in which they could be used to change and cope. The theory is highly useful as a way to holistically treat customers by assisting bring together the entire image of the individual choices, behaviour and thoughts within their greater ecology of influence (Harlow, 2021). It has been analyzed that the objective of social work is to authorize communities and people to overcome challenges and live rewarding lives. In order to attain this, service users might emphasize on a specific framework or strategy. By noticing and evaluating the systems which lead towards the welfare and behaviour of social workers which could work in enhancing those systems as per the unique situation of an individual. Attachment theory proves to be helpful in analyzing the manner in which individuals associate with one another and the manner in which they manage with challenges. This could assist in enhancing service delivery and the quality of care. Furthermore, attachment theory could assist in anticipating and analyzing problematic behaviours such as hostility and brutality (McClean et al., 2021). It could also assist in analyzing the manner in which individuals could react to stress. Moreover, it assists on recognizing the protective factors as well as the risks into individual lives. The theory states that individuals cope with hardship. For instance, individuals with protected attachments could gain advantages through caring associations. Furthermore, attachment theory has impacted the manner in which professionals approach education and childcare.
Figure 1: Attachment theory
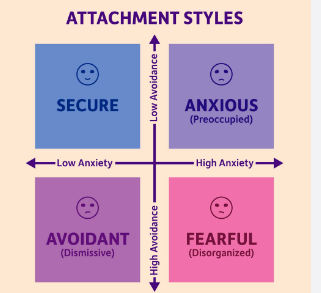
(Source: Kerschbaumer et al., 2023)
Primary Socialisation Theory
Primary socialisation theory is the theory that states how people learn and adapt the behaviour, values, and norms of the culture and society they see or belong to from birth to early childhood. Thus, in other words according to this theory, social behaviour like deviance and the use of drugs are learned through interactions with peers, families, and educational institutions. Influence on the behaviours are due to the strengthening of the bonds between people and their major sources of primary socialisation (Portes, 2024). The primary factor of primary socialisation theory is gaining knowledge from interactions. For example, children learn from people they meet, interacting with them, and imitating what others do. Families play a major role in socialisation as families shape their children from birth and thus children learn their behaviour and culture from their families from their birth. Children play with various types of people belonging to their age or older than them. Thus, interacting with people belonging to different age groups helps children to adopt various types of behaviour. Thus, early childhood is an important period as it is the base from which children adopt their social development and thus it acts as a foundation of future social development.
Secondary socialisation theory
The secondary socialization theory is a concept or idea which is effectively used for interacting with other people and foreign individuals in an immediate family. The theory majorly conveys around the place where children have to collaborate with other family members in a larger organisation or project. On various occasions, children have to learn about the authority figure as well as interpret their cultural norms outside their family. In this aspect, the children become significantly confident about achieving social competence and following the norms for meeting the expectations of their family and other society members (Portes, 2024). Most of the time the major agents of secondary socialisation include teachers, peers, religious institutions and many more. Sometimes government bodies also create significant rules and regulations to maintain the behaviour of children in society. The secondary socialization approach can be compared with the primary method of socialization. The secondary socialization majorly occurred outside the home where the family doesn't involve as much as other participants. Whereas in primary socialization mostly children learn from their family members and parents about the fundamentals of values and ethics. Maintaining an effective understanding of societal values and its amount the children's mindset can shape their behaviour among others and maintain a better approach in their future life.
Concept of discrimination and its impact on families and service users
The idea of discrimination can be created in the mindset of children from their families and society. According to primary socialization, the family can significantly influence the children about the necessary values and ethics for society. Children must interpret cultural standards outside of their household and learn about the authority figure (Portes, 2024). In this area, the kids gain a great deal of confidence in their ability to become socially competent and in adhering to the rules to satisfy their family and other members of the community. Peers, instructors, religious organizations, and many more are frequently the main forces for secondary socialisation. On the other hand, during primary socialization, children primarily learn the principles of ethics and values from their parents and family. Having a solid grasp of societal values and how much of an impact they have on children's mindsets can influence their behaviour and help them adopt healthier habits in the future. Interactions with friends, families, and educational institutions teach social behaviours including drug use and deviance (Portes, 2024). Stronger ties between individuals and their key socialization sources have an impact on their behaviours. Learning from interactions is the main component of the primary socialization theory. Children learn, for instance, by interacting with others and copying their actions. Families have a significant influence on socialization because they mould their children from birth, teaching them attitudes and cultural norms. Youngsters engage in play with a variety of individuals who are either their age or older (Portes, 2024). Through primary socialisation theory, discrimination can be reduced as children’s through interacting with different types of individuals can learn to respect people, lifestyle, and their culture. Primary socialisation will help children to learn and understand about various types of stereotypes. This will help children learn about diverse cultures and groups and it will help in reducing discrimination and prejudice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be depicted that the main concern of this assignment is to deliver the sociological and psychological perspectives in the human behaviour. Research has consistently indicated that individuals with insecure attachment styles tend to exhibit higher levels of sexism. Furthermore, those with secure attachment styles demonstrate lower tendencies towards disgrace in relation to discrimination, psychological well-being, prejudgment, and exclusion. In contrast, individuals with fearful attachment styles show elevated levels of disgrace concerning discrimination, psychological health dimensions, labeling, and exclusion. Through the lens of primary socialization theory, it is possible to mitigate discrimination by enabling children to engage with a variety of individuals. Such interactions foster respect for different people, lifestyles, and cultures. Primary socialization plays a crucial role in educating children about various stereotypes, thereby enhancing their understanding of diverse cultures and communities. This process ultimately contributes to the reduction of discrimination and prejudice.
References
- Allen, K.R. and Henderson, A.C., 2022. Family theorizing for social justice: A critical praxis. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 14(3), pp.364-383.
- Causadias, J.M., Morris, K.S., Cárcamo, R.A., Neville, H.A., Nóblega, M., Salinas-Quiroz, F. and Silva, J.R., 2022. Attachment research and anti-racism: Learning from Black and Brown scholars. Attachment & Human Development, 24(3), pp.366-372.
- Choate, P. and Tortorelli, C., 2022. Attachment theory: A barrier for indigenous children involved with child protection. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(14), p.8754.
- Guhin, J., Calarco, J.M. and Miller-Idriss, C., 2021. Whatever happened to socialization?. Annual Review of Sociology, 47(1), pp.109-129.
- Harlow, E., 2021. Attachment theory: Developments, debates and recent applications in social work, social care and education. Journal of Social Work Practice, 35(1), pp.79-91.
- Harrison, R., Moisio, R., Gentry, J. and Commuri, S., 2021. Processes of consumer socialization: study of single-father households. European journal of marketing, 55(10), pp.2649-2673. Kerschbaumer, R.H., Kreimer, D., Foscht, T. and Eisingerich, A.B., 2023. Subscription commerce: an attachment theory perspective. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 33(1), pp.92-115.
- McClean, S.T., Yim, J., Courtright, S.H. and Dunford, B.B., 2021. Transformed by the family: An episodic, attachment theory perspective on family–work enrichment and transformational leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 106(12), p.1848.
- Murry, V.M., Gonzalez, C.M., Hanebutt, R.A., Bulgin, D., Coates, E.E., Inniss-Thompson, M.N., Debreaux, M.L., Wilson, W.E., Abel, D. and Cortez, M.B., 2022. Longitudinal study of the cascading effects of racial discrimination on parenting and adjustment among African American youth. Attachment & Human Development, 24(3), pp.322-338.
- Pak, T.Y., Fan, L. and Chatterjee, S., 2024. Financial socialization and financial well‐being in early adulthood: the mediating role of financial capability. Family Relations, 73(3), pp.1664-1685.
- Stern, J.A., Barbarin, O. and Cassidy, J., 2022. Attachment perspectives on race, prejudice, and anti-racism: Introduction to the special issue. Attachment & human development, 24(3), pp.253-259.
- Stern, J.A., Barbarin, O. and Cassidy, J., 2022. Working toward anti-racist perspectives in attachment theory, research, and practice. Attachment & Human Development, 24(3), pp.392-422.
- Portes, A., 2024. Social capital: Its origins and applications in modern sociology. New Critical Writings in Political Sociology, pp.53-76.

