Introduction of Impact Of The Covid Pandemic On Businesses In UK Assignment
The topic is all about the impact of the covid pandemic on businesses in the UK, a large drop in sales occurred in businesses as a result of the spread of Covid-19 and measures taken to contain it. The coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) has wreaked unexpectedly strong, institutional, and cultural havoc. It is now regarded as the most significant danger to globalized trade since the 2008 recession. The study helps to understand the positive as well as the negative impact of the covid pandemic on the business in the UK. The progression of the pandemic, metrics taken to safeguard human safety, and how gov'ts, homes, and companies reply to these considerations will all have a significant impact on the UK economic system.
Click here for expert assignment help from New Assignment Help, a leading provider in the UK.
Aims and Objectives
The aims and objectives of the reports are given below:
- To understand the positive and negative impact of the Covid pandemic on business in the UK
- To analyze key strategies to overcome the negative impact of Covid on UK businesses.
Literature Review
Definition
As per the Nicola, and et.al., 2020, Price increases were especially pronounced in industrial production, supply chains, retail trade, and lodging and food producers. Inflation is most likely to rise due to a range of factors, along with a recovery in demand, replenishment and human labor scarcities, and increased energy prices.
Positive impact
According to Pantano, & et.al., 2020, everyone is aware of the global pandemic situation where things changed continuously. There has been a major disruption in the UK's infrastructure as a result of the Coronavirus outbreak. Some companies thrived, while others failed, and a slew of new ones emerged. And those who made it out alive an emergency were changed in a broad way in which the flu epidemic only speeded up. Shang, Li, & Zhang, 2021 states that there are some of the positive impacts of the Covid pandemic on UK businesses are as follows:
- Typical business practices had to be abandoned, and new techniques of supplier relationships, goods and services distribution, and client ability to connect were prioritized. The rate of digitalization, which was happening in many business owners, accelerated from 'fast' to 'furious.' All was digitized, and your device or mobile phone had become the hub of commercial activity, wellness, accommodation, as well as government.
- According to He, & Harris, 2020, the advent of new technologies was already intrusive. The global epidemic accelerated it, providing customers with an once-in-a-lifetime chance to assess their new ways of doing things in a reasonably safe environment. Clients were knowledgeable and physicians and providers were unsurprisingly more flexible. Business owners could expand, introduce novel products, and innovate with little risk of opposition. The technology helps the food companies like Kingsmill to provide services online which is considered a major change in UK businesses.
- Covid Pandemic in the UK gives a new way of working for businesses as the companies implement changes according to the requirement. Further, many businesses like food and IT business highly rely on technology, and in terms of that, it will be helpful for them to take it positively (Abdelrhim, & Elsayed, 2020).
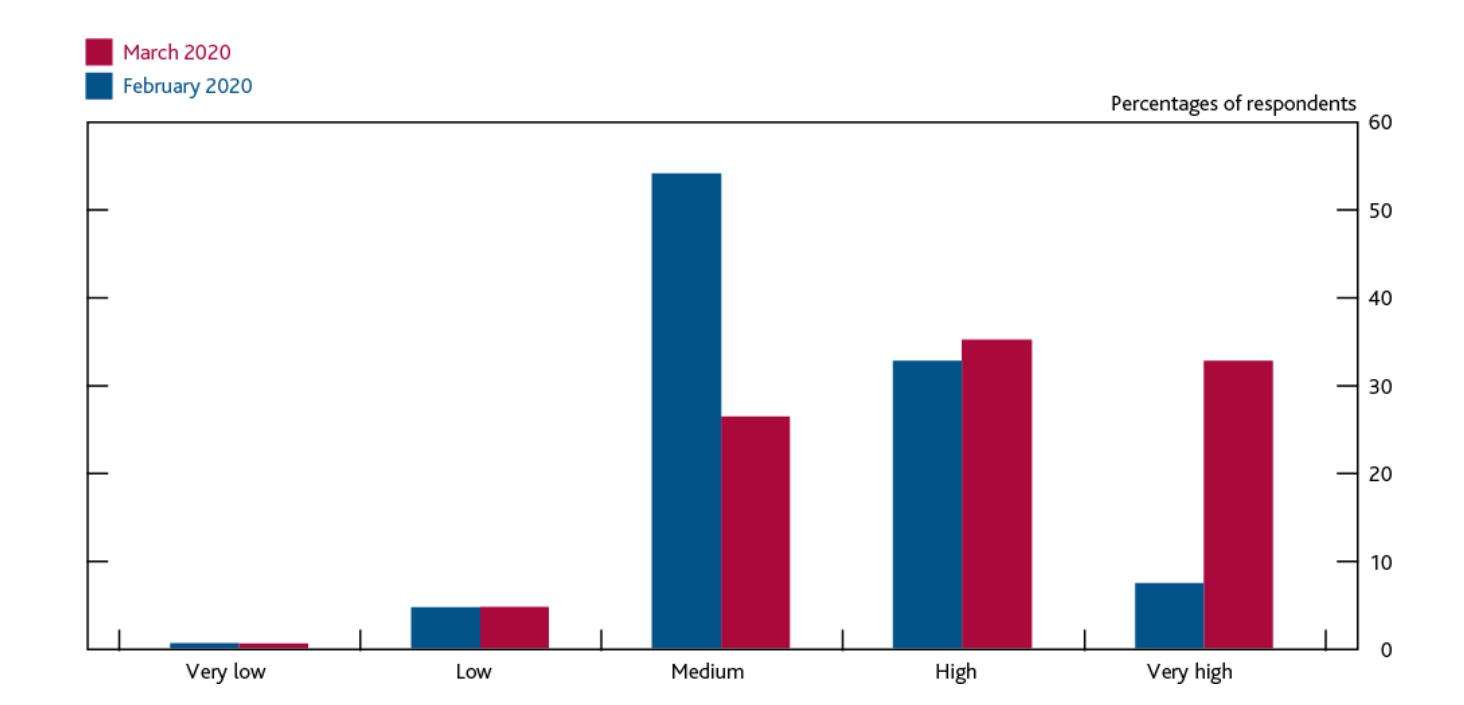
Figure 1: Overall Uncertainty Facing Businesses
Negative Impact
As per the opinion of Williams, & Kayaoglu, 2020 travel restrictions, social distancing, limitations on the sale of certain commodity markets, and clients having to resort to funding cuts and postponing projects have all resulted in a significant drop in sales. Businesses cannot recoup fixed costs in the absence of income generated due to a significant drop in sales.
- The coronavirus (COVID-19) global epidemic has had far-reaching consequences for businesses registered between and within "high-contact" industry sectors such as wholesale and retail transport and storage, food and lodging services, arts, recreation, entertainment, and other assistance.
- According to Belitski, & et.al., 2022 although "within" consequences demonstrate that major non-essential retailers were more negatively impacted, while exterior stores' patterns were similarly stronger, the wholesale/retail industry experienced the lowest drop in turnaround going to follow these same nationwide lockdowns. Sales of televisions and computer games, as well as likes to watch and jewelry, are examples. Retail sales in non-specialized shops, on the other hand, experienced the smallest drop in businesses registered at 7% in the first 2 months of 2020, including essential grocery stores, but were exempt from closing necessities during the first nationwide lockdown.
- The liquor thread and hotels and comparable housing post experienced the largest declines in turnover in the first half of 2020 in the housing and catering-related industries, whereas holiday, as well as other short-stay lodging, campsites, motor home parks, as well as other lodging, performed better all through the coronavirus disease outbreak.
- However, Bloom, & et.al., 2020 states that the largest drops in revenue in the arts, enjoyment and amusement sector were all for enjoyment and recreational, wagering and betting actions, and fine arts and fun activities; however, between reimagining a shift in choice toward outdoors over sedentary activities. On the other hand, advertisements representing travel threads have been less impacted by the coronavirus pandemic, which might also mirror the more critical nature of these travel agencies. The littlest decreases in turnover were seen in highway cargo transit and expulsion amenities, as well as overland cargo waterways.
Key Strategies to overcome the negative impact
As per the opinion of Brown, Rocha, & Cowling, 2020 Businesses in the UK are beginning to experience serious influences, regardless of size, and are being forced to rethink how those who handle and continue operating their operations, along with a review of their marketing plan. The impact on small businesses and start-ups can be far more severe since they have as there are less cash on hand and a tinier percentage for dealing with unexpected downturns. There are certain key strategies suggested by Phillipson, & et.al., 2020 to overcome the negative impact of Covid on businesses in the UK.
- Putting the health and safety of people as the priority is considered to be the key strategy to overcome the negative impact of covid on UK business. Businesses that have employees need to be aware of the government announcement and provide them with work-from-home opportunities. It is also prudent to put systems in place for workers to attend if they are feeling ill, are missing, or presume coronavirus publicity or disease.
- A detailed understanding of your distribution chain will aid in identifying any potential weaknesses. Alber, & Dabour, 2020 state that this begins with the most device is ideal and expands your search over and above first- and second-tier vendors, all the way back down to raw resources, if feasible.
- The major key strategy to overcome negative impact is communication where the ideal way to be transparent with the customers so that the business can easily run with loyalty. Clients can empathize with businesses in emergencies as long as the conversation is open and honest. Contact clients to learn about their perceptions of the goods offered by the company.
- It is important to manage a healthy relationship with the different parties the companies in the UK. It is comprehensible that paying distributors may be challenging during the lockdown. Nevertheless, it would also be beneficial to provide proper notice to your resellers, vendors, property owners, and others in case of a late payment so that they can be prepared. Hence, there is no anger and resentment in an already challenging period.
In addition to this, Budd, Ison, & Adrienne, 2020 states that UK businesses need to implement certain strategies to overcome the impacts. All companies must assess the risks of their core business processes to address the following new threats or gaps in the control environment for future circumstances such as pandemic influenza, recessions, and global political circumstances risks. As the global epidemic progresses and new data is available, laws will have to be evaluated, revised, and conveyed. In most cases, occurrence management is a highly segmented activity engrained inside a process. In times of rapid change, a strong and united corporation mechanism is required as an insight to examine the efficacy of prevention and legislation operations or to maintain specific exemptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while a global epidemic speeded up business transformation in the UK, how business owners responded to the pandemic had been critical in moving that conversion forward. Due to lower income attrition and insufficient understanding of the world's economic surroundings, it’s become difficult for most companies to manage their economic wheels spinning during the shutdown time frame. Businesses in the United Kingdom must understand the risk remediation strategies to handle this small-chance, greater events with a much larger view. COVID-19 has revealed specific supplier base, operations, and maintenance flaws that must be acknowledged as part of business perseverance and contingency planning. While the causes of future disruption may be hard to forecast, the same business consequences of an acute crisis can be predicted. At the very slightest, a renewed emphasis on perseverance and the delivery of much stronger operations must keep challenging deeply engrained lean and agile attitudes.
References
Abdelrhim, M., & Elsayed, A. (2020). The Effect of COVID-19 Spread on the e-commerce market: The case of the 5 largest e-commerce companies in the world. Available at SSRN 3621166.
Alber, N., & Dabour, M. (2020). The dynamic relationship between FinTech and social distancing under COVID-19 pandemic: Digital payments evidence. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 12(11).
Belitski, M., Guenther, C., Kritikos, A. S., & Thurik, R. (2022). Economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on entrepreneurship and small businesses. Small Business Economics, 58(2), 593-609.
Bloom, N., Bunn, P., Mizen, P., Smietanka, P., & Thwaites, G. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on productivity (No. w28233). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Brown, R., Rocha, A., & Cowling, M. (2020). <? covid19?> Financing entrepreneurship in times of crisis: exploring the impact of COVID-19 on the market for entrepreneurial finance in the United Kingdom. International Small Business Journal, 38(5), 380-390.
Budd, L., Ison, S., & Adrienne, N. (2020). European airline response to the COVID-19 pandemic–Contraction, consolidation and future considerations for airline business and management. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 37, 100578.
He, H., & Harris, L. (2020). The impact of Covid-19 pandemic on corporate social responsibility and marketing philosophy. Journal of business research, 116, 176-182.
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., .. & Agha, R. (2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International journal of surgery, 78, 185-193.
Pantano, E., Pizzi, G., Scarpi, D., & Dennis, C. (2020). Competing during a pandemic? Retailers’ ups and downs during the COVID-19 outbreak. Journal of Business research, 116, 209-213.
Phillipson, J., Gorton, M., Turner, R., Shucksmith, M., Aitken-McDermott, K., Areal, F., ... & Shortall, S. (2020). The COVID-19 pandemic and its implications for rural economies. Sustainability, 12(10), 3973.
Shang, Y., Li, H., & Zhang, R. (2021). Effects of pandemic outbreak on economies: evidence from business history context. Frontiers in Public Health, 9, 632043.
Williams, C. C., & Kayaoglu, A. (2020). The coronavirus pandemic and Europe’s undeclared economy: Impacts and a policy proposal. South East European Journal of Economics and Business, 15(1), 80-92.

