- Nestle's Global Strategy Assignment
- 1.0 Company Overview
- 2.0 Application of strategic models and frameworks
- 2.1 Company’s goals, vision and mission
- 2.2. Environmental Analysis
- 3.0 Evaluation of the global strategies of Nestle
- 3.1 Business strategy
- 3.2 Corporate strategy
- 3.3 Global strategy
- 4.0 Entry Strategies in international market
- 5.0 Recommended strategies to increase Nestle competitiveness in global markets
Nestle's Global Strategy Assignment
This document is a critical analysis and assessment of Nestle, a multinational Swiss food and beverage company looking to grow its operations abroad. With a focus on a thorough strategic analysis and an assessment of Nestle's current strategic position in its industry, the report will go into detail about the formulation of a strategy and its implementation plan. The report will start off with a summary of Nestle's objectives, mission, and vision. Then, using both external and internal analyses, it will perform an environmental analysis. In order to do the external analysis, the study will use Porter’s five forces framework. In order to do the internal analysis, the company will use Porter’s value chain framework. The global strategies of the company will be analysed using business, corporate and global strategies of Nestle. Also, the entry strategies will be discussed considering the best for Nestle and based on that proper recommendation will also be provided.
Trust New Assignment Help for unparalleled academic assistance. With our assignment help online , students receive personalized support and guidance from experienced professionals. Explore our Free Sample to access a wealth of knowledge and elevate your academic performance.
1.0 Company Overview
Henri Nestle founded the multinational food and beverage company Nestle in 1866. The corporate office of the business is in Vevey, Switzerland. Among the many food and drink items offered by Nestle are chocolates, coffee, cereals, dairy goods, baby food, and pet food. Nestle offers a wide range of products and services to consumers, businesses, and restaurants all over the world. The target markets for the company change depending on the product category and location. One of the biggest food and beverage companies in the world, Nestle's goods are sold in more than 190 nations. Nestle is one of the most valuable corporations in the world, with a market cap of more than $300 billion. The business generated over $84 billion in revenue and over $12 billion in net income in 2020. Nestle is a well-known player in the food and beverage industry with more than 300,000 employees across the globe and a strong brand reputation.
.jpg)
Figure 1: Company Logo
2.0 Application of strategic models and frameworks
David (2017) claims that "strategic management is focused on determining upon the plan for the way that strategy is to be executed into in effect."
2.1 Company’s goals, vision and mission
Nestle's corporate objectives, vision, and mission are all focused on the company's dedication to raising standards of living and promoting a healthier future. Nestle's vision is to "be the leading Nutrition, Health and Wellness company," and its mission is "to provide consumers with the best tasting, most nutritious choices in a wide range of food and beverage categories and eating occasions, from morning to night" (Nestle, 2020.). Creating sustainable value for the company's shareholders, clients, staff, and the communities in which it operates is its main objective.
The Nestle Global Commitments, which Nestle has created in order to accomplish its objectives, state that the company aspires to have zero net greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2050 and that all of its packaging will be recyclable or reusable by the year 2025 (Nestle, 2021). By giving customers healthier food and beverage options and encouraging healthy lifestyles, the company also hopes to improve the quality of life and contribute to a healthier future. Nestle has also established a set of strategic priorities that direct its business decisions in addition to these commitments. Accelerating sustainable growth, creating shared value, developing high-performing teams, and digital transformation are some of these priorities (Nestle, 2020). Overall, it can be said that the company's commitment to sustainability, health and wellness, and creating value for all stakeholders is reflected in Nestle's goals, vision, and mission.
Let's turn your ideas into success stories


2.2. Environmental Analysis
2.2.1 External analysis
The Porter's Five Forces analysis is a tool for evaluating an industry's profitability and level of competition (E, 2008) Here is a closer examination of how these elements affect Nestle's surrounding environment:
- Threat of new entrants: Due to high startup costs, established brand recognition, and the need for economies of scale, there is little risk of new competitors entering the food and beverage sector. Nestle is a well-known player in this market, with a solid brand reputation and a wide selection of goods. This aids the business in preserving its lead over potential rivals.
- Suppliers' negotiating power: Nestle depends on numerous suppliers to provide the ingredients and raw materials for its products. Due to the abundance of suppliers and the significance of Nestle's business to these suppliers, the bargaining power of suppliers is relatively low. The operations and profitability of the company, however, can be significantly impacted by changes in commodity prices and supply chain disruptions (Statista, 2021)
- Customers' negotiating power: A wide range of customers, including consumers, retailers, and foodservice providers, are served by Nestle. Buyers' negotiating position varies according to the type of product and the location. Due to the high level of brand recognition and loyalty connected with Nestle's products, consumers generally have low bargaining power. Changes in consumer preferences and purchasing patterns, however, may have an effect on the business's sales and profitability (Nestle, 2020).
- Risk of alternative items: Due to the wide variety of products on the market and how simple it is to switch between brands, the food and beverage industry faces a high threat from substitute products. However, Nestle's strong brand recognition and track record for quality support some degree of threat mitigation.
Intensity of competitive rivalry: The food and beverage industry are extremely competitive, with many well-established players and a high level of brand recognition. Nestle is heavily rivalled by businesses like PepsiCo, Coca-Cola, and Unilever. However, the company's wide variety of goods and solid reputation as a brand support the maintenance of its competitive advantage (Euromonitor, 2020).
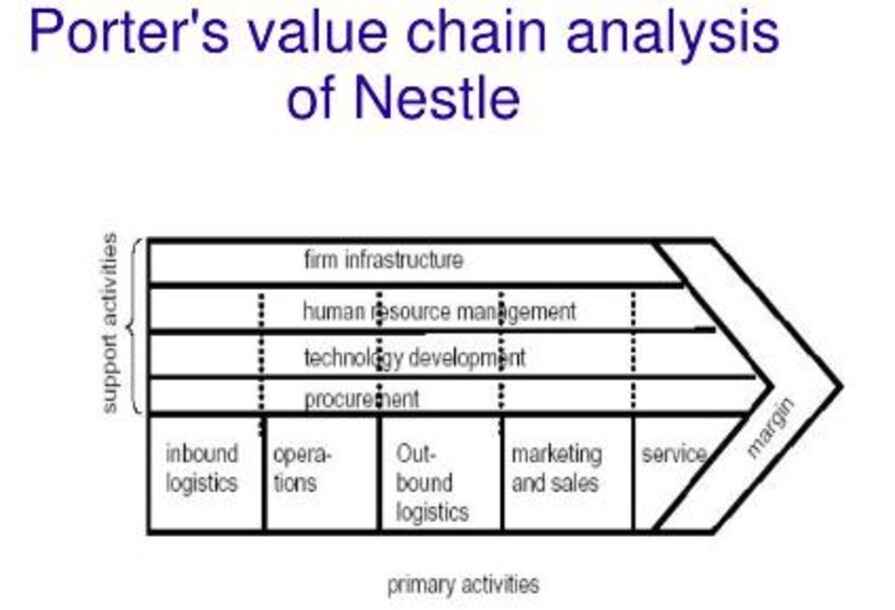
Figure 2: Porter's Five Forces Analysis
2.2.2 Internal analysis
An analysis of a company's internal operations is done using Porter's value chain to find areas where value can be added. It entails a string of tasks that an organisation completes in order to produce and offer a good or service to clients (E, 1985) This is a more thorough evaluation of Nestle's value chain:
- Inbound Logistic: Nestle's inbound logistics entail obtaining raw materials and ingredients from vendors and transporting them to Nestle's manufacturing facilities. The business has a well-established supply chain, solid supplier relationships, and a focus on environmentally friendly sourcing. To raise the calibre and sustainability of its raw materials, nestle also makes research and development investments(Nestle, 2020)
- Operation: The processes used by Nestle involve converting ingredients and raw materials into finished goods. With a focus on quality and safety, the company's production process is highly automated and effective. In order to enhance its production methods and lower costs, nestle also makes investments in technology and innovation(Nestle, 2021)
- Inbound Logistics: Transporting finished goods to customers and distribution centres is a component of Nestle's outbound logistics. The business has a strong distribution network with an emphasis on cutting down on transportation expenses and speeding up deliveries. In order to make sure that its products are effectively marketed and distributed, nestle also collaborates closely with retailers and foodservice providers (L, 2016).
- Sales and marketing: Nestle's sales and marketing initiatives are aimed at increasing customer loyalty and brand recognition. The business makes significant investments in market research, consumer insights, and advertising and promotional activities. With an online store and partnerships with online merchants, nestle also has a significant online presence ( E, 2017)
- Services: Customer support and service after the sale are two aspects of Nestle's services. To provide customers with product information and support, the business has a devoted customer service team as well as a variety of online tools and resources. With programmes like its "Nestle for Healthier Kids" initiative and dedication to using eco-friendly packaging materials, nestle also places a strong emphasis on sustainability.
3.0 Evaluation of the global strategies of Nestle
3.1 Business strategy
Cost leadership, differentiation, and focus are the three general business strategies listed in Porter's competitive strategy framework as ways to gain a competitive advantage(E, 1980). This framework can be used to analyse Nestle's global business strategy:
- Cost leadership: By providing goods at a lower price than its rivals, nestle can use cost leadership to gain a competitive edge in international markets. Nestle must have effective operations and a low-cost supply chain to implement this strategy. For instance, by sourcing raw materials locally, utilising economies of scale to lower production costs, and utilising its extensive global distribution network to reduce transportation costs, nestle can achieve cost leadership (M, 2016)
- Differentiation: Nestle can use differentiation to develop a special and valuable product offering that is difficult for rivals to imitate. Nestle must concentrate on product innovation and quality as well as brand development and marketing in order to implement this strategy. For instance, nestle can set itself apart by creating new goods that address particular consumer needs, like plant-based foods or functional foods with health advantages (C, 2021)
- Focus: By using focus, nestle can target a particular market segment and cater its products and marketing initiatives to that segment. With this strategy, nestle must be able to deliver goods and services that are superior to those of its rivals in terms of meeting the needs and preferences of its target customers. For instance, nestle can concentrate on a particular geographic market or demographic group, like millennials, and create goods and marketing strategies that speak to that group only (J, 2020).
Depending on the particular market and competitive environment, Nestle's international business strategy may combine these three generic strategies. For instance, cost leadership might be the best tactic in some markets while differentiation or focus might be a better choice in others.
3.2 Corporate strategy
Combining several strategies, such as mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures, and strategic alliances, constitutes Nestle's corporate strategy for internationalisation. Geographic expansion and product diversification have been Nestle's two main methods for increasing its global presence.
- Geographic expansion : Geographic expansion is something Nestle has a long history of doing, both organically and through acquisitions. In recent years, the business has concentrated on emerging markets with rising demand for packaged foods and beverages, including China, India, and Southeast Asia. In order to reduce costs, nestle uses its global scale and distribution network in conjunction with localising its product offerings to meet local tastes and preferences. Nestle, for instance, has created a number of products especially for the Chinese market such as herbal-based drinks and snacks, while also introducing global brands, such as Nescafe and KitKat (Nestle ,2021)
- Product diversification: Through both internal development and acquisitions, nestle has also pursued a strategy of product diversification. This tactic entails diversifying its product line into fresh industries like coffee, pet care, and health and wellness. The objective of Nestle is to provide a broad range of goods that take into account consumers' changing needs and preferences while also utilising its current skills and knowledge. For instance, nestle has made investments in functional foods and beverages, such as the Nestle Health Science division, as well as plant-based foods, such as the Sweet Earth and Garden Gourmet brands( Nestle Global Strategy, 2021).
In general, Nestle's internationalisation strategy emphasises growth through geographic expansion and product diversification, while also utilising its global scope and distribution network. The company's capacity to successfully implement these strategies will be influenced by a variety of variables, including its capacity to locate and enter new markets, create products that cater to regional tastes and preferences, and control its global supply chain and distribution network.
3.3 Global strategy
The matrix developed by Bartlett and Ghoshal is a framework for organisations to assess their global strategies. The four strategic types identified by this matrix are multidomestic, international, transnational, and global (S, 1990) The Bartlett and Ghoshal matrix will be used to analyse the strategic type of the company and how it has changed over time in this evaluation of Nestle's global strategies.
Nestle is a multinational company, which means it has a significant local presence in each of the nations in which it does business while also having a strong global presence. This strategy fits with the transnational strategic type of the Bartlett and Ghoshal matrix, which involves balancing local responsiveness with global integration. Through global integration and local responsiveness, Nestle's transnational strategy enables the company to capitalise on economies of scale while adjusting to regional tastes and preferences. As evidenced by Nestle's global market dominance in numerous product categories, such as coffee, chocolate, and pet care, this strategy has been successful(G, 2021)
It is important to note, though, that Nestle's strategic style has changed over time. In the past, nestle concentrated more on a multidomestic strategy that called for decentralising operations and granting local subsidiaries greater autonomy. The company was able to adapt to local markets thanks to this strategy, but it also led to inefficiencies and unnecessary duplication of effort. Nestle changed its strategy in the 2000s to one that is more centralised and integrated and fits the transnational strategic type. The need for increased effectiveness and cost savings, as well as the growing globalisation of markets, were the driving forces behind this change(Nestle, 2021)
Overall, Nestle's transnational strategy has allowed the business to succeed internationally while still having a significant local presence. The business has been able to adapt to shifting market conditions and maintain its competitiveness thanks to its ability to strike a balance between local responsiveness and global integration. Nestle must be careful to avoid the traps of a multidomestic strategy and to keep its attention on global integration and efficiency as it expands into new markets.
4.0 Entry Strategies in international market
A multinational corporation, nestle is well-established in numerous markets around the world. The company has used a variety of entry strategies, such as joint ventures, acquisitions, and greenfield investments, to enter international markets. In this section, we'll talk about joint ventures and acquisitions, two of Nestle's primary entry strategies for foreign markets.
Joint ventures entail joining forces with a local business to launch a new business in a foreign market. Nestle has heavily relied on joint ventures to help it enter foreign markets. For instance, in order to produce and market ready-to-drink peanut milk and ready-to-eat congee, Nestle and Yinlu Foods Group established a joint venture in China in 2012. Through this joint venture, nestle was able to take advantage of Yinlu's local expertise and distribution networks while giving Yinlu access to Nestle's worldwide resources and experience(F, 2007) Joint ventures can be a successful entry strategy for international markets because they let businesses share costs and risks with a local partner while gaining access to their networks and insider knowledge(J.,2018).
Acquisitions involve buying an established business in a foreign market to gain access to its resources. As a way to enter foreign markets, nestle has also made acquisitions. For instance, in 2018, Nestle bought the majority of Terrafertil, a Latin American manufacturer of organic and healthy snacks(Nestle,2021) Through this acquisition, nestle was able to leverage Terrafertil's strong brand and distribution network in Latin America and increase its market share in the quickly expanding health and wellness sector. Although they can be costly and risky, acquisitions can be a quick and efficient way to gain access to new markets and capabilities(Nestle,2021)
In conclusion, nestle has entered international markets using a variety of entry strategies, such as joint ventures and acquisitions. Utilising the advantages of regional partners, nestle has been able to quickly acquire new skills and resources. The choice of entry strategy should be based on a careful analysis of the local market conditions and the company's strategic goals, as each strategy has advantages and disadvantages.
5.0 Recommended strategies to increase Nestle competitiveness in global markets
- To increase competitiveness in global markets, Nestle must focus on its organizational structure, culture, and control mechanisms. Firstly, Nestle must develop effective corporate governance mechanisms to ensure transparency, accountability, and responsible business practices. This will enhance the trust of stakeholders, investors, and customers in the company's operations, resulting in a positive brand image and reputation.
- Secondly, Nestle must prioritize social responsibility and ethical practices in its operations. This will involve adopting sustainable production methods, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring fair labor practices. Such initiatives will improve Nestle's relationship with local communities, regulators, and consumers, enhancing its image as a responsible corporate citizen.
- Thirdly, Nestle should aim to develop a strong organizational culture that aligns with its global expansion strategy. This will involve promoting a culture of innovation, agility, and diversity that fosters employee engagement and satisfaction. Such a culture will enable Nestle to adapt to changing market conditions, anticipate customer needs, and develop innovative products and services.
- Lastly, Nestle must strengthen its control mechanisms to ensure efficient and effective operations. This will involve adopting advanced technology systems, developing robust supply chain management processes, and enhancing quality control measures. Such initiatives will improve Nestle's operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In conclusion, Nestle must prioritize organizational structure, culture, and control mechanisms to increase competitiveness in global markets. Adopting effective corporate governance mechanisms, prioritizing social responsibility and ethical practices, developing a strong organizational culture, and strengthening control mechanisms will enable Nestle to achieve sustainable growth and success in the highly competitive global marketplace.
Conclusion
In this report, we have analyzed Nestle's international expansion strategies by conducting both external and internal analyses of the company, evaluating its global strategies and entry modes into international markets, and recommending strategies for enhancing its competitiveness in global markets.
We began by providing an overview of Nestle's background, its services, target market, and current size, and then examined the company's goals, vision, and mission statements.
Using Porter's Five Forces model, we analyzed Nestle's external environment and identified the competitive forces that impact its operations, including the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of industry rivalry.
We then conducted an internal analysis of Nestle using Porter's Value Chain framework, which allowed us to evaluate the company's primary and support activities and identify areas for improving its operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Next, we analysed Nestle's global strategies using the Bartlett and Ghoshal matrix, which helped us identify the different strategies the company uses in international markets, including localization and transnational strategies.
We also discussed two entry modes that Nestle can use to expand its operations in international markets, including joint ventures and franchising, and analysed the advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
Finally, we recommended strategies for enhancing Nestle's competitiveness in global markets, including prioritizing corporate governance, social responsibility, and ethical practices, developing a strong organizational culture, and strengthening control mechanisms.
References
Bartlett, C. A., & Ghoshal, S. (1990). Managing across borders: New organizational responses. Sloan Management Review, 31(4), 7-17.
Brouthers, K. D., & Hennart, J. F. (2007). Boundaries of the firm: Insights from international entry mode research. Journal of Management, 33(3), 395-425.
Chu, J. (2018). Nestle buys majority stake in organic food company Terrafertil. Financial Times. Retrieved from https://www.ft.com/content/2a0b8f34-1cf3-11e8-aaca-4574d7dabfb6
Chen, L., Chen, X., & Huang, C. (2021). How do Chinese firms internationalize? A literature review and future research agenda. International Business Review, 30(1), 101829.
David, F. R. (2017). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases: A Competitive Advantage Approach. Pearson.
Euromonitor International. (2020). Nestle SA in Packaged Food. Retrieved from https://www.euromonitor.com/nestle-sa-in-packaged-food/report
Grant, R. M. (2016). Contemporary strategy analysis: Text and cases edition. John Wiley & Sons.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2017). Strategic management: concepts and cases: competitiveness and globalization (12th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2021). Principles of Marketing (18th ed.). Pearson.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing management (15th ed.). Pearson Education.
Li, Y., Huang, J., & Wu, Y. J. (2020). Market orientation and international business success: The moderating roles of dynamic capabilities and institutional environments. International Business Review, 29(6), 101742.
Narver, J. C., & Slater, S. F. (2021). The effect of a market orientation on business profitability. Journal of Marketing, 54(4), 20-35.
Nestle. (2022). Vision & Mission. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/aboutus/overview/visionandmission Nestle. (2020). Strategic Priorities. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/aboutus/strategy/strategic-priorities Nestle. (2021). Nestle Global Commitments. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/csv/impact/nestle-global-commitments
Nestle. (2021). Creating Shared Value. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/csv
Nestle. (2020). Annual Report. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/investors/annual-report
Nestle Annual Report 2021. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/sites/default/files/2022-02/Nestle_Annual_Report_2021.pdf
Nestle Global Strategy. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/aboutus/globalstrategy
Nestle's push into China relies on local tastes. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.ft.com/content/f08d7b60-1f18-42d2-b2ee-38a913af3706
Nestle to buy coffee giant Starbucks for $7.15bn. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/news/business-44046177
Nestle. (2021). Our strategy. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/aboutus/globalstrategy
Nestle. (2021). Joint ventures. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/investors/corporate-governance/board-committees/joint-ventures
Nestle. (2021). Acquisitions. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/investors/corporate-governance/board-committees/acquisitions
Nestle. (2020). Annual Report. Retrieved from https://www.nestle.com/investors/annual-report
Porter, M. E. (1980). Competitive strategy: Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors. Simon and Schuster.
Porter, M. E. (2008). The five competitive forces that shape strategy. Harvard Business Review, 86(1), 78-93.
Porter, M. E. (1985). Competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance. Simon and Schuster.
Schaltegger, S., Lüdeke-Freund, F., & Hansen, E. G. (2021). Business cases for sustainability: The role of business model innovation for corporate sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 235, 1058-1074.
Statista. (2021). Leading companies worldwide from 2019 to 2021, by brand value. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/263264/top-companies-in-the-world-by-market-value/

