- Chapter: Matlab Horizontal And Vertical Alignment Assignment
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Background of Study
- 1.3 Research Aim
- 1.4 Research Objective
- 1.5 Research Questions
- 1.6 Research Rationale
- 1.7 Research significance
- 1.8 Research Framework
- 1.9 Conclusion
- Chapter 2: Literature Review
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Empirical Study
- Optimization of Earthmoving Activities Using Genetic Algorithms
- Application of Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning in Highway Construction Cost Prediction
- Automation in Construction Site Layout Planning Using BIM and Optimization Algorithms
- 2.3 Theories and Models
- 2.4 Literature Gap
- 2.5 Conceptual Framework
- 2.6 Conclusion
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Method outline
- 3.3 Research Philosophy
- 3.4 Research Approach
- 3.5 Research Design
- 3.6 Research Strategy
- 3.7 Research Method
- 3.8 Data Collection Method
- 3.9 Research Ethics
- 3.10 Research Limitations
- 3.11 Time Horizon
- 3.12 Research Onion
- 3.13 Conclusion
Chapter: Matlab Horizontal And Vertical Alignment Assignment
1.1 Introduction
With modern infrastructure development, the design of efficient and sustainable road networks is important. Automation of the road design process, especially the horizontal and vertical alignments, can solve the problem of time consuming manual calculations and suboptimal resource use. The objective of this study is to develop a MATLAB based earthwork optimization algorithm that will combine earthwork optimization to minimize construction costs and environmental impacts. Practical and innovative to road planning, the proposed solution balances cut-and-fill operations and complies with geometric and safety standard proportions. This research fills the gap between conventional methods and modern computational methods and provides the means for sound sustainable, cost efficient, and efficient road design conduct.
1.2 Background of Study
Transportation infrastructure is well represented by a road network design, which decisively determines the level of economic growth, connectivity and environmental sustainability. Without the benefits brought by the automatic design workflow, the road design process traditionally follows manual calculations and iterative processes, which is inefficient to time, cost and environmental impact. Road geometry, safety and overall construction feasibility greatly depends on horizontal and vertical alignment (Laali et al. 2022). Directly relating to earthwork, in particular the balancing of cut-and-fill operations, these alignments determine both the quantity and quality of earth removed, as well as the area of the next contiguous spoil site. Yet manual methods fail to deliver a best earthwork solution, driving up costs and degrading the environment. Automation has come as a drastic approach to solve these challenges due to the advancement in the computational tools and algorithms. However, the implementation of earthwork optimization techniques in road design processes using MATLAB as a powerful platform for numerical computation and optimization, can lead to creating a more efficient road design scheduling (Huang et al. 2022). Using computational models, road alignments are generated that meet engineering standards, reduce material handling and ecological disruption. This paper further develops the analysis by proposing a novel algorithm that automates the planning of horizontal and vertical alignment, with the additional objective of earthwork optimality. It is expected that the outcome will generate cost-effective and efficient, and environmentally friendly road designs for modern infrastructure projects.
1.3 Research Aim
This research aims to develop an automated MATLAB based algorithm for road design that combines horizontal and vertical alignment planning with earthwork optimization. Construction costs and cut and fill operations are minimized, environmental impacts are reduced, and engineering standards for efficient and sustainable infrastructure development are met.
1.4 Research Objective
- The development of an algorithm which may be used to automate the planning of horizontal and Vertical Alignment values.
- As a solution to the above problem, the following was carried out: To incorporate earthwork optimization in ROAD software using MATLAB.
- In order to assess the impact of the proposed algorithm in the context of cutting costs and environmental load.
1.5 Research Questions
- What form can the application of horizontal and vertical alignment planning take to be integrated using MATLAB?
- How can earthwork be effectively and efficiently done with respect to costs and impacts on the environment?
- How efficient is the current proposed algorithm in contrast to real urban road design?
1.6 Research Rationale
Due to this increasing demand for efficient, cost effective and environmentally sustainable road networks, the need for innovative design solutions is apparent. But traditional road design methods tend to be task-intensive, error prone, and inefficient at utilizing resources, all and often manually. Earthwork, a dominant feature of road development, has a significant influence on cost and ecology (Xiang et al. 2021). In poorly optimized earthwork, too much material is handled, waste is created, and environmental disruption occurs. Computational tools, such as MATLAB can now be used to automate and optimize road design processes to enable engineers to achieve better outcomes. This research addresses the inefficiency of conventional methods achieved by combining horizontal and vertical alignments planning with earthwork optimization (Zhao et al. 2024). The approach proposed in this thesis minimizes the construction costs, reduces the ecological impact, and is compliant within the engineering standards. Still relevant to a world trying to find sustainable means of transportation development, this research supports global initiatives in that regard.
1.7 Research significance
Significance of the research lies in the addressing of the critical inefficiencies in traditional road design process by proposing an automated approach for integrating earthwork optimization into horizontal and vertical alignment planning process. MATLAB based algorithm developed for the development of a cost effective and efficient solution that addresses the modern road design challenge of lowering construction costs, reducing materials waste and limiting environmental impact (Li et al. 2022). The research helps develop sustainable infrastructure by balancing cut-and-fill operations and meeting engineering standards, two considerations that become more important as the resource constrained and environmentally aware world grows. The results contribute to practical implications for engineers, policymakers, and transportation planners, and this can be used in designing roads that not only maximize efficiency, but also are environmentally responsible (Xu et al. 2022). The research also expands the realm of computational engineering by showing how automation can enhance traditional design approaches that will lead to greater innovation in infrastructure development in the future.
1.8 Research Framework
Figure 1: Research Framework
1.9 Conclusion
An important advancement in transportation engineering is the automation of road design, to combine horizontal and vertical alignment planning with earthwork optimization. A MATLAB based method is proposed to address inefficiency issues in traditional methods, resulting in lowering of construction costs, environmental impact and manual effort. The research aligns with modern engineering practices regarding sustainability, efficiency, and innovation, and leverages computational tools. The overall findings are intended to provide an economic framework for designing efficient and environmentally friendly road networks. The purpose, background, and significance of the study have been introduced in this chapter, with which the detailed exploration and implementation of the proposed algorithm have been secured in following chapters.
Struggling with deadlines? Turn to New Assignment Help for reliable Best Assignment Help that takes the pressure off and boosts your academic success.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
An analysis of the existing knowledge, methodologies and advancements in the field of automated road design and earthwork optimization constitute the main content of the literature review. It investigates the ideas concerning horizontal and vertical alignment planning, optimization procedures, and application of computational tools like MATLAB in infrastructure making. Previous studies document the shortcomings of conventional manual methods, for example in their insufficiencies to balance ability and cut and fill operations and shown environmental impacts. Research into genetic algorithms and linear programming algorithms shows their usefulness for improving road design processes. Furthermore, the review looks into the integration of the principles of sustainability in transportation engineering for environmental purposes. Through analysis of these studies gaps in existing research are created, suggesting that what is needed is a united, automated solution which integrates road design with earthwork optimization. The theoretical framework and technical foundations for the developed proposed MATLAB based algorithm are provided in this review.
2.2 Empirical Study
Optimization of Earthmoving Activities Using Genetic Algorithms
According to the authors Shehadeh et al. 2022, the earthmoving activities encompassed among the most critical and cost intensive components of construction projects and play a significant role in the total project cost budget. At the heart of the efficiency in terms of cost, time and environmental tradeoffs is the selection and use of the best equipment on earth, such as trucks and excavators. However, the earthmoving planning project has either been limited to the root cause by traditional methods or has been necessary leading to poor execution of the project. In order to address this issue optimization techniques with genetic algorithms (GAs) have become prominent. These algorithms provide a sound suite of paradigms to solve multi objective optimization problems, namely minimizing costs, diminishing project durations, and minimizing environmental stresses. A GA-based approach involves three main steps: This thesis will identify decision variables, develop a mathematical model, and apply an objective optimization technique. With this approach, key factors including number of equipment units and work capacity as well as travel speeds are optimized to desired outcomes. Because the model is so detailed, it enables project cost and timeline analysis as well as fuel consumption and carbon emissions analysis, and the engaging predictions can help inform contractors and project managers.
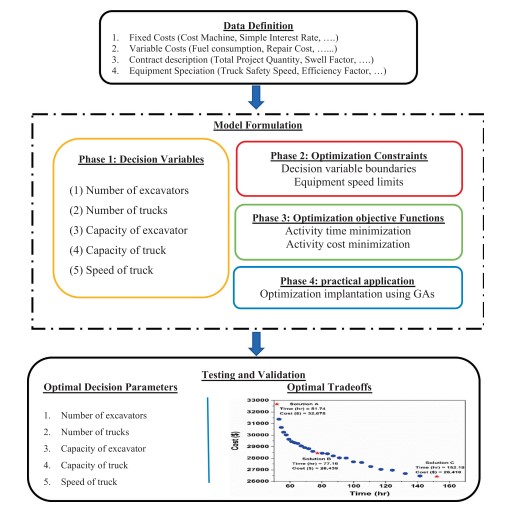
Figure 2: The proposed approach
The model is validated on real world projects and shows very significant cost and time savings and reductions in fuel usage and CO2 emissions. The improvements demonstrated by such advancements in GA based optimization show the efficacy of GA based optimization in achieving better decisions, better project sustainability and resolving environmental conflicts in construction. Integration of models such as these into planning practices allows the contractor and engineer to improve resource management and eliminate waste whilst aligning with global sustainability goals. The results demonstrate the usefulness of developing computational optimization strategies to advance the efficiency in earthmoving operations within construction projects.
Application of Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning in Highway Construction Cost Prediction
According to the authors Meharie et al. 2022, the accurate prediction of cost for highway construction projects is critically important both in terms of enabling stakeholders to plan adequate resources and reducing financial risks. Cost estimation is inherently complex and variable and traditional methods of cost estimation are usually unable to attain high accuracy measurements. Such challenges can be addressed through the use of machine learning techniques such as stacking ensemble models, and indeed this promising approach has been developed. The stacking ensemble models combine the predictive power of multiple base models including linear regression, support vector machines and artificial neural networks, to create a more robust and powerful predicting model. The stacking ensemble model maximizes the potential of each of individual model strengths, and this results in significantly lower prediction error, compared to its meta-regression such as gradient boosting algorithm. The approach also compares favorably to standalone models on critical performance metrics including root mean square error, improving accuracy and robustness.
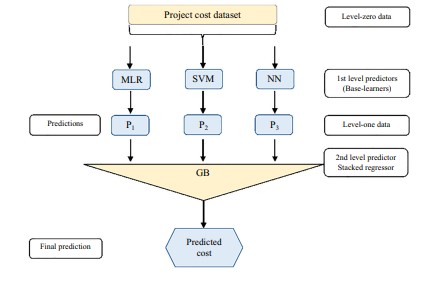
Figure 3: Proposed stacking ensemble model structure
The methodology allows precise forecasting of highway construction costs at those early stages of project planning when uncertainty is high. Moreover, the model effectiveness gives construction practitioners and estimators a valuable tool to cut the decision making costs, minimize the budgeting error and get better project outcomes. This study demonstrates the potential of computational models to transform the cost estimation practices in the construction industry by taking the advantage of advanced machine learning algorithms. These also help predict more accurately and in doing so, help optimize resources to complete construction projects on time and within budget. On real world data validation, the stacking ensemble model provides a glimpse into what future construction cost forecasting applications will look like, and how machine learning has taken on such an important role in construction engineering.
Automation in Construction Site Layout Planning Using BIM and Optimization Algorithms
According to the authors Yang et al. 2022, construction site layout planning plays a very significant role in construction management because it has a direct impact on the efficiency, cost and time of the project. Manual parameter extraction and configuration are time consuming and prone to human error, as most of the traditional CSLP methods are. As the advances of digital technologies continue, Building Information Modeling (BIM) with optimization algorithms are gaining its prominence as a revolutionary solution for the issue described above. BIM Digital representation of building components, which is a rich data source for optimizing the site layout. However, manually extracting parameters from BIM for optimization still constitutes a bottleneck. In order to simplify this process, an automated framework linking BIM and optimization algorithms like genetic algorithms (GA) or particle swarm optimization (PSO) is offered as a practical and effective solution. With these integration the Dynamo visual programming platform the integration of BIM and the optimization algorithms enables the exchange of data via an information channel.
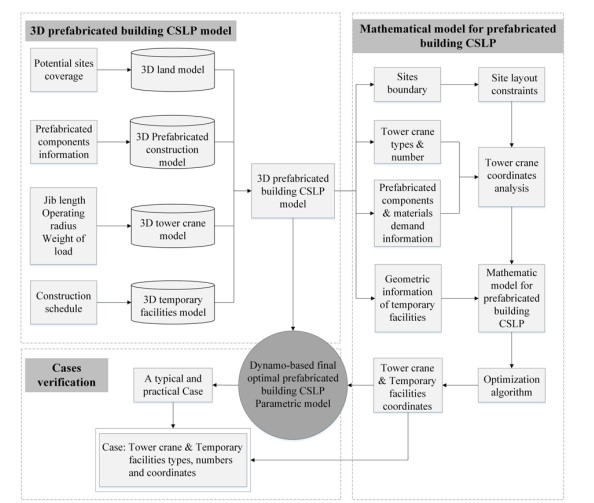
Figure 4: Framework of BIM-Based Automated Prefabricated Building CSLP System
This automated approach dramatically cuts toxic material transportation costs, improves allocation of resources, and eliminates unnecessary delays. This framework was presented through practical case studies that have shown its ability to improve efficiency and cost savings from prefabricated building site layouts. Complemented by automation, the use of advanced optimization techniques dwarfs the manual effort and inefficiencies of traditional methods, freeing construction managers to concentrate on higher level decision making. The findings foresee the effectiveness of combining BIM with optimization algorithms to change the perspective of site layout planning towards a revolutionary scalable and adaptive resolution for construction projects of the modern era. Not only does this integration improve project performance, this integration also corresponds with growing interest in digitalization and automation in construction helping set the stage for more efficient and sustainable construction site management practices.
2.3 Theories and Models
Optimization of Earthmoving Activities Using Genetic Algorithms
Earthmoving activity trades-off among cost and time can be effectively achieved via the multi objective optimization theory in construction projects while considering environmental issues. The principal approach to solve these complex problems is the Genetic Algorithms (GAs) which operate on the basis of natural selection. In this GA-based approach the decision variables, numbers of equipment units, work capacity and travel speed will be determined, mathematical model will be designed and optimization techniques will be used (Burggraef et al. 2021). Such a model is capable of determining the cost of all the projects, time frame, fuel consumption and carbon emissions and proves the efficiency of using a model of such a nature in resource management, minimization of wastage and aligning construction practices with the sustainable development agenda as enshrined internationally.
Application of Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning in Highway Construction Cost Prediction
This thesis applies the principles of stacking ensemble machine learning models and predictive modeling along with other superior computational methods to the establishment of highway construction cost prediction. While using stacking, several base learner models such as linear regression, vector support machines, and artificial neural networks are utilized and included in a single prediction. It performs better with less prediction error as compared to the standalone models using a Meta regression in a form of a gradient boosting model (Liu et al. 2022). This approach corresponds to the ensemble learning theory whereby it is said that should one want to build models of models, then he or she should make models which are different among themselves. The model also allow accurate cost prediction, efficient resource utilization, fewer mistakes, and positive project performance.
Automation in Construction Site Layout Planning Using BIM and Optimization Algorithms
Theories of optimization and digital integration provide support to the automation of construction site layout planning (CSLP). The model exploits the sketching tools amenities available in the humanities of Building Information Modeling (BIM) as a holistic digital representation of solid construction components coupled with optimization algorithms like genetic algorithms (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) (Nguyen, 2021). Theories under these approaches address the problem of increasing efficiency through reduction of resource allocation error and automated data extraction bottleneck. Platforms such as Dynamo are used to 'integrate' the BIM and the optimization algorithm via the information channel. This approach facilitates designing of scalable, adaptive solutions for efficient site layout planning compatible with the modern principles of digitalization and automation in construction.
2.4 Literature Gap
Although many have contributed to optimization techniques and digital tools for construction project management, there exist several gaps addressed missing in current literature. While a number of previous studies have investigated integration of genetic algorithms (GA), particle swarm optimization (PSO) and machine learning models for construction site layout planning, cost prediction, and resource optimization, these are applied to restricted contexts or are impractical to scale (Wei et al. 2022). As an example, existing models generally aim to minimize a single metric, for instance, cost or time, but do not consider environmental impacts or multi objective optimization. Additionally, although Building Information Modeling (BIM) is accepted as a transformative tool for construction management, it does not integrate the optimization algorithms in a fully automated manner from its features, which results in work that is awkward and cumbersome and resource intensive. The second space has a gap in the validation of these models in real projects because most studies are based on theoretical or small scale datasets that limit generalization of their findings (Xia et al. 2022). Second, stacking ensemble machine learning models are shown to be effective at improving the accuracy of cost prediction, but their application to early stage construction project planning has been underexplored. However, these gaps are addressed via the development of more automated, scalable, and validated models, which simultaneously integrate multiple optimization objectives, biophysical considerations, and sophisticated computational techniques to serve the needs of modern construction projects in an optimal way.
2.5 Conceptual Framework
Figure 5: Conceptual Framework
2.6 Conclusion
Finally, it argues that a shared use of advanced optimization techniques, machine learning models, and digital tools such as BIM can play an important role in formulating effective solutions to the most pressing issues in construction management. These technologies can improve site layout planning, cost prediction, prediction, and optimize resource use, and the efficiency improves and cost savings are realized in all of these activities. Although previous works reveal significant achievements, gaps exist in the automation, scalability, and real world validation. Closing these gaps will depend on the development of more comprehensive, multi-objective, and validated frameworks, exploiting the full potential of digitalization and the computational advancements that enable more efficient and sustainable construction practices.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Introduction
The planning and optimization of horizontal and vertical alignments in road construction are essential to effective, safe and economical road infrastructure. This thesis automates road alignment design using advanced algorithms incorporated in MATLAB and combines geometric parameters with earthwork optimization to provide the most efficient alignment solution. The developed algorithms utilize data driven methodologies to provide smooth transitions, minimal amount of earthwork and adherence to engineering constraints at the same time as optimizing radii, angles and curve lengths of both horizontal and vertical alignment. The implementation demonstrates a practical balance between computational precision and practical implementation, resulting in a full framework for automated road design. Application of this approach increases efficiency and sustainability in modern infrastructure projects.
3.2 Method outline
The approach involved in the proposed method is self-driving as it combines earthwork and alignments throughout the use of MATLAB. First of all, elementary information, for example, ground coordinates, slopes, or elevation profiles, may be multiple analyzed. The algorithm identifies various points, geometry of angles, radii and length of curves and positions them in manner that facilitate transition for horizontal alignment. Curves and optimised radii mitigate risk while maintaining construction functionality in regards to vertical alignment (Sushma et al. 2022). It has smoothing mechanism that fits selected points to a certain geometric constraints. In the optimization phase, curves are readjusted and points arranged making earthwork as close to zero as possible given the standard design parameters. Results are visualized and three main parameters, angles, radii and length of curved line are stored for iterations and finally output.
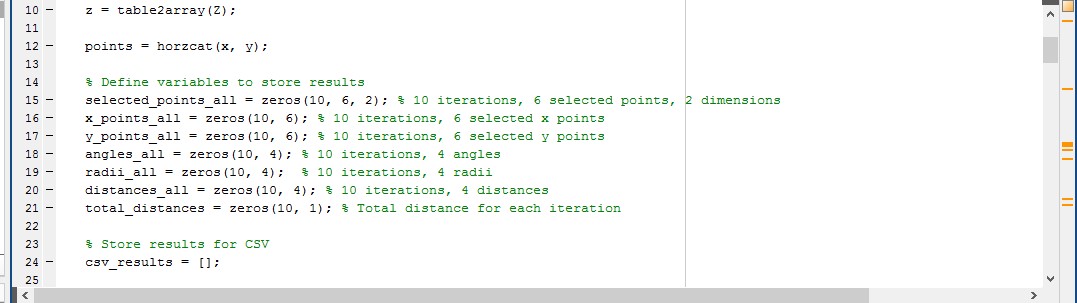
Figure 6: Automated Road Design Optimization
3.3 Research Philosophy
On the challenges of road design optimization the present research assumes pragmatic and data oriented philosophy. The systems solution fits the problem with mathematical models, algorithmic approaches and computational solving steps solutions that are not minimal isoperimetric solutions, but solutions that are workable in efficiency- accuracy-sustainability tradeoff. This is illustrated by the research where systematic methodology integrating theory with imposition of practical constraints in establishment of automated processes for horizontal and vertical alignment design is emphasized. A cycle of improvement allows for the creation of the proposed algorithms capable of expanding scale or range of constraints necessary for earthwork minimization to meet design conditions. By applying optimization and automation to the research, the processes encourage innovation and the future sound advancement of infrastructure by closing the existing gap between established road design practice and advanced numeric design applications.
3.4 Research Approach
It performs a systematic and computational approach which entail theoretical modeling accompanied by algorithm design. The work begins by gathering and preparing the terrain and elevation data as the base knowledge of road alignment. MATLAB models of both the horizontal and vertical alignment models which include the geometric principles, curve smoothing and optimisé radii are created. The strategy integrates grading and excavation algorithms which although they keep the design as ideal as possible they will minimize the amount of material transport needed as well as safety requirements (Alshboul et al. 2024). The model is tested through further simulations and data visualization and updated to yield the best results in each mode. The utilization of computational methods in combination with engineering thinking leads to a very stable and efficient, as well as highly practical approach to the automated road design optimization.
3.5 Research Design
The research design of the study leads to the development of a quantitative and computational framework for automation of road alignment solution. The data collection of terrain profiles, elevation, and geometric constraint data are then pre-processed in order to synchronize them for analysis. The horizontal alignment is made when looking at some important points, and determining appropriate radii and angles as well as good transitions; the vertical alignment is to blend curves and eliminate steep grades (Zhang et al. 2024). These processes are automatically run using MATLAB algorithms with earth work optimization techniques incorporated to reduce time, material transport, and construction cost. Simulations, iterative tests and visualization are used to corroborate and improve the models. It is important to note that this structured design also gives accuracy, efficiency and safety and describes all the engineering necessities.
3.6 Research Strategy
An automated road design framework development strategy is used based on the rationale of combining computational measures with engineering concepts. First, geomorphology and altitude are used in the identification of significant alignment locations. MATLAB algorithms search for horizontal and vertical alignments typically seeking perpendicular parallelism smooth transitional and safety requirements. To reduce the costs of the materials movement, earthwork optimization is performed to reduce material transport (Artar and Carbas, 2021). In fact the model is tested iteratively through simulation and testing and made more accurate for better results. This makes findings easier to interpret because they are embodied in data visualisation for usability in practical contexts. It is here this strategy is devised and formulated with due consideration to computational pragmatism, utility and relevance for real world application within the context of establishing symbiotic, optimised and efficient forms of conceptualisation of the contemporary road networks.
3.7 Research Method
The research method uses computations and algorithms in the road alignment process and automation of the process. The concepts that the ground work is founded on include forms such as data collection including terrain coordinates, elevation profiles, and geometric constraints. Other information essential in performing horizontal alignments includes angles, radii, and curve lengths needed to facilitate a smooth transition among these two points. Vertical alignment tries to achieve curves, gradients and bending radius for safe speed, resist constructiveness. To cut costs and lessen the quantity of spoil that must be transported, an earthwork optimization is provided while still maintaining structural integrity. With MATLAB algorithms are created, simulations performed, and outcomes shown. The calculated values of Tangent points, radius and curve length were verified and checked against design standards needed for practical purpose of the output because after several cycles of testing and getting improved values by variation guarantee the accuracy and scalabilities of the output.
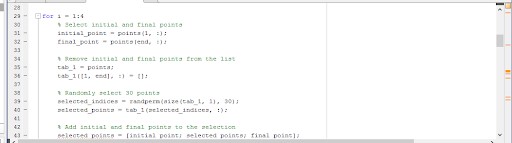
Figure 7: Earthwork Optimization
3.8 Data Collection Method
The data collection is done by gathering accurate and relevant inputs relative to automated road alignment design. Some terrain data such as coordinates, elevation profiles and slope are collected using geographic information systems (GIS), digital elevation models (DEMs) and field surveys. Detailed topographical insights are given through satellite imagery and LiDAR scans which measure with precision the elevation and slope. Alignment optimization is guided by secondary data such as road design standards and geometric constraints. Raw data is to some basic processing and is then refined for algorithmic processing using preprocessing techniques such as noise filtering and interpolation. Developing these algorithms requires reliable input data and this structured approach guarantees the reliability of the input data.
3.9 Research Ethics
Methodology and outcomes of research are based on strict ethical principles of integrity, transparency and sustainability. The data is collected from all known trustworthy sources, and it is accurate and follows the copyright and intellectual property laws. Integration of the environmental considerations into the road design process is also given top priority to arrive at the least ecological disruption and most sustainable construction practices. It designs algorithms and methods to mate with engineering standards to guarantee the public safety and welfare. The data selection and processing is not biased, therefore results are also objective. Methods and limitations are laid out for stakeholders, but keep the information transparent. This research upholds these ethical guidelines to ensure that research leading to these advancements is responsible, fair and socially beneficial to automated road design optimization.
3.10 Research Limitations
Several limitations of this research are acknowledged that may affect its scope and conclusion. The precision of the proposed algorithms can also be influenced by the dependence of the algorithms on the accuracy of the data (terrain profiles and elevation models) in regions where the data is not complete or outdated. However, computational models developed based upon predefined geometric and safety standards may not take into consideration all local variations or unanticipated constraints in the actual environment until it is too late (Castañeda et al. 2021). Optimization of earthwork commonly focuses on reducing movement of material, but ignores other practical considerations, such as soil stability and drainage requirements. Furthermore, the framework may need adaptation to large scale implementation in the MATLAB based method. To address these limitations they will need to draw on better data sources and wider field validation in future work.
3.11 Time Horizon
Figure 8: Time Horizon
3.12 Research Onion
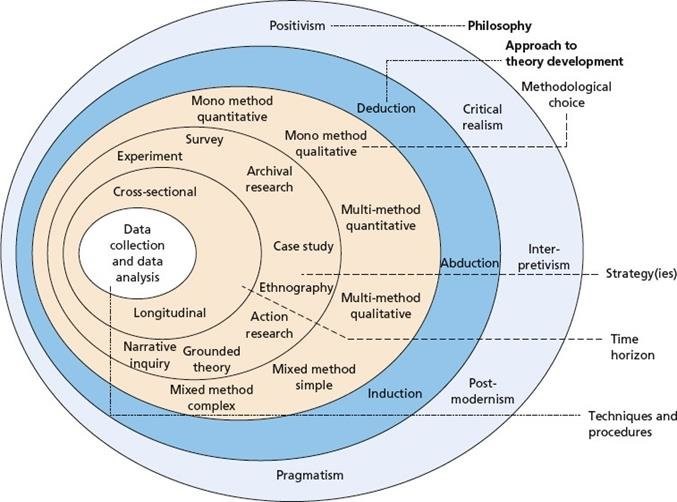
Figure 9: Research Onion
3.13 Conclusion
Finally, the presented research provides a computational framework to automate road alignment design with earthwork optimization to improve efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability in infrastructure building. The study has successfully utilized MATLAB algorithms to optimize these horizontal and vertical alignments to such a degree that there are smooth transitions as material moves from one alignment to the other, minimizing material movement, and maintaining adherence with engineering standards. The iterative methodology and data driven approach yield scalable and practical solutions to real world applications. In spite of certain limitations (data accuracy, local constraints), the research provides a solid basis for future research on automated road design. By overcoming these limitations, the proposed framework can make a substantial contribution towards developing safer, less expensive and more environmentally friendly road infrastructure projects.
Reference List
Journals
- Shehadeh, A., Alshboul, O., Tatari, O., Alzubaidi, M.A. and Salama, A.H.E.S., 2022. Selection of heavy machinery for earthwork activities: A multi-objective optimization approach using a genetic algorithm. Alexandria engineering journal, 61(10), pp.7555-7569.
- Meharie, M.G., Mengesha, W.J., Gariy, Z.A. and Mutuku, R.N., 2022. Application of stacking ensemble machine learning algorithm in predicting the cost of highway construction projects. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 29(7), pp.2836-2853.
- Yang, B., Fang, T., Luo, X., Liu, B. and Dong, M., 2022. A BIM-based approach to automated prefabricated building construction site layout planning. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 26(4), pp.1535-1552.
- Laali, A., Nourzad, S.H.H. and Faghihi, V., 2022. Optimizing sustainability of infrastructure projects through the integration of building information modeling and envision rating system at the design stage. Sustainable Cities and Society, 84, p.104013.
- Huang, M.Q., Zhu, H.M., Ninić, J. and Zhang, Q.B., 2022. Multi-LOD BIM for underground metro station: Interoperability and design-to-design enhancement. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 119, p.104232.
- Xiang, X., Liu, C., Lee, L.H. and Chew, E.P., 2021. Performance estimation and design optimization of a congested automated container terminal. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 19(3), pp.2437-2449.
- Zhao, Y., Lu, B. and Alipour, M., 2024. Optimized structural inspection path planning for automated unmanned aerial systems. Automation in Construction, 168, p.105764.
- Li, J., Liu, T., Wang, X. and Yu, J., 2022. Automated asphalt pavement damage rate detection based on optimized GA-CNN. Automation in Construction, 136, p.104180.
- Xu, B., Jie, D., Li, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, H. and Fan, H., 2022. A hybrid dynamic method for conflict-free integrated schedule optimization in U-shaped automated container terminals. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), p.1187.
- Zhang, J., Yang, X., Wang, W., Guan, J., Ding, L. and Lee, V.C., 2023. Automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots for recognition and tracking in civil engineering. Automation in Construction, 146, p.104699.
- Baduge, S.K., Thilakarathna, S., Perera, J.S., Arashpour, M., Sharafi, P., Teodosio, B., Shringi, A. and Mendis, P., 2022. Artificial intelligence and smart vision for building and construction 4.0: Machine and deep learning methods and applications. Automation in Construction, 141, p.104440.
- Zhang, Q., An, Z., Huangfu, Z. and Li, Q., 2022. A review on roller compaction quality control and assurance methods for earthwork in five application scenarios. Materials, 15(7), p.2610.]
- Zhang, F., Chan, A.P., Darko, A., Chen, Z. and Li, D., 2022. Integrated applications of building information modeling and artificial intelligence techniques in the AEC/FM industry. Automation in Construction, 139, p.104289.
- Burggraef, P., Adlon, T., Hahn, V. and Schulz-Isenbeck, T., 2021. Fields of action towards automated facility layout design and optimization in factory planning–A systematic literature review. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 35, pp.864-871.
- Liu, C., Wu, L., Huang, X. and Xiao, W., 2022. Improved dynamic adaptive ant colony optimization algorithm to solve pipe routing design. Knowledge-Based Systems, 237, p.107846.
- Nguyen, P.T., 2021. Construction site layout planning and safety management using fuzzy-based bee colony optimization model. Neural Computing and Applications, 33, pp.5821-5842.
- Wei, P., Yu, X., Di, Z., Dai, X., Wang, B. and Zeng, Y., 2022. Design of robot automatic navigation under computer intelligent algorithm and machine vision. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 28, p.100366.
- Xia, T., Yang, J. and Chen, L., 2022. Automated semantic segmentation of bridge point cloud based on local descriptor and machine learning. Automation in Construction, 133, p.103992.
- Sushma, M.B., Roy, S. and Maji, A., 2022. Exploring and exploiting ant colony optimization algorithm for vertical highway alignment development. Computer‐Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 37(12), pp.1582-1601.
- Garcia, J., Villavicencio, G., Altimiras, F., Crawford, B., Soto, R., Minatogawa, V., Franco, M., Martínez-Muñoz, D. and Yepes, V., 2022. Machine learning techniques applied to construction: A hybrid bibliometric analysis of advances and future directions. Automation in Construction, 142, p.104532.
- Alshboul, O., Shehadeh, A., Tatari, O., Almasabha, G. and Saleh, E., 2024. Multiobjective and multivariable optimization for earthmoving equipment. Journal of Facilities Management, 22(1), pp.21-48.
- Zhang, L., Li, Y., Pan, Y. and Ding, L., 2024. Advanced informatic technologies for intelligent construction: A review. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 137, p.109104.
- Artar, M. and Carbas, S., 2021, December. Discrete sizing design of steel truss bridges through teaching-learning-based and biogeography-based optimization algorithms involving dynamic constraints. In Structures (Vol. 34, pp. 3533-3547). Elsevier.
- Castañeda, K., Sánchez, O., Herrera, R.F., Pellicer, E. and Porras, H., 2021. BIM-based traffic analysis and simulation at road intersection design. Automation in Construction, 131, p.103911.

