- Introduction Of Strategic Management Assignment
- Definition of strategic management
- A critical assessment of the process used by organizations to determine their strategy
- A critical evaluation of the impact of internal and external environmental variation on organizational strategy
- A review of an organization’s strategic plan (Business Plan), providing an action plan for the organization based on a change in either the internal OR external environment
Introduction Of Strategic Management Assignment
Need expert guidance for your assignments? Look no further than New Assignment Help. Our online assignment help is designed to meet the unique requirements of students across various disciplines. Utilize our Free Sample to hone your skills and ace your academic tasks.
Strategic management can be described as a procedure of preparing, executing, and evaluating business objectives to attain a sustainable competitive advantage. Further, the report is based on Tesco, and there is a discussion about the critical assessment of the procedure used by them for analyzing their strategy. In addition to this, an evaluation of the effect of internal and external aspects on the strategy of the business is also necessary (Fuertes, and et.al., 2020). At last, it covers the strategic plan of the business based on the changes that occurred in the internal or external environment. The use of PEST and VRIO helps Tesco understand the impact on business.

Figure 1: Tesco
Definition of strategic management
Strategic management is determining the most effective ways to achieve long-term goals and objectives for an organization. It entails analyzing internal and external factors, trying to identify advantages and disadvantages, and formulating strategies to capitalize on prospects and mitigate threats (Clauss et al., 2019). Strategic management also entails choosing resource distribution, organizational structure, and core skill building. The ultimate objective of strategic management is to guarantee the organization's long-term achievement and viability by aligning its operations with its goals and principles and adapting to environmental changes. Organizations can use efficient strategic management to align their assets and skills with their aims, recognize and seize opportunities, and react promptly to shifts in the economic climate.
It also aids in the establishment of a straightforward mission and intent for the organization, as well as the promotion of a heritage of constant enhancement and creativity (Bogers, and et.al., 2019). Generally speaking, strategic leadership is a vital component for any organization that needs protracted accomplishment in a competitive industry. Needs a huge understanding of the internal and external environment of an organization for anticipating and adopting certain changes in the marketplace. Setting targets and goals, undertaking a SWOT analysis, planning, operating the system, and keeping tabs on efficiency are all basic processes in strategic administration.
A critical assessment of the process used by organizations to determine their strategy
Tesco's strategy development procedure is essential to the team's operations there in a highly saturated retail company. In this article, people will analyze Tesco's strategy-making method, trying to highlight its advantages and disadvantages.
Market Analysis:
Tesco has a strong market analytical method that involves surveying customers, holding focus group interviews, and analyzing data. This approach empowers Tesco to better understand consumer requirements and tastes, as well as relevant sections of market dynamics. Tesco's market analysis approach offers helpful knowledge of the economy, and this provides an essential element to their tactic selection phase (Ferlie, and Ongaro, 2022). One of Tesco's industry research system's strong points is that it collects information about customers using both qualitative and quantitative techniques. This allows for a thorough comprehension of consumer requirements, priorities, and behaviors. But even so, one of Tesco's industry research system's weak spots is the possibility of failing to adequately reflect the entire scope of client requirements and tastes. For instance, the firm may not record the needs and preferences of consumers that aren't enrolled in its loyalty card. This may restrict the company's capacity to fully comprehend the industry as well as establish an approach that meets the requirements of all consumers (Priyono, Moin, and Putri, 2020).
Internal Analysis:
Tesco also needs to conduct extensive analysis, examining its abilities, flaws, opportunities, and threats. This aids the organization in discovering ways to enhance possibilities for expansion. Tesco's internal factor offers an in-depth awareness of the industry's strengths and assets, which would be critical in developing its strategic plan. One of Tesco's internal strategic process's strong points is that it includes stockholders throughout the organization. This assists in guaranteeing that now the examination is thorough and that every one of the viewpoints is taken into account (Wang, and et.al., 2019). However, one of Tesco's internal strategic factors process's shortcomings is the possibility of failing to define each of the industry's dangers and weaknesses. For instance, the method may fail to detect new problems from strong competition or regulatory issues. This may limit the industry's capacity to completely comprehend the internal as well as outside factors that may influence its strategic plan.
Strategy Formulation:
Tesco's strategic planning operation includes a variety of stockholders, which include managers, management staff, and staff members. To grow its tactic, the company employs a variety of tools, which include the Swot matrix, Porter's Five Forces, and the Performance Measurement system. Tesco's strategic analysis process is founded on extensive market data as well as the organization's corporate skills, helping to ensure here that seemed as with its aims. One of Tesco's strong points is that it tends to involve a broad spectrum of interested parties, which ensures that now the tactic is thorough and considers all viewpoints. However, perhaps one of Tesco's strategic analysis component's weak points is that it can be too slow to adapt to shifting markets (Boukoberine, Zhou, and Benbouzid, 2019). The general merchandise business is rapidly modifying, and businesses must be capable of adapting rapidly to stay ahead of the competition. Tesco's strategic analysis method could fail to maintain up with developments, limiting the industry's capacity for responding to recent developments and risks.
Implementation:
The entire organization is involved in Tesco's strategy execution procedure. To implement its strategic plan, the currently hires a variety of tactics, which include branding, procedures, but also client service efforts. Tesco's execution process is aided by the industry's culture of constant enhancement, which ensures that the company will always be looking for ways to improve its activities. One of Tesco's strong points is that it includes the entire agency, which makes sure that the plan is majority groups among all facets of the company (George, Walker, and Monster, 2019).
However, one of Tesco's application process's flaws is that it might not prove efficacious in all parts of the company.
A critical evaluation of the impact of internal and external environmental variation on organizational strategy
Tesco, a global retailer organization,'s plan is swayed by both internal and outside environmental aspects. To assess the effect these variables have on Tesco's strategic plan, use the PEST analysis and VRIO framework (Jiang, Ritchie, and Verreynne, 2019).
PEST Analysis: The PEST evaluation is an instrument for identifying and analyzing various environments that can have an impact on a company's productivity. Let's look into how these variables might affect Tesco's organizational change.
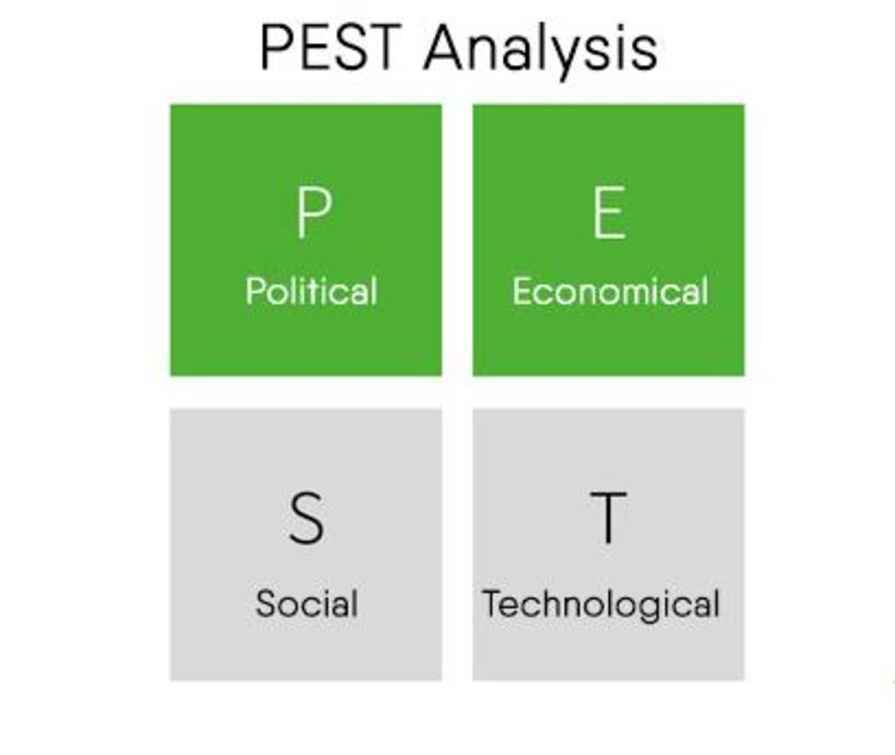
Figure 2: PEST Analysis
| Political Factors | Economic Factors | Social Factors | Technological Factors |
| Tesco's strategy can be subject to political aspects in a wide range of ways (Correani, and et.al., 2020). Reforms to government regulations concerning taxation, job growth, and commerce, for instance –, can have an impact just on the industry's profit growth and distribution network effectiveness. Furthermore, civil turmoil in certain of Tesco's operating markets can pose difficulties for the business. | Monetary policy, market prices, and private consumption can all have a massive effect on Tesco's technique. For illustration, market volatility can affect customer funding, reducing Tesco's earnings and revenue. | Tesco's strategy may be affected by cultural issues like shifting customers’ preferences, demographic groups, and lifestyle choices. For instance, the recent trend to environmentally friendly and nutritious goods may present the business with possibilities to broaden its brand portfolio but also boost its competitive edge (Hanelt, and et.al., 2021). | Technological advancements in e-commerce, big data, and supplier technology can all influence Tesco, for example, can use these tools to enhance its customer satisfaction, improve productivity, and reduce corners |
- VRIO Analysis: The VRIO framework serves as an instrument for assessing a company's internal assets and capacities. Let's look at the way these aspects might affect Tesco's organizational change.
- Value: Tesco's internal assets and skills, like its huge brand good name, effective logistics system, and large customer base, add significant value to the business. Tesco has been able to operate internationally but also actually compete there in the retail market thanks to these assets and capacities.
- Rareness: Tesco's internal assets and skills are not unique, as they can be reproduced through other sector resellers. To keep up with rivals, Tesco should keep reinventing itself and make a distinction between its services (Hanelt, and et.al., 2021).
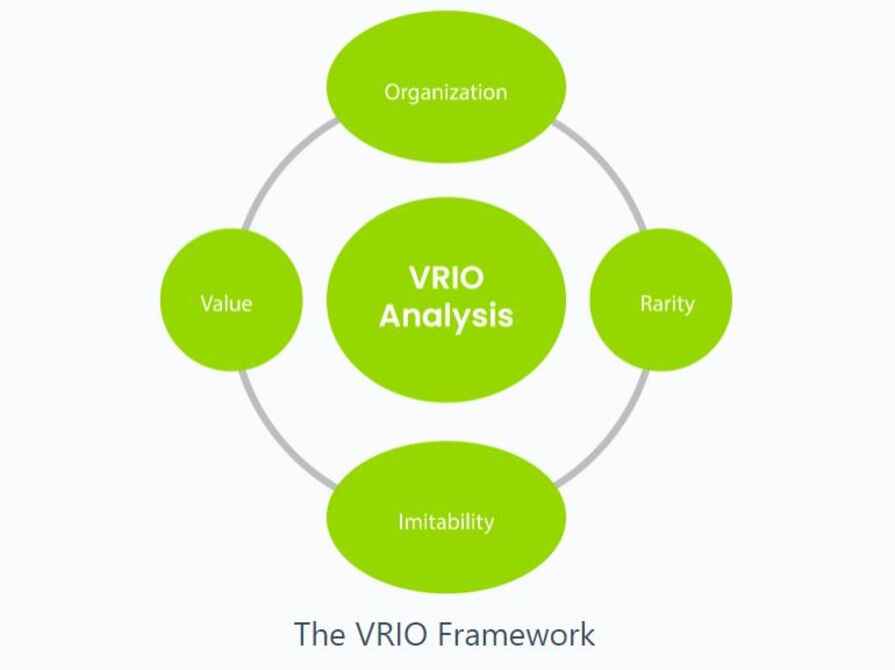
Figure 3: VRIO Framework
- Imitability: Other retail stores inside the industry can learn from Tesco's internal assets and skills. To stay ahead of the competition, Tesco must keep investing in technology and concentrate on customer satisfaction.
- Organization: Tesco's intrinsic assets and expertise are structured in such a way that now the business can meet its targets and purposes. Nevertheless, to keep up with competitors in the sector, the corporation must keep making investments in its organizational system and procedures (Falqueto, and et.al., 2020).
Tesco's organizational strategy can be influenced by both internal but also ancillary natural conditions. Tesco can ascertain its competitor setting and create efficient tactics for retaining its position in the market by evaluating these circumstances that used tools that include the PEST analysis and the VRIO model. To compete effectively in the volatile retail sector, Tesco must closely monitor the above variables but also make adjustments to its position accordingly.
A review of an organization’s strategic plan (Business Plan), providing an action plan for the organization based on a change in either the internal OR external environment
Tesco's national strategy lays out all the focus on the long purposes, priorities, and doings for its future success (Namugenyi, Nimmagadda, and Reiners, 2019). The plan hinges here on the organization's purpose of becoming the more highly valued corporation by consumers, workers, and stockholders. Tesco's business strategy consists of the following essential parts:
- Core Purpose and Values: Tesco's primary objective is to satisfy clients and assist people in cutting costs. Customer satisfaction, dignity toward individuals, and a dedication to excellence and entrepreneurship are all essential to the business (Salim, Ab Rahman, and Abd Wahab, 2019).
- Marketing Strategy: Tesco ranks among the biggest retailers worldwide, with the mere existence in many regions. The price position that the organization holds is centered on its track record of excellence, valuation, and comfort.
- Goals and Objectives: Tesco's targets and objectives are consistent with its central goals and principles. The company's goals include providing outstanding client care, offering great goods at cost-effective rates, and boosting its market share and revenue growth.
- Business Strategy: Tesco's corporate plan relies on multiple key pillars: (a) being a multichannel retail outlet, (b) winning in the UK, (c) being an online market, and (d) being a forward-thinking company. The company is planning to use innovation to enhance consumer encounters, boost its item line, and increase supply chain efficiency.
- Financial Performance: Tesco's financial performance is meticulously scrutinized, and the company pays for long-term profitable growth (Cillo, V., Petruzzelli, A.M., Ardito, L. and Del Giudice, M., 2019). The company's primary goal is to maximize shareholders' wealth while keeping a solid cash flow and putting money into expansion plans.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Tesco attributes stockholder involvement and strives to accomplish what it wants in collaboration with its consumers, workers, vendors, and communities. The corporation is dedicated to promoting ethical and environmentally friendly company practices while minimizing its environmental effects.
All in all, Tesco's national strategy lays out a detailed blueprint for lengthy expansion and financial success. The plan focuses on the company's current mission and principles and is aimed at satisfying evolving consumer demands and tastes (Hofmann, and Jaeger‐Erben, 2020). Tesco's emphasis on distribution channels, new tech, and innovative thinking is projected to fuel potential development, and the firm's dedication to addressing consumer engagement and economically sustainable practices are worthy of praise.
If Tesco's micro-environmental changes, such as a shift in organizational behavior, a leadership change, or an interruption in its production process, the basic process might well be useful in putting together a strategy:
- Recognize the change: Tesco must immediately define the alteration influencing its processes, effectiveness, or customer relations.
- Evaluate the impact: Tesco must evaluate the impact of structural conflict on its stockholders, which includes clients, workers, distributors, and stockholders. Grasp the causative factors of the transition and also its possible future short- but also protracted consequences is required (Li, and et.al., 2021).
- Create a plan: Tesco must put together an extensive strategy for tackling alteration. This helps identify consistency's goals, and targets, but instead key indicators of success (KPIs). Tesco must involve relevant parties in trying to plan procedures and make sure that the road map is in line the with business's strategic objectives.
- Implement the plan: Tesco must enact the implementation plan in stages, guaranteeing that now the scheme is made clear to all interested parties (George, Walker, and Monster, 2019). Ascribing duties, demonstrating better, and monitoring performance against Performance metrics are all part of this process.
- Evaluate and adjust: Tesco must determine the efficacy of the initiative and adapt it if needed. This includes assessing the effect that the modification will have on Tesco's results, and client experience, and consultation and revising the implementation plan if necessary.
If Tesco's macro-environmental changes, such as a shift in customer needs, the entry of a new entrant into the business, or a policy change from the government, the basic process may be useful in creating a strategy for responding:
- Determine the modification: Tesco must determine the imbalance in the ecosystem impacting its processes, effectiveness, or guest experience (Svensson, and Funck, 2019). This includes keeping an eye on various stakeholders and soliciting input from clients, vendors, and other decision-makers.
- Evaluate the impact: Tesco must evaluate the effect of external modification on its interested parties, which include buyers, workers, providers, and stockholders. Knowledge of the causative factors of the transition and also its possibility of short and lengthy consequences is required.
- Create a plan: Tesco must develop an extensive improvement plan in to react to the changing circumstances. This entails determining the targets, priorities, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that seem to be meaningful toward the alteration. Tesco must encompass relevant parties in the preparation procedure while guaranteeing that now the exit strategy is still in line with the business's long-term objectives (Hock-Doepgen, and et.al., 2021).
- Implement the plan: Tesco must enforce the implementation plan in stages, guaranteeing that the plan is conveyed to all stockholders. Ascribing duties, demonstrating better, and tracking progress against KPIs are all part of this process.
- 5. Evaluate and adjust: Tesco must determine the efficacy of the implementation strategy and adapt it if needed. This entails assessing the effects of outside change on Tesco's effectiveness, and customer satisfaction, but also capacity building and adapting the intervention plan as needed (Volberda, and et.al., 2021).
In synopsis, developing a plan of action for Tesco involves determining its transition, trying to assess its effect, creating a plan, carrying it out, and analyzing and adapting as needed. Involving main players in the organizing procedure as well as guaranteeing that now the course of action is aligned with Tesco's stated priorities are essential for achievement.
Conclusion
From the above study, it can be summarized that strategic management helps Tesco to consider various changes for the development and growth of its business. Further, the PEST Analysis provides an understanding of the different factors and their impact on the activities of the business. The report helps to understand various scenarios related to external environment changes and implement certain changes according to the requirement of the business. At last, the strategic plan can help handle various scenarios of changes in the business activities to consider the valuable impact.
References
Bogers, M., Chesbrough, H., Heaton, S. and Teece, D.J., 2019. Strategic management of open innovation: A dynamic capabilities perspective. California Management Review, 62(1), pp.77-94.
Boukoberine, M.N., Zhou, Z. and Benbouzid, M., 2019. A critical review on unmanned aerial vehicles power supply and energy management: Solutions, strategies, and prospects. Applied Energy, 255, p.113823.
Cillo, V., Petruzzelli, A.M., Ardito, L. and Del Giudice, M., 2019. Understanding sustainable innovation: A systematic literature review. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 26(5), pp.1012-1025.
Clauss, T., Abebe, M., Tangpong, C. and Hock, M., 2019. Strategic agility, business model innovation, and firm performance: an empirical investigation. IEEE transactions on engineering management, 68(3), pp.767-784.
Correani, A., De Massis, A., Frattini, F., Petruzzelli, A.M. and Natalicchio, A., 2020. Implementing a digital strategy: Learning from the experience of three digital transformation projects. California Management Review, 62(4), pp.37-56.
Falqueto, J.M.Z., Hoffmann, V.E., Gomes, R.C. and Onoyama Mori, S.S., 2020. Strategic planning in higher education institutions: what are the stakeholders’ roles in the process? Higher Education, 79, pp.1039-1056.
Ferlie, E. and Ongaro, E., 2022. Strategic management in public services organizations: Concepts, schools and contemporary issues. Routledge.
Fuertes, G., Alfaro, M., Vargas, M., Gutierrez, S., Ternero, R. and Sabattin, J., 2020. A conceptual framework for the strategic management: a literature review—descriptive. Journal of Engineering, 2020, pp.1-21.
George, B., Walker, R.M. and Monster, J., 2019. Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta‐analysis. Public Administration Review, 79(6), pp.810-819.
George, B., Walker, R.M. and Monster, J., 2019. Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta‐analysis. Public Administration Review, 79(6), pp.810-819.
Hanelt, A., Bohnsack, R., Marz, D. and Antunes Marante, C., 2021. A systematic review of the literature on digital transformation: Insights and implications for strategy and organizational change. Journal of Management Studies, 58(5), pp.1159-1197.
Hanelt, A., Bohnsack, R., Marz, D. and Antunes Marante, C., 2021. A systematic review of the literature on digital transformation: Insights and implications for strategy and organizational change. Journal of Management Studies, 58(5), pp.1159-1197.
Hock-Doepgen, M., Clauss, T., Kraus, S. and Cheng, C.F., 2021. Knowledge management capabilities and organizational risk-taking for business model innovation in SMEs. Journal of Business Research, 130, pp.683-697.
Hofmann, F. and Jaeger‐Erben, M., 2020. Organizational transition management of circular business model innovations. Business strategy and the environment, 29(6), pp.2770-2788.
Jiang, Y., Ritchie, B.W. and Verreynne, M.L., 2019. Building tourism organizational resilience to crises and disasters: A dynamic capabilities view. International Journal of Tourism Research, 21(6), pp.882-900.
Li, H., Wu, Y., Cao, D. and Wang, Y., 2021. Organizational mindfulness towards digital transformation as a prerequisite of information processing capability to achieve market agility. Journal of Business research, 122, pp.700-712.
Namugenyi, C., Nimmagadda, S.L. and Reiners, T., 2019. Design of a SWOT analysis model and its evaluation in diverse digital business ecosystem contexts. Procedia Computer Science, 159, pp.1145-1154.
Priyono, A., Moin, A. and Putri, V.N.A.O., 2020. Identifying digital transformation paths in the business model of SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(4), p.104.
Salim, N., Ab Rahman, M.N. and Abd Wahab, D., 2019. A systematic literature review of internal capabilities for enhancing eco-innovation performance of manufacturing firms. Journal of cleaner production, 209, pp.1445-1460.
Svensson, N. and Funck, E.K., 2019. Management control in circular economy. Exploring and theorizing the adaptation of management control to circular business models. Journal of Cleaner Production, 233, pp.390-398.
Volberda, H.W., Khanagha, S., Baden-Fuller, C., Mihalache, O.R. and Birkinshaw, J., 2021. Strategizing in a digital world: Overcoming cognitive barriers, reconfiguring routines and introducing new organizational forms. Long Range Planning, 54(5), p.102110.
Wang, W., Hoang, D.T., Hu, P., Xiong, Z., Niyato, D., Wang, P., Wen, Y. and Kim, D.I., 2019. A survey on consensus mechanisms and mining strategy management in blockchain networks. Ieee Access, 7, pp.22328-22370.

