Introduction - RES7002 Research Methods Empirical Assignment Sample
Pro-social behaviour plays an important role in an individual’s life, as helping people is a good practice in life. Helping people arouses the feeling of contentment within oneself and promotes life satisfaction. When an individual helps another individual, then it creates a sense of well-being, which contributes to the life satisfaction of the individual. Several research is conducted on pro-social behaviour and life satisfaction, which significantly show the relationship between the two factors. Engaging in generosity like helping people and building connections with them can present new opportunities for the persons.
Discover the difference a professional Assignment Helper can make! From research to final submission, we're with you every step of the way toward academic success.
A positive relationship is shown between the variables which shows that helping others triggers positive emotions in the individuals such as happiness, pride, and gratitude. These positive emotions are very useful in playing an essential role in individuals’ lives to promote life satisfaction. Several studies show that spending time helping others is related to emotional benefits for the person who helps. Additionally, several studies suggest that the relationship between helping and well-being appears to be strong in the setting of building trust.
The research aims to find out the relationship between pro-social behaviours and life satisfaction, and how helping others can enhance satisfaction over life. The research will be done through survey analysis and statistical analysis. The importance of pro-social behaviours in daily life will be assessed how adopting the good practice of pro-social behaviours can help people to come out of depression and anxiety will be analysed.
Method
Participants
The data for the research were collected from eighty participants, these participants were both male and female. The highest range of the participants was recorded at 50 and the lowest range was 18. The data were taken from different countries such as the United Kingdom, Singapore, Denmark, the United States, France, Japan, Australia, and Spain. The target participants for this research were divided into strangers and in-game peers. Among the 80 participants, the total number of male participants was 43 and the total number of female participants was 37. The data was collected through a random sampling method as it helps to show a representative sample from a large population. Choosing people randomly can be beneficial to reduce the chances of personal biases in the research (Ahmed, 2024).
Design
To conduct the research systematically, an experimental research design was followed for researching as it is one of the suitable research designs to find the cause-and-effect relationships. In the experimental research design, the independent groups design was followed, as people from different countries participated in the research. The demographic of the participants was not the same. In this research, the independent variable is pro-social behaviour, and the dependent variable is life satisfaction. The effect of pro-social behaviour over life satisfaction was tested in this research. To specify the gender of the participants, the number 1 was used to specify the male participants, and the number 2 was used to specify the female participants. The conditions were applied as giving rewards for helping the people and not rewarding people for help. This acted as motivation to the genders, The number 1 represented the reward value, and the number 2 represented the non-reward value.
Materials
The research was done by following a survey method, and different measuring scales were used to measure the values of the variables. A total of 80 participants were valid in this research who belonged to different countries. The three categorical variables used in the research were the participant’s gender, targeted pro-social behaviour, and motivational pro-social behaviour. The continuous variables were life satisfaction and baseline satisfaction. A total of 7 questions were used in the survey. The highest value in the life satisfaction variable was 35 and the lowest value was 14. The highest value in the life satisfaction variable was 29 and the lowest value recorded was 8.
Procedure
The survey method was followed to conduct the research by sending the invitation to the participants through different online platforms. In this regard, a Google form was used containing all the questions, and then the form was sent to the participants using social media platforms. The participants were assured that hiding their information was not sharing their information with another party through informed consent. It is the responsibility of a researcher to be careful about the participant's information. This is one of the ethical considerations that must be followed in conducting research (Drolet et al., 2023). The participants were assured that completing the questionnaire would not take much time but another few minutes of the participant's responses.
Results
Parametric assumption checks
Descriptive Statistics
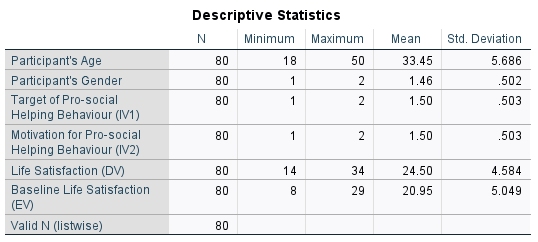
Figure 1: Descriptive Statistics
Figure 1 demonstrates that the means of the data points of pro-social helping behaviors in both targeted and motivation (1.50) are higher than their corresponding standard deviations (0.503). This highlights that the data points are clustered around their mean positions and are not skewed which demonstrates a more stringent distribution of the data. Similarly, the mean value of life satisfaction and the baseline life satisfaction which is an explanatory variable have higher mean values (24.50, 20.95) than their standard deviations (4.58, 5.04) highlighting that the data points are not spread wide apart. This also highlights that the life stratification of the participants is superior as their mean values are more towards the maxim values.
Correlation
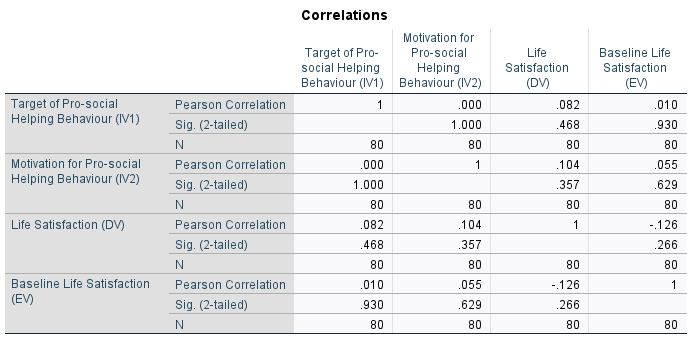
Figure 2: correlation statistics
Figure 2 demonstrates the output of the correlation where it is reflected that the target of pro-social helping behaviour is less correlated with life satisfaction (r=0.082). Therefore, the relationship between these variables is positive but weak and also non-significant as the significance or p-value (0.468) is higher than 0.05. In comparison, the motivation for pro-social helping behaviors is more positively correlated with life satisfaction (0.104). However, their p-value resulted in 0.357 which is greater than the usually accepted alpha level of 0.05 thereby underscoring a non-significant relationship.
Regression
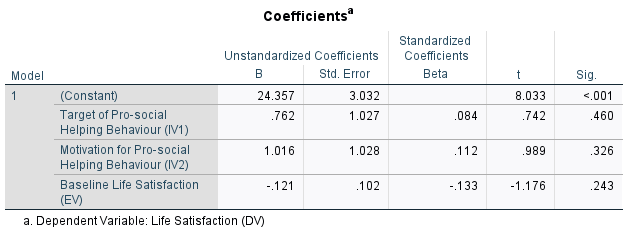
Figure 3: regression statistics
Figure 3 demonstrates the output of the regression statistics where the model summary reflects the correlation coefficient (R) and coefficient of variance (R-squared). The R-value (0.188) indicates a positive and weak direction of the relationship among the variables. The R-squared value reveals that only a 3.5% variance can be explained in the life satisfaction by the pro-social helping behaviors (target and motivation). In addition, the ANOVA output suggests that the significance of this result is 0.433 which is greater than the standard p-value of 0.05. Therefore, the results in not statistically significant. This further indicates that the independent variables are not the significant predictors of the dependent variable (stats.oarc.ucla.edu, 2025).
On the other hand, the coefficient (undersized B) values of target and motivation for pro-social helping behaviour are 0.762 and 1.016 respectively which are also not statistically significant as the p>0.05 in both cases. Therefore, the predictors are not statistically significant to predict any changes in the life satisfaction of the participants in the sample population.
Independent t-test
Hypothesis
H0: there is no statistically significant difference in life satisfaction between the target of pro-social helping behaviour and motivation for pro-social helping behaviour.
H1: there is a statistically significant difference in life satisfaction between the target of pro-social helping behaviour and motivation for pro-social helping behaviour.
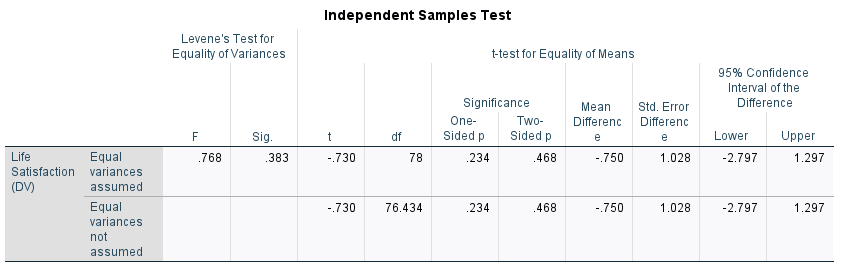
Figure 4: Independent t-test
In Figure 4, the independent t-test discloses that the significance (two-sided p) value is 0.468 > 0.05. This highlights that the observed differences in the mean values of strangers (24.13) and in-game peers (24.88) are not statistically significant.
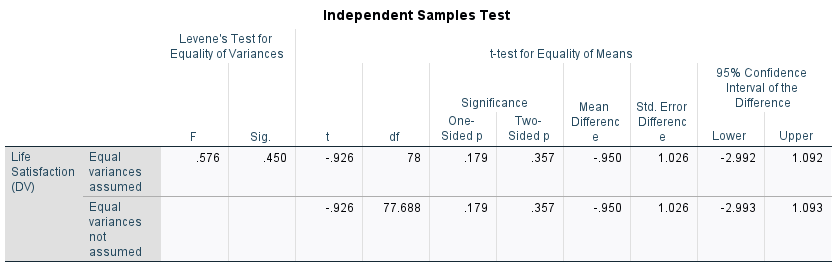
Figure 5: Independent t-test
In Figure 5, the two-sided p-value in the independent t-test is 0.357 which is greater than 0.05. This emphasizes that the observed differences in the mean values of rewards (24.03) and non-rewards (24.98) are not statistically significant. Therefore, the null hypothesis is retained and there is no significant difference in the life satisfaction between the target and motivations for pro-social helping behaviour.
Discussion
The research aimed to find the effect of the independent variable pro-social behaviour on the dependent variable life satisfaction. To conduct the research the experimental research, in which the independent group design was followed. To find out the effect of the independent variable over the dependent variable, these research designs are the most suitable methods. The statistical analysis method was followed in which the regression, correlational, and descriptive analytics were followed to find out the relationship between the variables. It showed that these two variables are strongly connected, so the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable is greatly impacted. Statistical analysis is a beneficial analytics method to enhance the decision-making of the researchers.
To test the hypothesis the T-test was followed, as it is the easy way to test the different types of data. There are no important differences in life satisfaction between the target of pro-social helping behaviour and motivation for pro-social helping behaviours. A significant statistical difference was found in life satisfaction between the target of pro-social helping behaviour and motivation for pro-social helping behaviour. To test a large data set, a t-test might be not enough, which represents the limitation of the research (Akpan & Clark, 2023). Statistical analysis may not be enough to represent a satisfactory result and sometimes can lead to bias within the researcher. The limitation of the survey method is that it can be manipulated sometimes and using online surveys has the possibility of harming the personal data of the participants. Being careful about the sample size and thorough analysis of each step can resolve the issue and being careful about using the surveys online can be beneficial in fixing the issues that can lead to manipulation of the research.
Conclusion
The effect of pro-social behaviour on life satisfaction is tested in this research by collecting data from 80 participants through the survey method. To examine the values of the variables the statistical analytics methods were followed, and the hypothesis was tested with the help of the t-test. A strong relationship was recorded within the variables.
References
- Ahmed, S. K. (2024). How to choose a sampling technique and determine sample size for research: a simplified guide for researchers. Oral Oncology Reports, 12, 100662. Retrieved on: 12th February 2025 from: https://hal.science/hal-04718988/
- Akpan, E. E., & Clark, L. J. (2023). Independent T-Test Statistics: It’s Relevance in Educational Research. Int. J. Eminent Sch, 10, 79-88. Retrieved on: 12th February 2025 from: https://mail.globalacademicstar.com/download/article/independent-t-test-statistics-it-s-relevance-in-educational-research.pdf
- Drolet, M. J., Rose-Derouin, E., Leblanc, J. C., Ruest, M., & Williams-Jones, B. (2023). Ethical issues in research: Perceptions of researchers, research ethics board members and research ethics experts. Journal of Academic Ethics, 21(2), 269-292. Retrieved on: 12th February 2025 from:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10805-022-09455-3
- stats.oarc.ucla.edu, (2025). Regression Analysis. Retrieved on 12th February 2025 from: https://stats.oarc.ucla.edu/spss/output/regression-analysis/#:~:text=If%20the%20p%2Dvalue%20were,reliably%20predict%20the%20dependent%20variable.

