Introduction of Tesco's HR Practices & Leadership Theories in Action
The pandemic has led to various organizational and operational changes in organizations in different sectors and industries. Tesco is one of the organizations which has changed from the pandemic era. The Tesco brand is owned by Tesco Plc, a British global retailer. It does business through a variety of shop formats as well as the Internet. It runs several different store types, including big ones, little ones, ones that sell only online, and even a one-stop shop. Fresh food, beverages, bakery, groceries, home and entertainment items, baby products, apparel, and domestic applications are some of the many categories covered by Tesco. The corporation has an employee strength of 231,223 as of 2022. The company has more than 6800 stores globally operating in different countries such as Ireland, Hungary, Slovakia, and many more. The current customer base of the organization has been identified as $80 million globally. The present report illustrates the HRM functions and their role in assisting the business in achieving its goals and objectives. The impact of strategic HRM and leadership theories is also discussed in the report.
Connect with New Assignment Help's experts in the UK for personalized assistance with your tasks.
Critical analysis of the role of distinct HR functions
There are several functions of HRM in Tesco that help the business in achieving its strategic objectives. In the phase of Covid - 19, the organization has strictly focused on some of the functions of HRM. Due to the remote working process of the employees and workers, the HRM focuses on performance management functions. By systematically guiding employee motivation and development, continuous performance management helps Tesco to gain a competitive edge. Successful collaboration across departments is possible when management and employee objectives are aligned with the company plan (Fenech et al., 2019). It aids in making sure that the company's long-term goals are achieved. When HR is in charge of the performance management process, everyone in the company can be certain that they will be treated equally and fairly. Effective and efficient outcomes are provided by a performance management program that also contributes to the growth of its employees.
Learning and development is another function included in the HRM of Tesco. Due to the remote work process, the employees and workers are isolated from effective leadership and development sessions and events. The HRM news to develop an L&D strategy to achieve strategic objectives. To preserve their worth, companies must continue to pour resources into their workers' training and education. To keep workers' knowledge fresh, it is essential to provide them with regular training and new responsibilities (Okolie and Udom, 2019). Companies in today's highly competitive business world can't survive without L&D, which slows the decline in value that would otherwise render them obsolete. Strong financial benefits are realized by companies that invest in L&D and the development of their future leaders.
Incentives for further education and training go a long way toward keeping workers invested in their jobs. Making an investment in learning and development (L&D) helps workers develop the skills they need to take on more responsibility at work and demonstrates appreciation for their efforts. Engaged workers stay with a company longer and perform better when given the opportunity to develop their skills and are given meaningful tasks.
Collaboration, quick learning, testing, troubleshooting, modifying, iterating, and launching are all essential to the innovative process. Learning and development aid in mastering the aforementioned to create an innovative environment in the workplace. Employees also need to be comfortable with ambiguity because of competition and the rapid development of new technology (Yusliza et al., 2019). Whenever there is a degree of ambiguity, there is also a degree of danger. Only workers who have the necessary professional abilities will be able to confidently accept uncertainty and danger. The greatest way to enable people to confidently handle uncertainty and risk is via training, which may be provided through the company's learning and development efforts.
Evaluating job performance is a technical HR function. The HR division of Tesco's ability to assess HR operations is critical to the organization's strategic and operational success. The business must provide the necessary degree of service while acting strategically. In practice, a function assessment will include looking at how different HR processes measure up against one another. Things including the quality and availability of employees, the location of the employment, the hours worked, the state of the economy, the nature of the work, and the value the position provides to the company may all play a role (Falletta and Combs, 2020). Function assessment is based on the principle that like tasks should be compensated in a like manner. In shifting to a remote process, Tesco also had a focus on recruiting more talent in its organization. In recruiting talent the company considered compensation and benefit to be one of the effective functions that need to be considered by the HRM. The role of compensation management function of HRM enabled recruiting and attracting more talent thus assisting the organization in accomplishing its strategies goals and objectives (Longoni et al., 2018). The role of the compensation and benefits functions is to monitor and ensure that employees are fairly paid for their contribution and effort towards the organization. On the other hand, the function also facilitates the performance and the recognition of the employees depending on their job performance (Stone et al., 2020). The compensation function considers the overall pay structure of the employees and workers ranging from their pay structure to the rewards and recognition they receive in form of monetary and non-monetary benefits. Monitoring the pay structure of the employees and staff allows the function to achieve the strategic objectives of employee satisfaction in the organization.
Impact of strategic HRM
Strategic HRM increases the efficiency and productivity of Tesco's operational process by tying together an organization's people, strategy, values, and performance. The strategic human resource department of the organization views the management of these human assets and their employees' skills and knowledge as their top priority, which makes sense given the significance of people in any given enterprise (Bouaziz and Hachicha, 2018). Human resource management as practiced by SHRM is forward-thinking in that it places a premium on predicting future requirements in terms of expertise and education, and then tailoring hiring, performance assessment, salary and benefits packages, and education and development opportunities accordingly. These strategic HR strategies are referred to as "high-performance work practices". By emphasizing high achievement, mutual trust, and commitment, and developing a combined group/entrepreneurial approach to management, the organization can maintain high commitment and high performance among employees and, ultimately, organizational effectiveness (Al-Ayed, 2019).
Linking an organization's business plan with its human resource strategy is a primary objective of the strategic HRM of Tesco. Strategic human resource management's ultimate objective is to recruit, develop, and retain workers who are both committed to their work and capable of producing exceptional results (Fahim, 2018). Attracting, developing, and keeping top employees should also be high on every company's strategic HR agenda. In addition, a major objective of strategic human resource management will be the facilitation of high performance. Tesco, however, is growing its company and increasing its profit year after year despite the economic downturn. Its effective strategic HRM policy is the driving factor (Armstrong, M. and Brown, 2019).
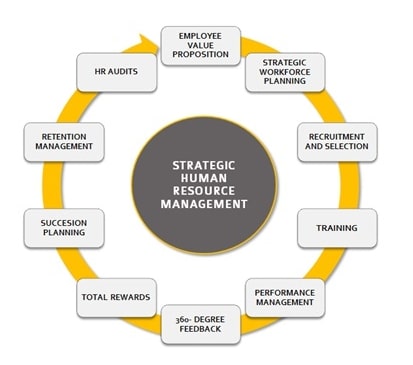
Figure 1: Roles of strategic HRM
(Source: Mbaskoll.com, 2020)
Tesco's plan for expansion is tried and true. Following clients into major growing areas at home, such as financial services, non-food, and telecommunications, and new markets overseas, originally in Central Europe and Asia, and most recently in the United States, is the driving force behind the approach. Tesco's business strategy and human resources strategy are intertwined since the company invests heavily in its employees in order to realize its growth objective (Paauwe and Boon, 2018). Tesco regularly reviews its five-year personnel strategy and makes adjustments as necessary. Tesco's upper management conducts an annual survey to find out what employees value most about working for the company, and the answers are always the same: a manager who supports them, the opportunity to advance, an engaging position, and respect. Every aspect of Tesco's strategy is geared around improving these (Choi et al., 2018). That is because Tesco keeps a close eye on its workers, gives enough opportunities for advancement, encourages continuous growth, and appreciates its staff highly. Simply put, Tesco's HR strategy is designed to maximize employee performance so that the company may realize its growth objectives.
Supermarkets are labor-intensive companies by today's standards; thus, how they manage, develop, and reward their employees is of utmost importance (Sareen, 2018). Tesco's strategic human resource management is one of the company's many strengths. Tesco's personnel strategy centers on the recruitment, development, and retention of its employees. The strong connection that modern supermarkets make between their workers and shoppers is a major innovation in the industry.
Tesco's strategic HRM plays a crucial role in helping the company reach its goals. Tesco's well-trained, appreciated, and motivated personnel is largely responsible for the company's growth in consumers, international reach, and revenue despite the current economic downturn (Sareen, 2018). Tesco's staff maintains its global market dominance by establishing a reliable reputation for the company via superior customer service.
Organizations may solve HR issues more strategically when they use sound HRM practices and policies. Because of this, workers are able to maintain a high standard of service quality despite any internal or external pressures that may be exerted. Organizations may better prioritize their overall company strategy with the help of sound human resource management policies. Human resource administration is important because it helps businesses find and hire new workers who are both skilled and motivated, as well as keep their best performers on staff. It also aids managers and various groups of workers in adjusting to organizational change, and it facilitates the application of expertise in determining how work will get done.
Hiring smart people, investing in their growth while they're on the job, and keeping them around all have a positive impact on a company's bottom line because they help employees better understand and contribute to the organization's operational, business, and strategic goals (Armstrong and Brown, 2019). These HR practices also ensure the company has access to and can keep, a talented workforce that can boost output, adapt to new situations, and foster new ideas.
A business's bottom line can benefit from training, development, and education in several ways, including the following: expanding the proficiency foundation and developing the levels of competence essential in the employees; encouraging flexible learning, which occurs when people enthusiastically pursue advanced the information and services that upkeep the goals of the company; and building a climate of learning, a growth medium in which self-managed learning, in addition to training and mentoring, is encouraged.
Leadership theories and their implication
Transformational leadership theory is one of the theories that can be applied in Tesco’s working environment. According to the transformational idea, leaders who have strong bonds with their teams are more effective. Leaders who are able to inspire their employees to high heights and direct them toward the achievement of organizational objectives are called transformational leaders. In order to prevent problems, the leaders at Tesco also make sure the team's objectives match those of the company (Alrowwad, A.A. and Abualoush, 2020). A favorable shift in the workplace may be sought with the help of transformational leadership theory in the modern corporate world. An additional benefit is that it may assist leaders and their teams form close bonds.
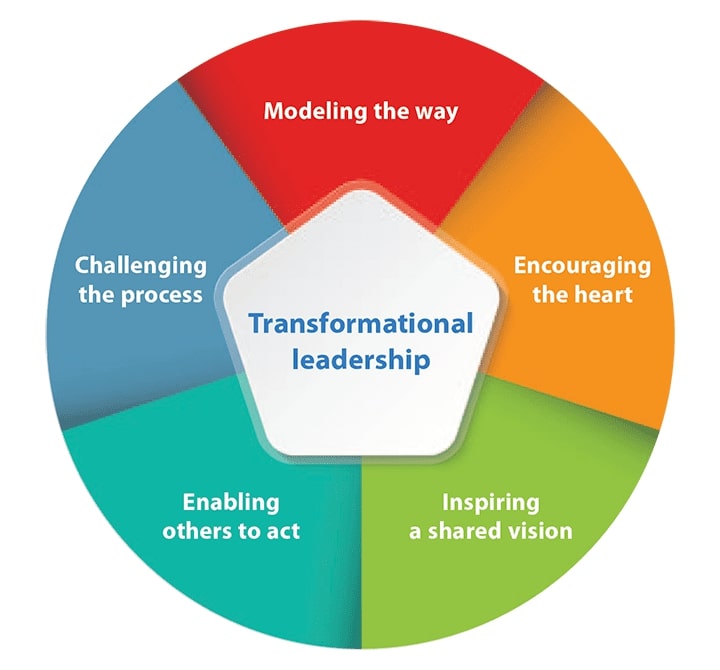
Figure 2: Transformational leadership
(Source: Myamericannurse.com, 2018)
These leaders are able to unite their teams around a common purpose because of their ability to forge strong bonds and articulate a compelling vision. In addition, their great preference for open announcements and cooperation gives them the ability to elicit thoughts from their followers. Transformative leadership may also be used to effect change inside the organization (Azizaha et al., 2020). Sometimes groups or companies just stop moving forward and become uninspired and unmotivated. In order to get out of this issue, Tesco’s leaders will need to adopt a strategy that prioritizes creating a new visualization that will excite and encourage employees by giving them a feeling of belonging to the team's mission as a whole. In a similar vein, employees might lose motivation while dealing with their own problems or the state of the company as a whole. To boost morale in such a dire situation, transformational leaders of the organization must step in and provide guidance, refocus, and praise to their team members (Hansen and Pihl-Thingvad, 2019). Furthermore, transformational leadership may be used to help employees and workers realize their greatest potential. Leaders that adopt this approach are responsible for ensuring that their teams are able to accomplish their goals and objectives, making the most of their current skills and knowledge, and developing themselves professionally. When certain factors come into play, teamwork is essential.
Planned preparation, merchandise expansion, and problem-solving are a few examples of transformational leadership behavior. Collaboration via open communication is fundamental to a transformational leader's philosophy because it allows for a wider range of perspectives to be heard, which in turn fosters greater creativity and innovation. As with any group, team, or company, disagreements are inevitable (Jacobsen, 2022). Disagreements between individuals are almost inevitable because of remote policies for employees. Alteration itself is a source of friction. Leaders who transform their teams do so by keeping lines of communication open, fostering conversation, and stressing the value of working together to achieve a common goal. In addition, a multicultural group or company must learn to balance competing ideals.
Because of their commitment to innovation, employee development, transparency in relationships, and teamwork, transformational leaders are most suited to this position. On the other hand, transformational leadership behavior helps in motivating employees. This enables the employees to gather a supportive attitude and behavior of the leaders which in turn increases productivity and quality of the work of the employees and staff (Crews et al., 2019). Increase in the productivity of the employee results in the development and growth of the organization. In the remote work process, it is essential to motivate and assist employees to a greater extent. With transformational leadership behavior, the corporation will be able to transform the employees and staff to adapt themselves to the remote work process.
Transactional leadership theory is another leadership theory that is considered to be suitable for Tesco. The core structure of this kind of leadership theory centers on the use of incentives and sanctions. Members of the team should be rewarded anytime they help the leader reach his or her goals, and vice versa. One of the main tenets of transactional leadership is prioritizing organizational objectives. According to this model, there is no emotional connection between a boss and an employee (Berkovich and Eyal, 2021). Due to its simplicity and consistency, transactional leadership is commonly seen in big and even medium-sized firms with well-established operational procedures and human supply administration techniques. Keep in mind that this leadership style represents the bare bones of any effective management or supervision of people.
In the remote work policy at Tesco, there are times when the organization may need to act instantly and make decisions. Leaders with a transactional style are most suited for time-sensitive and mission-critical situations that call for rapid and effective decision-making procedures since these situations emphasize efficient communication and faithfulness to a clear and unambiguous chain of command (Berkovich and Eyal, 2021). Transactional leadership behavior also involves rewards and punishment based on the performance of the employees and workers. In a remote working environment, it is beneficial to monitor employees and implement actions based on their performances. The more the employees perform effectively the more they will receive awards. This will upsurge the motivation of the employees towards their job roles.
During the phase of Covid - 19 it is essential to support and assist employees with their tasks and activities instead of authorizing them to completion of their tasks. In such a scenario transformational leadership behavior is considered to be the suitable leadership behavior for Tesco. Using this kind of leadership, intellectual stimulation is understood to entail fostering creative problem-solving (Berkovich and Eyal, 2021). It also requires an ability to think creatively and solve problems which is much needed for remote work processes. Leaders that can bring about a transformation in their teams will share what they know with them. They support open, honest leadership.
They talk freely to one another in order to increase their creative output and develop their capacity for analysis. When people are able to express their thoughts and opinions freely, it helps the company as a whole make better decisions (Azizaha et al., 2020). Communicating freely and effectively allows employees to build a strong and positive bond with the leaders. The culturally diverse environment of Tesco requires transformative leaders for discussing and sharing concerns and ideas on a particular situation. Therefore, it can be considered that transformational leadership behavior is the relevant leadership theory to be used in Tesco. When leaders exhibit empathy and compassion, they are held up as role models. One such way in which people are held up as ideals is when they put the requirements of others ahead of their own.
This kind of leader works to instill a sense of purpose in their group. They put an emphasis on working together and modeling morally and ethically responsible conduct. They provide morals and discipline to the group they work with. Leaders who can transform organizations are cognizant of the ethical weight of their choices.
Analysis of the factors driving change
The modern world is already changing, transforming, and evolving. The patterns of this contemporary globe are dynamic, the only constant being change. With the world already undergoing modifications and changes the Covid-19 pandemic that hit in 2020 evolved the planet into a new light. The world since the pandemic has changed dramatically. The Covid-19 pandemic has brought transformation in this world, around all the sectors possible, including business, organisations, and work culture. Governments across the world have adopted various methods to combat the pandemic, and among them, physical distancing, quarantine, and overall shutdown of general life were the new normal (Aiello et al., 2020). Physical distancing and the overall lockdown of various facilities, that included transportation has affected public life. These regulations were strictly followed to contain the infection from spreading, however, these rules transformed the life of humans forever. Under the direction of the World Health Organisation, governments across the world have strictly implemented regulations of physical distance across workplaces and any places of public gatherings. With no physical distancing and lockdown as the new rules companies were forced to adopt various new methods to adapt to this new situation. The HRM department which forms the most important part of a company has changed as well. The policies brought about by the HRM have also changed which now ensures bringing back suitable employees and recruiting new ones adapted to a wide range of skills.
Tesco, a retail company based in the UK is a public limited company that deals with daily grocery items and basic merchandise products. The company as described earlier is one of the largest in the UK market and is also famous with a wide customer base in the world. The company, consisting of four thousand plus stores in the world, faced a hard blow when the pandemic hit. Initially, like all others, its sales dropped to the ground and it faced tremendous losses. However, as change is the only constant in this dynamic world, as correctly understood by the management team of Tesco, there came certain factors that drove changes. Among them, the three most important factors driving changes in the HR planning of Tesco were to make the employees efficient enough to handle the trend of online shopping that increased drastically. The second one is the new trend of buying grocery items from Tesco that are sustainable and have a longer shelf life. Thirdly, people began to order larger lists full of items, so that they do not need to buy them often. and lastly, the demand for fast and sanitised delivery of the ordered items. These are the factors born during the pandemic and contributed to the initiation of change of policies and structures within the organisation. As the world changes in these contemporary times, there are quite a lot of challenges that are being posed upon organisations and companies to adapt to such changes, especially in HR practices and policies (Stouten, Rousseau, and De Cremer, 2018).
There are quite a lot of change management theories and strategies with which companies and organisations undertake the challenge that comes with changes. There are numerous theories and models which companies can intentionally implement or execute to overcome the changes. Tesco has also been facing changes, especially from the time of the pandemic, and certain change management theories are now deemed necessary for execution. The two most suitable change management theories for Tesco might be Lewin’s Change Model and the Beckhard and Harris Model (Cameron, and Green, 2019). These two theories or strategies might benefit Tesco to adopt the changes that are coming after the pandemic.
Lewin’s change model or theory has three steps, namely the unlearning or unfreezing period, the period of change, and lastly the refreezing or relearning period (Hussain et al., 2018). The first unfreezing phase involves the employees of an organisation unlearning all the previously learnt issues and they are intentionally made to unlearn their previous notions, behaviours, and attitudes. This phase is deliberately initiated by the HRM of an organisation. The second phase involves the process of the actual change in which the employees would transform their behaviours in a positive and impactful way, in which they would be able to address the changes in the organisation in a holistic manner.
The last phase involves the overall continuation of the changes that are adopted and it also shows the permanent change in the employees' behaviour (Lewis et al., 2019). Lewin’s change model might be quite effective for Tesco especially in the pandemic times as the whole world is changing. The retail sector saw changes unlike ever before, for instance, the shutting of the in-store centres and increasing online modes of shopping. For Tesco to adapt to such changes, the employees must get rid of their older habits and adopt new ones through which they can cater to the needs of its customers. These changes are only possible if the HRM of Tesco begins the training and development of its employees holistically. The department also brought new policies of remote workplace rules to make the change smooth and effective (Aiello et al., 2020).
The second model is the Beckhard and Harris Model, and it also has three phases through which a complete change takes place. The three phases consist of the present, transition, and future. In the first phase, an analysis is made of whether an organisation requires any transformation in the first place (Galli, 2018.). If the management decides so by analysing the current state then the second phase initiates.
The transition phase is about the real change when the organisation transforms in all manners, that is, structurally and organisationally. And lastly, the future phase is the phase in which the structural and organisational change has already taken place and the transformation has settled in (Harmon, 2019). For Tesco, this model serves the purpose as the changes that the pandemic has brought might be addressed by this. Tesco's logistics department requires this transformation due to the new demand for doorstep or touchless delivery for lockdown and physical distancing regulations. The employees engaged in delivery must undergo training and adopt new methods from the HRM department by which deliveries will be done by maintaining the pandemic regulations. The HRM department might also recruit workers who have special skills for the proper execution of these changes.
The initial strategy that Tesco might adopt is the habit of adaptability. This habit will enable the company to adapt to the changing world without much resistance. The CEO of the firm has undertaken various strategies to overcome the resistance posed by the pandemic, one being fast to adopt the organisational changes (Harris, 2019). Strategies might include the inclusion of additional staff of almost fifty thousand to the company to combat the sudden rise in demand for grocery items. The recruitment of those workers is done by the HRM department in alignment with the new policies for remote workplaces. The HRM department hatched a strategy to focus more on enhancing work efficiency in remote workplaces by implementing new training and development methods (Fry, 2021).
|
Change Management Implementation Plan |
|
Organisation - Tesco |
|
Proposed Change |
Reason For Change |
Intended Outcomes |
Estimated Duration |
Estimates Costs |
|
1) Inclusion of AI |
1) This will make the employees more efficient to deal with the online processes working from home (Aiello et al., 2020). |
1) The creation of a band of technologically sound workers. |
1) Six months. |
1) Per employee a thousand dollars. |
|
2) Inclusion of a Hybrid mode of work. |
2) To adopt the post-pandemic new normal. |
2) To produce workers who will be skilled in both in-store and online services. |
2) One year. |
2) Over a thousand dollars per employee. |
|
3) Training and development. |
3) To enter the new work culture of the post-pandemic period. |
3) Employees will be able to handle their work more professionally from home (Aiello et al., 2020). |
3) Four to seven months. |
3) Depending on the training period duration. |
|
Communication plan |
|
Strategy |
Project phase |
Targeted Stakeholders |
Reason for communication |
Method of communication |
|
Announcement of change |
1 |
Executives, managers, chief officers, employees, and investors. |
To make all the working members of the company aware of the new work-from-home policies. |
Online meetings in the zoom, google meet platforms due to physical distance regulations (Przytuła, Strzelec, and Krysińska-Kościańska, 2020). |
|
Change Implementation Training |
2 |
Employees, training executives, and HRM. |
To make the trainers and the trainees aware of the new strategies and plans (Aiello et al., 2020). |
Online meetings using applications. |
|
Activity 1- policy introduction class |
3 |
Employees. |
To make the employees learn about the new policies that the company is bringing about. |
Online meetings and calls. |
|
Activity 2- work from home policy practice. |
4 |
Employees. |
To make the employees efficient enough so that they do not face any hindrances while working. |
Online meetings, group calls, and personal calls. |
|
Activity 3- Doubt clearing sessions. |
5 |
Employees and executives. |
To clear any doubts about the new work-from-home policies brought by the company (Przytuła, Strzelec, and Krysińska-Kościańska, 2020). |
Group meetings and personal calls via online platforms. |
Recommendations
As the effects of the pandemic have been discussed earlier, it is quite normal for Tesco employers and employees to undergo various constructive changes. These changes are deliberately brought for bringing the employees and the customer base to adapt to the new normal after the pandemic. Tesco has analysed various theories and models of change and has concluded with two of them which have been regarded as the best choice among the rest. The company has a communication and change management implementation plan which they might deploy to combat the waves of new issues arising from the contemporary world (Hamouche, 2021). However, these are not enough, as Tesco requires a series of recommendations through which it can sharpen its strategies and plans to adapt to the changes in a more effective manner. The first strategy or recommendation for Tesco’s HRM department is to recruit employees with the soft skill of creativity and innovation. This will result in the production of new products which Tesco can market throughout its stores. This might provide an impetus in the rise of sales of the company after a tremendous loss during the pandemic years. The second recommendation is mainly aimed at the marketing team of Tesco, as to initiate an aggressive marketing policy in which they will be redesigning their brand image and the brand value will automatically increase (Hamouche, 2021).
Thirdly the company should focus on post-pandemic sales and adopt new methods to attract customers to its stores. Tesco should increase advertisement on social and digital platforms vigorously. Many people have lost their jobs during the pandemic, and Tesco's HRM department must increase their investment in human resources by employing them for increasing the person-to-person contacts and advertisements. The new employees might distribute handbills and pamphlets for the same purpose. These new employees might assist the new standees Tesco might install at every gate of the stores. The company, especially the HRM must modify the policy of health and personal cleanliness of the employees which will contain the spread of the disease and would ensure the safety of its customers. The company must bring about a guideline in which every employee must behave and follow cleanliness. The HRM department should arrange proper training and development for making the employees understand the purpose of such actions (Aiello et al., 2020).
Another recommendation might be the maintenance of both the online and offline, in-store experiences for the customers. That is the adoption of a hybrid mode of work. The world is returning to its pace slowly after the pandemic has slowed down its ferocity. The stores have been opened and customers are returning. However, the online mode has been helpful to quite a lot of people, for instance, the elder and disabled people. So the recommendation is to balance between the two, both online and offline catering to specific audiences. Tesco has been able to adapt to changes quickly throughout the pandemic period for its efficient HRM department. This management team has been responsive to all the challenges that came along the way and it has been quite successful in bringing about the necessary changes that were deemed essential for the survival of the company.
Conclusion
In enhancing the remote work process it is essential for the organization to focus on leadership styles and behavior along with Tesco Leadership Behaviours & HR Practices. It can be concluded that Tesco is focusing on strategic HR activities and leadership ideas for developing the effectiveness of remote workplace policies and procedures. It has been found that a change management plan and communication plan have been developed to execute the change effectively and efficiently. The findings of the report also illustrate that transformational and transactional leadership behavior are two theories that are suitable for the organization. On the other hand, transformational leadership is more effective than the transactional leadership model as it helps in assisting and mentoring employees through the remote work model. With transformational leadership theory, leaders are able to motivate and inspire employees and staff in handling their duties through remote work environments. This also helps in creating satisfaction and less anxiety and stress among the employees and staff. Strategic HRM activities offer a lot of positive impact on the organization that helps in accomplishing the organizational objectives.
References:
Aiello, L.M., Quercia, D., Schifanella, R. and Del Prete, L., 2020. Tesco Grocery 1.0, a large-scale dataset of grocery purchases in London. Scientific data, 7(1), pp.1-11.
Al-Ayed, S.I., 2019. The impact of strategic human resource management on organizational resilience: an empirical study on hospitals. Verslas: Teorija Ir Praktika/Business: Theory and Practice, 20, pp.179-186.
Alrowwad, A.A. and Abualoush, S.H., 2020. Innovation and intellectual capital as intermediary variables among transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and organizational performance. Journal of Management Development.
Armstrong, M. and Brown, D., 2019. Strategic Human Resource Management: back to the future. Institute for Employment Studies reports, pp.1-36.
Azizaha, Y.N., Rijalb, M.K., Rumainurc, U.N.R., Pranajayae, S.A., Ngiuf, Z., Mufidg, A., Purwantoh, A. and Maui, D.H., 2020. Transformational or transactional leadership style: which affects work satisfaction and performance of Islamic university lecturers during COVID-19 pandemic. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(7), pp.577-588.
Berkovich, I. and Eyal, O., 2021. Transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and moral reasoning. Leadership and Policy in Schools, 20(2), pp.131-148.
Bouaziz, F. and Hachicha, Z.S., 2018. Strategic human resource management practices and organizational resilience. Journal of Management Development.
Cameron, E. and Green, M., 2019. Making sense of change management: A complete guide to the models, tools and techniques of organizational change. Kogan Page Publishers.
Choi, B., Ravichandran, T. and O'Connor, G.C., 2018. Organizational conservatism, strategic human resource management, and breakthrough innovation. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 66(4), pp.529-541.
Crews, E.R., Brouwers, M. and Visagie, J.C., 2019. Transformational and transactional leadership effects on communication styles. Journal of Psychology in Africa, 29(5), pp.421-428.
Fahim, M.G.A., 2018. Strategic human resource management and public employee retention. Review of Economics and Political Science.
Falletta, S.V. and Combs, W.L., 2020. The HR analytics cycle: a seven-step process for building evidence-based and ethical HR analytics capabilities. Journal of Work-Applied Management.
Fenech, R., Baguant, P. and Ivanov, D., 2019. The changing role of human resource management in an era of digital transformation. Journal of Management Information & Decision Sciences, 22(2).
Fry, R., 2021. Beckhard, Richard: The Formulator of Organizational Change. The Palgrave Handbook of Organizational Change Thinkers, pp.147-161.
Galli, B.J., 2018. Change management models: A comparative analysis and concerns. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 46(3), pp.124-132.
Hamouche, S., 2021. Human resource management and the COVID-19 crisis: Implications, challenges, opportunities, and future organizational directions. Journal of Management & Organization, 1, pp.1-16.
Hansen, J.A. and Pihl-Thingvad, S., 2019. Managing employee innovative behaviour through transformational and transactional leadership styles. Public Management Review, 21(6), pp.918-944.
Harmon, P., 2019. Business process change: a business process management guide for managers and process professionals. Morgan Kaufmann.
Harris, D.B., 2019. Examining the Hermeneutic Bridge Between the Past and Present Constructed by Early Organization Development Pioneers: An Exploration Using the Life of Richard Beckhard. Benedictine University.
Hussain, S.T., Lei, S., Akram, T., Haider, M.J., Hussain, S.H. and Ali, M., 2018. Kurt Lewin's change model: A critical review of the role of leadership and employee involvement in organizational change. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 3(3), pp.123-127.
Jacobsen, C.B., Andersen, L.B., Bøllingtoft, A. and Eriksen, T.L.M., 2022. Can leadership training improve organizational effectiveness? Evidence from a randomized field experiment on transformational and transactional leadership. Public Administration Review, 82(1), pp.117-131.
Lewis, L., 2019. Organizational change. In Origins and Traditions of Organizational Communication (pp. 406-423). Routledge.
Longoni, A., Luzzini, D. and Guerci, M., 2018. Deploying environmental management across functions: the relationship between green human resource management and green supply chain management. Journal of Business Ethics, 151(4), pp.1081-1095.
OKOLIE, U.C. and UDOM, I.D., 2019. Disciplinary actions and procedures at workplace: The role of HR managers. Journal of Economics and Management Research, 8(1), pp.90-105.
Paauwe, J. and Boon, C., 2018. Strategic HRM: A critical review. Human resource management, pp.49-73.
Przytuła, S., Strzelec, G. and Krysińska-Kościańska, K., 2020. Re-vision of future trends in human resource management (HRM) after COVID-19. Journal of Intercultural Management, 12(4).
Sareen, D., 2018. Relationship between strategic human resource management and job satisfaction. International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences, 7(03), pp.1229-1233.
Stone, R.J., Cox, A. and Gavin, M., 2020. Human resource management. John Wiley & Sons.
Stouten, J., Rousseau, D.M. and De Cremer, D., 2018. Successful organizational change: Integrating the management practice and scholarly literatures. Academy of Management Annals, 12(2), pp.752-788.
Yusliza, M.Y., Choo, P.W., Jayaraman, J., Rimi, N.N. and Muhammad, Z., 2019. HR Line Manager’s Reflections on HRM Effectiveness through HR Roles and Role Stressors. The South East European Journal of Economics and Business, 14(1), pp.34-48.

